Drimane
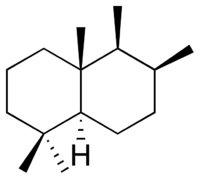
Drimane is a bicyclic sesquiterpene. It is the parent structure of many natural products with various biological activity.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Drimane | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(4aR,5S,6S,8aS)-1,1,4a,5,6-Pentamethyldecahydronaphthalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 2959385 | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H28 | |
| Molar mass | 208.389 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Among the notable drimanes are:
- Polygodial, found in several different plants
- Multiple compounds found in several members of the family Canellaceae
References
- Jansena, B. J. M.; de Groota, Ae. (2004). "Occurrence, biological activity and synthesis of drimane sesquiterpenoids". Nat. Prod. Rep. 21 (4): 449–477. doi:10.1039/B311170A. PMID 15282630.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.