Eastern Thailand
Eastern Thailand is a region of Thailand bordering Cambodia on the east, Northeastern Thailand in the north, and central Thailand on the west.
Eastern Region | |
|---|---|
     From upper-left to lower-right: Pattaya in daytime, Port of Laem Chabang, Khao Khitchakut, Ko Chang and Wat Sothonwararam | |
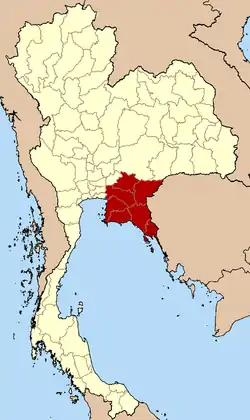 Eastern Region in Thailand | |
| Largest city | Chaophraya Surasak City |
| Provinces | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 34,481 km2 (13,313 sq mi) |
| Population (2019)[2] | |
| • Total | 4,841,806 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (Thailand) |
Geography
Eastern Thailand lies between the Sankamphaeng Range, which forms a natural border with the Khorat Plateau to the north and the Gulf of Thailand to the south. The geography of the region is characterised by short mountain ranges (collectively grouped under the Chanthaburi Range) alternating with small basins of short rivers which drain into the Gulf of Thailand. Between the Chanthaburi and Sankamphaeng mountains lies the basin of the Bang Pakong River system.
Fruit is a major component of agriculture in the area, and tourism plays a strong part in the economy. The region's coastal location has helped promote eastern seaboard industrial development, a major factor in the economy of the region.[3]
Islands off Eastern Thailand's coast include Ko Sichang, Ko Lan, Ko Samet, and Ko Chang.
National parks
Within the eastern region there are some eight national parks. Pang Sida National Park covering 844 km2 in Sa Kaeo province, it constitutes a part of the Dong Phayayen-Khao Yai Forest Complex UNESCO World Heritage Site, covering in total around 6,100 km2. The total forest area is 8,205 km2 (3,168 sq mi) or 22.4 percent of this eastern region area (incl. Nakhon Nayok province).[1] Mu Ko Chang National Park in Trat province includes 85 per cent of Thailands second largest island Ko Chang. The beaches on the western coast of Ko Chang have been excluded from the national park for reason of facilitating the tourism industry. Mu Ko Samet National Park in Rayong province is just 6 km long by 3 km wide with beaches covered with some of the finest white sand in the country.
Administrative divisions
According to the six geographical regions established by the National Research Council of Thailand, the eastern region includes seven provinces.
The Thai Meteorological Department (TMD), the Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC) [4] and Royal Forest Department (RFD) also include province Nakhon Nayok in the Eastern region.
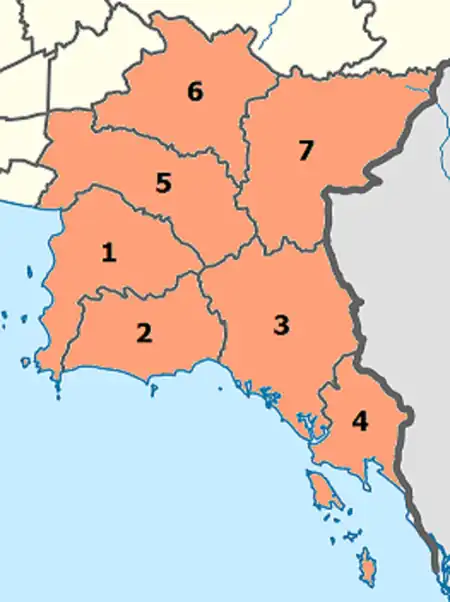
| Flag | Seal | Province | Capital | DOPA | Popul. | Area (km2) | Dens. | ISO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
1 | Chonburi | Chonburi | 9 | 1,558,301 | 4,508 | 346 | TH-20 |
 |
 |
2 | Rayong | Rayong | 50 | 734,753 | 3,666 | 201 | TH-21 |
 |
 |
3 | Chanthaburi | Chanthaburi | 7 | 537,698 | 6,415 | 84 | TH-22 |
 |
 |
4 | Trat | Trat | 16 | 229,958 | 2,866 | 78 | TH-23 |
 |
 |
5 | Chachoengsao | Chachoengsao | 8 | 720,113 | 5,169 | 139 | TH-24 |
 |
6 | Prachin Buri | Prachin Buri | 31 | 494,680 | 5,026 | 99 | TH-25 | |
 |
 |
7 | Sa Kaeo | Sa Kaeo | 63 | 566,303 | 6,831 | 83 | TH-27 |
Population is based on "Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2019" from Registration Office Department of the Interior. Reference date is 31 December 2019.[2]
Area is based on "Thailand boundary from Department of Provincial Administration.[1]
Economy
For FY 2018, Eastern Thailand Region had a combined economic output of 3,026 trillion baht (US$97.6 billion), or 18.5 percent of Thailand's GDP. Rayong province had an economic output of 1.045 trillion baht (US$33.7 billion). This amounted to a per-capita Gross Provincial Product (GPP) value of 1,067,449 baht (US$34,434), almost double the GPP per-capita of the three following provinces in the ranking.[5]
| Rank | Province | GPP (million baht) |
Population (x 1000) |
GPP per capita (baht) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rayong | 1,045.7 | 980 | 1,067,449 |
| 2 | Chonburi | 1,030.9 | 1,819 | 566,801 |
| 3 | Prachin Buri | 319.0 | 621 | 513,789 |
| 4 | Chachoengsao | 386.6 | 823 | 469,539 |
| 5 | Chanthaburi | 120.2 | 553 | 217,393 |
| 6 | Trat | 43.1 | 267 | 161,322 |
| 7 | Nakhon Nayok | 30.2 | 259 | 116,717 |
| 8 | Sa Kaeo | 50.8 | 630 | 80,716 |
| Eastern region | 3,026,495 | 5,951 | 508,568 |
Languages
The main language of Eastern Thailand is Central Thai language but also regionalism. Krungthep dialect (dominant variant) is spoken among Thai Chinese communities, that is EEC area (such as in Chonburi, Siracha, Pattaya, Padriew, Bangpakong etc.), dialect from Prachinburi Province pretty similar with Ayutthaya dialect (traditional working class dialect in Bangkok), while the Rayong dialect and Chantaburi dialect are pretty similar with Suphanburi dialect (another dialect in Central Thailand).
Isan language are minority status in Eastern Thailand, most are spoken in the eastern part of Prachinburi and upper part of Sa Kaeo Provinces, this is the same variant as the Khonkaen dialect (Standard Lao language). Khmer language in Eastern Thailand mostly spoken among older generation in Chantaburi and today become endangered language.
References
- "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019, Thailand boundary from Department of Provincial Administration in 2013
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ส.2562 [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2019]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- Eastern Seaboard Development Programme - Rayong Archived March 8, 2016, at the Wayback Machine
- "National account". p. 37. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Report 2562-2019: Economic Statistics - National Accounts. Phitsanulok Provincial Statistical Office (Report). National Statistical Office (NSO). 2020. pp. 93–94. ISSN 1905-8314.