Elastica theory
The elastica theory is a theory of mechanics of solid materials developed by Leonhard Euler that allows for very large scale elastic deflections of structures. Euler (1744) and Jakob Bernoulli developed the theory for elastic lines (yielding the solution known as the elastica curve) and studied buckling. Certain situations can be solved exactly by elliptic functions. Later elastica theory was generalized together by the Cosserat brothers François and Eugene into a geometric theory with intrinsic directions at each point (1907).

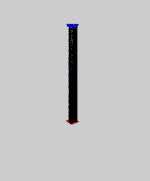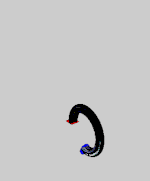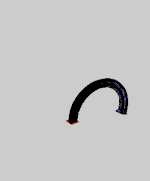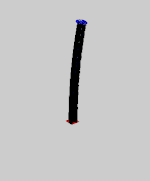
Elastica theory is an example of bifurcation theory. For most boundary conditions several solutions exist simultaneously.
When small deflections of a structure are to be analyzed, elastica theory is not required and an approximate solution may be found using the simpler linear elasticity theory or (for 1-dimensional components) beam theory.
A modern treatise of the planar elastica with full account of bifurcation and instability has been recently presented by Bigoni.[1]
See also
References
- Nonlinear Solid Mechanics: Bifurcation Theory and Material Instability by Davide Bigoni, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1107025417
- A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity by Augustus Edward Hough Love
- Antman, Stuart (2005). Nonlinear Problems of Elasticity. Applied Mathematical Series 107 (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-387-20880-0.
- Web site of Gert van der Heijden.
- A PhD thesis on elastic rods by Geoff Goss, June 2003.
- The elastica: a mathematical history by Raph Levien (about the curve)