Red lemur
The red lemur (Eulemur rufus), also known as the rufous brown lemur or northern red-fronted lemur, is a species of lemur from Madagascar. Until 2001, the species E. rufus was considered a subspecies of the common brown lemur, E. fulvus,[4] after which it was classified as its own species. In December 2008, the species was split into two separate species, the red lemur, E. rufus, distributed in dry lowland forests in northwestern Madagascar, and the red-fronted lemur, E. rufifrons, distributed in southwest and eastern Madagascar.[3] The species split was based on genetic and morphological evidence.[3] Mitochondrial DNA analysis indicates that E. rufifrons may be more closely related to the common brown lemur (E. fulvus), white-headed lemur (E. albifrons) and Sanford's brown lemur (E. sanfordi) than it is to E. rufus.[3]
| Red lemur | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Strepsirrhini |
| Family: | Lemuridae |
| Genus: | Eulemur |
| Species: | E. rufus |
| Binomial name | |
| Eulemur rufus | |
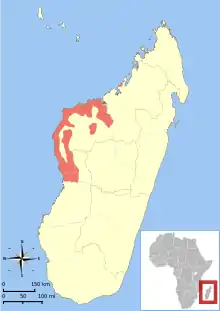 | |
| Distribution of E. rufus[1] | |
The red lemur's range covers dry deciduous forests in southwestern Madagascar between the Betsiboka River to the north and the Tsiribihina River to the south.[3][1][5] The Tsiribihina River forms the boundary between E. rufus, which lives north of the river, and E. rufifrons, which lives south of the river.[3] It has a head and body length of 35 to 48 centimetres (14 to 19 in) and with a 45 to 55 centimetres (18 to 22 in) tail.[5] Its weight ranges between 2.2 and 2.3 kilograms (4.9 and 5.1 lb). It has a gray coat and black face, muzzle and forehead, plus a black line from the muzzle to the forehead, with white eyebrow patches.[5] Males have white or cream colored cheeks and beards, while females have rufous or cream cheeks and beards that are less bushy than males.[5]
The species is currently listed by the IUCN as Vulnerable. The most important threats to the species are hunting, as well as habitat destruction resulting from slash-and-burn agriculture, clearing of land for pasture, fuelwood gathering and logging.[1] The hunting level is viewed as unsustainable.[1]
References
- Razafindramanana, J.; Eppley, T.M.; Rakotondrabe, R.; Rakotoarisoa, A.A.; Ravaloharimanitra, M.; King, T. (2020). "Eulemur rufus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T8209A115562696. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T8209A115562696.en.
- "Checklist of CITES Species". CITES. UNEP-WCMC. Retrieved 18 March 2015.
- Mittermeier, R.; Ganzhorn, J.; Konstant, W.; Glander, K.; Tattersall, I.; Groves, C.; Rylands, A.; Hapke, A.; Ratsimbazafy, J.; Mayor, M.; Louis, E.; Rumpler, Y.; Schwitzer, C. & Rasoloarison, R. (December 2008). "Lemur Diversity in Madagascar". International Journal of Primatology. 29 (6): 1607–1656. doi:10.1007/s10764-008-9317-y. hdl:10161/6237. S2CID 17614597.
- Groves, C. P. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 116. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- Mittermeier, R.; Louis, E.; et al. (2006). Lemurs of Madagascar (Second ed.). Conservation International. pp. 275–277. ISBN 1-881173-88-7.
Further reading
Scholz, Friederike; Kappeler, Peter M. (June 2004). "Effects of Seasonal Water Scarcity on the Ranging Behavior of Eulemur fulvus rufus". International Journal of Primatology. 25 (3): 599–613. doi:10.1023/b:ijop.0000023577.32587.0b. S2CID 23108766.
