Experiments in the Revival of Organisms
Experiments in the Revival of Organisms (Russian: О́пыты по оживле́нию органи́зма) is a 1940 motion picture, directed by David Yashin, that documents Soviet research into the resuscitation of clinically dead organisms. The operations in the film, as well as the design of the heart-lung machine demonstrated in it, the autojektor, were done by Sergei Brukhonenko, whose work in the film is said to have led to the first operations on heart valves.
| Experiments in the Revival of Organisms | |
|---|---|
 Screenshot from the film showing the dog's head attached to Brukhonenko's autojektor | |
| Directed by | David Yashin |
| Written by | Sergei Brukhonenko |
| Starring | Sergei Brukhonenko
|
| Narrated by | J. B. S. Haldane (English) |
| Cinematography | Yekaterina Kashina |
| Animation by | Alexander Prozorov |
Production company | Moscow Studio of Technical Films |
| Distributed by | Brandon Films, Inc. (USA) |
Release date | 1940 |
Running time | 19 minutes (Russian) 20 minutes (English) |
| Country | Soviet Union |
| Languages |
|
Synopsis
The film depicts and discusses a series of medical experiments. The English version of the film begins with British scientist J. B. S. Haldane appearing and discussing how he has personally seen the procedures carried out in the film at an all-Russian physiological congress. The Russian version lacks this explanation. The experiments start with a heart of a canine, which is shown being isolated from a body; four tubes are then connected to the organ. Using an apparatus to supply it with blood, the heart beats in the same manner as if it were in a living organism. The film then shows a lung in a tray, which is operated by bellows that oxygenate the blood.[1]
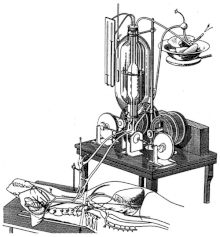
Following the lung scene, the audience is then shown the autojektor, a heart-lung machine, composed of a pair of linear diaphragm pumps, venous and arterial, exchanging oxygen with a water reservoir. It is then seen supplying a dog's head with oxygenated blood. The head is presented with external stimuli, which it responds to. Finally, a dog is brought to clinical death (depicted primarily through an animated diagram of lung and heart activity) by draining the blood from its body, triggering cardiac arrest. It is then left for ten minutes and connected to the heart-lung machine, which gradually returns the blood into the animal's circulation. After several minutes, the heart fibrillates, then restarts a normal rhythm. Respiration likewise resumes and the machine is disconnected. Over the ensuing ten days, the dog recovers from the procedure and continues living a healthy life.[2] According to the film, several dogs were brought back to life using this method, including one which is an offspring of parents who were both also resuscitated.[3]
Production
The film was shot at the Institute of Experimental Physiology and Therapy, in Moscow, and was directed by David Yashin.[4][5] The operations are credited to Doctor Sergei Brukhonenko and Boris Levinskovsky, who were demonstrating a special heart-lung apparatus called the autojektor, also referred to as the heart-lung machine, to the Second Congress of Russian Pathologists in Moscow.[6]
Legacy
The film was shown to an audience of a thousand US scientists in 1943 in the Congress of American-Soviet Friendship.[7] The audience considered that the film "might move many supposed biological impossibilities into the realm of the possible."[2]
Brukhonenko's decapitation experiment was remarked upon by George Bernard Shaw, who stated, "I am even tempted to have my own head cut off so that I can continue to dictate plays and books without being bothered by illness, without having to dress and undress, without having to eat, without having anything else to do other than to produce masterpieces of dramatic art and literature."[8]
Brukhonenko developed a new version of the autojektor for use on human patients in the same year; it can be seen today on display at the Museum of Cardiovascular Surgery at the Bakulev Scientific Center of Cardiovascular Surgery in Russia.[9] Brukhonenko was posthumously awarded the prestigious Lenin Prize.[10]
Some commentators have questioned the film's authenticity, given that none of the more dubious experiments are shown in any full-frame shots. According to some scientists who claimed to have seen the experiments in the film, the severed dog head only survived for a few minutes when attached to the artificial heart, as opposed to the hours claimed in the film.[11] Another source of skepticism are the dogs drained of blood and then brought back to life, as after 10 minutes of death they should have experienced serious brain damage. According to the institute’s records, the dogs only survived for a few days, not several years as the film claimed.[10]
The heart-lung machine demonstrated in the film, the autojektor, was designed and constructed by Sergei Brukhonenko, whose work in the film is said to have led to the first operations on heart valves. The autojektor is similar to modern extracorporeal membrane oxygenation machines, as well as the systems commonly used for renal dialysis in modern nephrology.[12][13]
In popular culture
- In 2004 MF Doom released his song "Fall Back/Titty Fat" (through his album Venomous Villain) which begins and ends with excerpts from the experiment. The music video for the song largely consists of segments from the film.
- Polish poet Wisława Szymborska discussed watching the film in her poem "Experiment".[14]
- Metallica's video for their song "All Nightmare Long" is partially based on the film, and shows Soviet scientists reanimating a dead cat.
- According to Neil Cicierega in the audio commentary for the 2016 Lemon Demon album Spirit Phone, the first track on the album ("Lifetime Achievement Award") was originally titled "Experiments in the Revival", in reference to this film.[15]
References
- Yashin, David (1940). Опыты по оживлению организма [Experiments in the Revival of Organisms] (Motion picture) (in Russian). Retrieved December 10, 2022.
- "Science: Red Research". TIME. November 22, 1943. ISSN 0040-781X. Retrieved May 25, 2006.
- Yashin, David (1940). Experiments in the Revival of Organisms (Motion picture). Techfilm Studio. Retrieved August 8, 2004.
- "Фильм Опыты по оживлению организма (СССР, 1940)" [Film Experiments in the Revival of Organisms (USSR, 1940)]. Афиша (in Russian). Retrieved December 10, 2022.
- Swain, Frank (June 11, 2013). How to Make a Zombie: The Real Life (and Death) Science of Reanimation and Mind Control. Oneworld Publications. p. 39. ISBN 9781851689446.
- Krementsov, Nikolai (June 2009). "Off with your heads: isolated organs in early Soviet science and fiction". Studies in History and Philosophy of Biological and Biomedical Sciences. 40 (2): 87–100. doi:10.1016/j.shpsc.2009.03.001. ISSN 1879-2499. PMC 2743238. PMID 19442924.
- "Betwixt life and death!". The Bombay Chronicle. October 7, 1945. p. 3. Retrieved December 10, 2022.
- Boese, Alex (November 5, 2007). Elephants on Acid: And Other Bizarre Experiments (1st ed.). Mariner Books. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-15-603135-6.
- "Отдел истории сердечно-сосудистой хирургии" [Department of Cardiovascular History]. Bakulev Scientific Center of Cardiovascular Surgery (in Russian). Archived from the original on February 8, 2006. Retrieved March 6, 2006.
- "Собачье сердце, собачья голова" [A dog's heart, a dog's head]. Naked Science (in Russian). January 23, 2014. Retrieved December 10, 2022.
- Bellows, Alan (2009). Alien Hand Syndrome: And Other Too-Weird-Not-to-Be-True Stories. Workman Publishing Company. pp. 31–33. ISBN 9780761152255 – via Archive.org.
- Glyantsev, Sergey P.; Bogopolsky, Pavel M.; Tchantchaleishvili, Vakhtang (2018). "Bryukhonenko's Autojector: The First Apparatus for Cardiopulmonary Bypass and Extracorporeal Life Support". ASAIO Journal. 64 (1): 129–133. doi:10.1097/MAT.0000000000000605. ISSN 1538-943X. PMID 28617693. S2CID 24010887.
- Konstantinov, Igor E; Alexi-Meskishvili, Vladimir V (2000). "Sergei S. Brukhonenko: the development of the first heart-lung machine for total body perfusion". The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 69 (3): 962–966. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(00)01091-2. ISSN 0003-4975. Retrieved April 28, 2017.
- Szymborska, Wisława (1995). "Experiment". View with a Grain of Sand: Selected Poems (1 ed.). New York: Harcourt Brace & Co. pp. 104–105. ISBN 978-0-15-600216-5.
- Cicirega, Neil (2018). Spirit Phone (Commentary track). Needlejuice Records. Event occurs at 50:39. Archived from the original on November 29, 2020. Retrieved January 7, 2021 – via YouTube.
Further reading
- Hill, J. D. (September 1982). "John H. Gibbon, Jr. Part I. The development of the first successful heart-lung machine". The Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 34 (3): 337–341. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62507-6. ISSN 0003-4975. PMID 7052001.
- Fou, Adora Ann (1997). "John H. Gibbon. The first 20 years of the heart-lung machine". Texas Heart Institute Journal. 24 (1): 1–8. ISSN 0730-2347. PMC 325389. PMID 9068131.
- Passaroni, Andréia Cristina; Silva, Marcos Augusto de Moraes; Yoshida, Winston Bonetti (2015). "Cardiopulmonary bypass: development of John Gibbon's heart-lung machine". Revista Brasileira De Cirurgia Cardiovascular: Orgao Oficial Da Sociedade Brasileira De Cirurgia Cardiovascular. 30 (2): 235–245. doi:10.5935/1678-9741.20150021. PMC 4462970. PMID 26107456.
- Blair-St Giles, B. A.; Hillman, H. (August 1983). "Dying and death, with special reference to brain death. A bibliography". Resuscitation. 10 (4): 235–251. doi:10.1016/0300-9572(83)90026-6. ISSN 0300-9572. PMID 6316444.
- Adamenko, N. P. (1969). "[Technic of experimental resuscitation of dogs with a variant of the method of extracorporeal circulation using S. S. Briukhonenko's autojector pump and a live parabiotic donor]". Patologicheskaia Fiziologiia I Eksperimental'naia Terapiia (in Russian). 13 (3): 69–71. ISSN 0031-2991. PMID 5264992.