FAM110A
Protein FAM110A, also known as protein family with sequence similarity 110, A, C20orf55[5] or BA371L19.3[6] is encoded by the FAM110A gene. FAM110A is located on chromosome 20[6] and is a part of the greater FAM110 gene family,[7] consisting of FAM110A, FAM110B, and FAM110C.
| FAM110A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | FAM110A, C20orf55, F10, bA371L19.3, family with sequence similarity 110 member A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 611393 MGI: 1921097 HomoloGene: 12862 GeneCards: FAM110A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gene
Overview
In humans, FAM110A is located on the plus strand at 20p13.[6] The gene transcript is found from base pairs 833,715 to 846,279, with a total transcript length of 12,564 base pairs.[5] The FAM110A mRNA transcript is predicted to contain two exons.[5] An upstream promoter region for FAM110A is predicted to be 1,111 base pairs long.[8] Six different mRNA transcripts of FAM110A are predicted, all differing in their 5' untranslated regions.[5]
Homology
219 organisms have been reported to have orthologs with the human FAM110A gene.[5]
| Species | Taxonomic group | Date of divergence (MYA) | Accession | Sequence length | Sequence identity | Sequence similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thirteen-lined ground squirrel (Ictidomys tridecemlineatus) | Mammal | 90 | XP_005320619.1 | 295 | 92% | 94% |
| Domesticated dog (Canis lupus familiaris) | Mammal | 96 | XP_005634952.1 | 295 | 91% | 93% |
| Armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) | Mammal | 105 | XP_023446141.1 | 284 | 85% | 85% |
| Garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis) | Reptile | 312 | XP_013922001.1 | 360 | 46% | 58% |
| Painted turtle (Chrysemys picta bellii) | Reptile | 312 | XP_005304966.1 | 362 | 48% | 59% |
| Hummingbird (Calypte anna) | Bird | 312 | XP_030319175.1 | 337 | 53% | 61% |
| Chicken (Gallus gallus) | Bird | 312 | XP_003642512.1 | 331 | 56% | 62% |
| Worm (Microcaecilia unicolor) | Amphibian | 351.8 | XP_030068004.1 | 381 | 39% | 49% |
| Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) | Fish | 435 | XP_033863480.2 | 350 | 43% | 54% |
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | Fish | 435 | XP_003201231.1 | 446 | 59% | 71% |
| Deer tick (Ixodes scapularis) | Arthropod | 797 | XP_029825208.1 | 337 | 31% | 40% |
Regulation
| Matrix family | Matrix information | Start position | End position | Strand | Matrix similarity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGF-β induced apoptosis proteins | Cysteine-serine-rich nuclear protein 1 (AXUD1, AXIN1 up-regulated 1) | 277 | 283 | (+) | 1.00 |
| CAS interacting zinc finger protein | Zinc finger protein 384 (Cas-interacting zinc finger protein - CIZ) | 305 | 315 | (+) | 1.00 |
| Lim homeodomain factors | LIM homeobox transcription factor 1, alpha | 342 | 364 | (-) | 1.00 |
| SWI/SNF related nucleophosphoproteins with a RING finger DNA binding motif | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 3 | 354 | 364 | (-) | 1.00 |
| SWI/SNF related nucleophosphoproteins with a RING finger DNA binding motif | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 3 | 357 | 367 | (+) | 1.00 |
| Cart-1 (cartilage homeoprotein 1) | Binding site for S8 type homeodomains | 421 | 441 | (-) | 1.00 |
| NKX homeodomain factors | Homeo domain factor Nkx-2.5/Csx, tinman homolog low affinity sites | 423 | 441 | (-) | 1.00 |
| TCF11 transcription factor | TCF11/LCR-F1/Nrf1 homodimers | 559 | 565 | (+) | 1.00 |
| EVI1-myleoid transforming protein | MEL1 (MDS1/EVI1-like gene 1) DNA-binding domain 2 | 612 | 628 | (-) | 1.00 |
| C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors 37 | Zinc finger protein 37 alpha (KOX21) | 770 | 778 | (-) | 1.00 |
| C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors 2 | Zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 | 819 | 841 | (-) | 1.00 |
| Myeloid zinc finger 1 factors | Myeloid zinc finger protein MZF1 | 1002 | 1012 | (-) | 1.00 |
| C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors 2 | KRAB-containing zinc finger protein 300 | 1014 | 1036 | (+) | 1.00 |
| C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors 2 | Zinc finger with KRAB and SCAN domains 3 | 1029 | 1051 | (-) | 1.00 |
Protein
Overview
All human FAM110A transcript variants encode the same protein, which is 295 amino acids in length.[5] The human FAM110A protein is projected to weigh 31.3 kiladaltons and have an isoelectric point of 10.5.[9]
| Species | Accession | Repeating structures | Positions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human (Homo sapiens) | NP_001035812.1 | SPARP | 162-166; 177-181 |
| Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) | XP_003316845.1 | SPARP | 162-166; 177-181 |
| Mouse (Mus musculus) | NP_001276079.1 | PATP | 11-14; 139-142 |
| Chicken (Gallus gallus) | XP_015151953.1 | AVRR | 88-91; 168-171 |
| PRSA | 104-107; 285-288 | ||
| SAGR | 106-109; 147-150 | ||
| PAAP | 158-161; 199-202 | ||
| Zebrafish (Danio rerio) | XP_009302562.1 | LARP | 88-91; 348-351 |
Human FAM110A is predicted to contain one standard deviation less than average frequencies of methionine, asparagine, and isoleucine residues, while containing one standard deviation higher frequencies of serine and proline residues.[10] Human FAM110A is also predicted to contain a frequency of arginine residues two standard deviations higher than average.[10] The presence of a high frequency of arginine residues is also apparent in the FAM110A chimpanzee, mouse, chicken and zebrafish orthologs,[10] indicating that it may play a vital role to the function of the gene due to its high conservation.
FAM110A is predicted to be hydrophilic and soluble.[12]
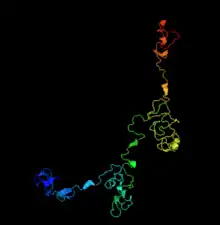
The tertiary structure of FAM110A is predicted to be 80% disordered.[14]
Post-translational modification
The N-terminal glycine residue FAM110A is not predicted to be myristolated (confidence: 0.97),[15] indicating that FAM110A is not membrane-associated.
It is predicted that FAM110A contains no sulfation of tyrosine residues,[16] suggesting that FAM110A is not secreted.
Phosphorylation analysis indicates FAM110A to be associated with the AGC and Akt kinase families.[17]
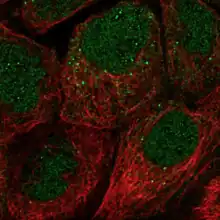
Immunofluorescent analysis of FAM110A reveals the protein to be localized in the nucleoplasm, cytosol, and vesicles.[11]
Interacting proteins
| Protein abbreviation | Protein name | Association type |
|---|---|---|
| CSNK1E | Casein kinase 1 isoform ε | Two hybrid |
| DYNA1I1 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain | Two hybrid |
| KRT15 | Type 1 cytoskeletal keratin | Two hybrid |
| TRIM23 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase | Two hybrid |
| GOLGA2 | Member 2 Golgin (subfamily A) | Two hybrid |
Clinical significance
Cancer pathogenesis
FAM110A has been observed to be abnormally expressed in prostate cancer metastasis, where it co-localizes with E-cadherin and β-catenin at cell-cell adherens junctions,[18] suggesting FAM110A’s involvement in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathogenesis. The greater FAM110 gene family is aberrantly methylated in breast cancer cells,[19] and has been shown to be associated with reduced time to distant metastasis in breast cancer patients.[19]
Cell cycle involvement
FAM110A has been found to localize to centrosomes and accumulate at the microtubule organizing center in interphase and at spindle poles in mitosis.[7]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000125898 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000027459 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "FAM110A family with sequence similarity 110 member A [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "FAM110A Gene". GeneCards. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- Hauge H, Patzke S, Aasheim HC (July 2007). "Characterization of the FAM110 gene family". Genomics. 90 (1): 14–27. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2007.03.002. PMID 17499476.
- "Genomatix". Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "ExPASy - Compute pI/Mw tool". web.expasy.org. Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "SAPS: Statistical Analysis of Protein Sequences". EMBL-EBI. European Molecular Biology Laboratory. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "Anti-FAM110A Antibody (HPA069240) - Atlas Antibodies". www.atlasantibodies.com. Atlas Antibodies. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "SOSUI: Classification and secondary structure prediction for membrane proteins". harrier.nagahama-i-bio.ac.jp. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "I-TASSER server for protein structure and function prediction". zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu. Zhang Lab, University of Michigan.
- "PHYRE2 Protein Fold Recognition Server". www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk. Structural Bioinformatics Group, Imperial College, London. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "ExPASy - Myristoylation tool". web.expasy.org. Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "ExPASy - Sulfinator tool". web.expasy.org. Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics. Retrieved 19 December 2020.
- "GPS 5.0 - Kinase-specific Phosphorylation Site Prediction". gps.biocuckoo.cn. The CUCKOO Workgroup.
- Tsuruta, H.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Schalken, J.A. (April 2014). "The expression and function of FAM110A in human prostate cancer". European Urology Supplements. 13 (1): e303. doi:10.1016/S1569-9056(14)60298-0.
- Locke WJ, Clark SJ (November 2012). "Epigenome remodelling in breast cancer: insights from an early in vitro model of carcinogenesis". Breast Cancer Research. 14 (6): 215. doi:10.1186/bcr3237. PMC 4053120. PMID 23168266.