Dryas drummondii
Dryas drummondii is a species of flowering plant in the rose family known by the common names yellow mountain-avens, yellow dryas, or yellow dryad.[3] It is native to Alaska, Canada, and northern states in the contiguous United States.[1][3] This species is actinorhizal, able to live in symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria.[4][5][6]
| Dryas drummondii | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Dryas drummondii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Dryas |
| Species: | D. drummondii |
| Binomial name | |
| Dryas drummondii Richardson ex Hook. | |
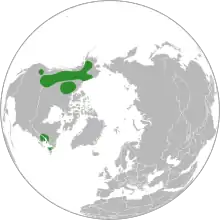 | |
| The distribution of Dryas drummondii.[1] | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
References
- "Dryas drummondii: Yellow Mountain Aven". Central Yukon Species Inventory Project: Botany. Friends of Dempster Country. 2011. Retrieved January 1, 2017.
- Govaerts R. "Dryas drummondii Richardson ex Hook.". Plants of the World Online. Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
- Dryas drummondii. NatureServe.
- Becking, J. H. (1984). "Identification of the endophypte of Dryas and Rubus (Rosaceae)". Plant and Soil. 78 (1/2): 105–128. doi:10.1007/BF02277844. JSTOR 42934565. S2CID 12172938.
- Becking, J. H. (1984). "Identification of the endophypte of Dryas and Rubus (Rosaceae)". Frankia Symbioses. Vol. 12. Springer. pp. 105–128. doi:10.1007/978-94-009-6158-6_11. ISBN 978-94-009-6160-9.
- Kohls SJ, Baker DD, van Kessel C, Dawson JO (2004). "An assessment of soil enrichment by actinorhizal N2 fixation using δ15N values in a chronosequence of deglaciation at Glacier Bay, Alaska". Plant and Soil. 254 (1): 11–17. doi:10.1023/A:1024950913234. S2CID 25039091.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
