Eucalyptus deflexa
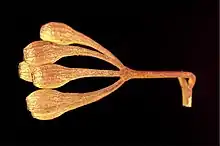
Eucalyptus deflexa, commonly known as Lake King mallee,[2] is a species of mallee that is endemic to Western Australia. It has smooth grey to whitish bark, linear to elliptic or curved adult leaves, pendulous flower buds arranged in groups of seven, cream-coloured or pink flowers and pendulous barrel-shaped fruit.

| Lake King mallee | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Eucalyptus deflexa near Lake King | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Myrtales |
| Family: | Myrtaceae |
| Genus: | Eucalyptus |
| Species: | E. deflexa |
| Binomial name | |
| Eucalyptus deflexa | |
Description
Eucalyptus deflexa is a mallee that typically grows to a height of 1–3 m (3 ft 3 in – 9 ft 10 in), has smooth grey to whitish bark and forms a lignotuber. The adult leaves are linear to curved or narrow elliptic, 50–75 mm (2.0–3.0 in) long and 9–11 mm (0.35–0.43 in) wide on a petiole 5–12 mm (0.20–0.47 in) long. The flower buds are arranged in leaf axils in groups of seven on a pendulous, unbranched peduncle 10–30 mm (0.39–1.18 in) long, the individual buds on a pedicel 6–18 mm (0.24–0.71 in) long. Mature buds are creamy white, cylindrical, 8–12 mm (0.31–0.47 in) long and 4–5 mm (0.16–0.20 in) wide with a conical to rounded operculum 2–2.5 mm (0.079–0.098 in) long and much shorter than the floral cup. Flowering occurs from March to November and the flowers are creamy white or pink. The fruit is a pendulous, woody, barrel-shaped capsule 9–12 mm (0.35–0.47 in) long and 7–9 mm (0.28–0.35 in) wide with the valves enclosed in the fruit.[2][3][4][5]
Taxonomy and naming
Eucalyptus deflexa was first formally described in 1976 by Ian Brooker from a specimen collected 35 km (22 mi) east of Lake King and the description was published in the journal Nuytsia.[5][6] The specific epithet (deflexa) refers to the deflexed flowers.[3][5]
Distribution and habitat
Lake King mallee grows in shrubland on flats or slight rises to the north and north-east of Lake King in the Coolgardie and Mallee biogeographic regions.[2][4]
Conservation status
This eucalypt is classified as "Priority Four" by the Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife,[2] meaning that is rare or near threatened.[7]
See also
References
- "Eucalyptus deflexa". Australian Plant Census. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
- "Eucalyptus deflexa". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Biodiversity, Conservation and Attractions.
- "Eucalyptus deflexa". Euclid: Centre for Australian National Biodiversity Research. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- Chippendale, George M. "Eucalyptus deflexa". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of the Environment and Energy, Canberra. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- Brooker, M. Ian (1976). "Six new taxa of Eucalyptus from Western Australia". Nuytsia. 2 (2): 106–108. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Eucalyptus deflexa". APNI. Retrieved 26 May 2019.
- "Conservation codes for Western Australian Flora and Fauna" (PDF). Government of Western Australia Department of Parks and Wildlife. Retrieved 26 May 2019.