Etanidazole
Etanidazole is a nitroimidazole drug that was investigated in clinical trials for its radiosensitizing properties in cancer treatment. Administration of etanidazole results in a decrease of glutathione concentration and inhibits glutathione S-transferase.[1][2] The result is that tissues become more sensitive to the ionizing radiation.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
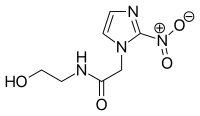
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.363 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H10N4O4 | |
| Molar mass | 214.181 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
- 18F-EF5, a related nitroimidazole
- Misonidazole
References
- Definition of etanidazole, National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary.
- DrugBank DB12736 . Accessed 27 April 2021.
- Inanami, O.; Sugihara, K.; Okui, T.; Hayashi, M.; Tsujitani, M.; Kuwabara, M. (2002). "Hypoxia and etanidazole alter radiation-induced apoptosis in HL60 cells but not in MOLT-4 cells". International Journal of Radiation Biology. 78 (4): 267–274. doi:10.1080/09553000110105695. PMID 12020438. S2CID 37923448.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.