format (command)
In computing, format, a command-line utility that carries out disk formatting. It is a component of various operating systems, including 86-DOS, MS-DOS, IBM PC DOS and OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS.
 The MS-DOS FORMAT command | |
| Written in | MS-DOS: x86 assembly language FreeDOS: C |
|---|---|
| Operating system | RT-11, 86-DOS, MS-DOS, PC DOS, OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS, ISIS-II, iRMX 86, TRIPOS, AmigaDOS, Z80-RIO, OS-9, MSX-DOS, FlexOS, PC-MOS, SpartaDOS X, DR DOS, ROM-DOS, 4690 OS, FreeDOS, PTS-DOS, SISNE plus, Windows, ReactOS |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | MS-DOS: MIT PC-MOS: GPLv3 FreeDOS: GPLv2 ReactOS: LGPL-2.0-or-later |
Overview
The command performs the following actions by default on a floppy disk, hard disk drive, solid state (USB), or other magnetic medium (it will not perform these actions on optical media):
- clearing the FAT entries by changing them to 0x00
- clearing the FAT root directory by changing any values found to 0x00[nb 1][1][2][3]
- checking each cluster to see if it is good or bad and marking it as good or bad in the FAT
Any storage device must have its medium structured to be useful. This process is referred to as "creating a filesystem" in Unix, Linux, or BSD.[4] Under these systems different commands are used. The commands can create many kinds of file systems, including those used by DOS, Windows, and OS/2.
Implementations
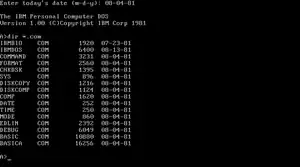
FORMAT.COM, among several other commands, in IBM PC DOS 1.0.
FORMAT.CMD in CP/M-86The command is also available in Intel ISIS-II,[5] iRMX 86,[6] MetaComCo TRIPOS,[7] AmigaDOS,[8] Zilog Z80-RIO,[9] Microware OS-9,[10] DR FlexOS,[11] TSL PC-MOS,[12] SpartaDOS X,[13] Datalight ROM-DOS,[14] IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS,[15] PTS-DOS,[16] SISNE plus,[17] and in the DEC RT-11[18] operating system.
Microsoft DOS and Windows
On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 1 and later.[19]
Optionally (by adding the /S, for "system" switch), format can also install a Volume Boot Record. With this option, Format writes bootstrap code to the first sector of the volume (and possibly elsewhere as well). Format always writes a BIOS Parameter Block to the first sector, with or without the /S option.
Another option (/Q) allows for what Microsoft calls "Quick Format". With this option the command will not perform steps 2 and 3 above. Format /Q does not alter data previously written to the media.
Typing "format" with no parameters in MS-DOS 3.2 or earlier would automatically, without prompting the user, format the current drive; however in MS-DOS 3.3 and later it would simply produce the error: "required parameter missing".
DR/Novell DOS
DR DOS 6.0 includes an implementation of the format command.[20]
ReactOS
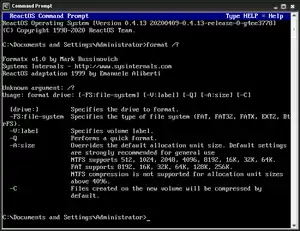
format command on ReactOSThe ReactOS implementation is based on a free clone developed by Mark Russinovich for Sysinternals in 1998. It is licensed under the GPL.[22] It was adapted to ReactOS by Emanuele Aliberti in 1999 and supports FAT, FAT32, FATX, EXT2, and BtrFS filesystems.
See also
Notes
- The directory entries get filled with
0x00since MS-DOS 1.25 and PC DOS 2.0. If the Format command line option /O is provided, the first byte of each directory entry is set to0xE5hto create a FAT format usable by PC DOS 1.0-1.1. However, not providing /O will significantly speed up directory searches under MS-DOS 1.25 and PC DOS 2.0 and higher. Older versions of MS-DOS, PC DOS, and 86-DOS only supported the0xE5marker.
References
- Paterson, Tim (2013-12-19) [1983]. "Microsoft DOS V1.1 and V2.0: /msdos/v20source/FORMAT.TXT". Computer History Museum, Microsoft. Retrieved 2014-03-25. (NB. While the publishers claim this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC DOS 2.11.)
- Shustek, Len (2014-03-24). "Microsoft MS-DOS early source code". Software Gems: The Computer History Museum Historical Source Code Series. Retrieved 2014-03-29. (NB. While the author claims this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC DOS 2.11.)
- Levin, Roy (2014-03-25). "Microsoft makes source code for MS-DOS and Word for Windows available to public". Official Microsoft Blog. Archived from the original on 2014-03-28. Retrieved 2014-03-29. (NB. While the author claims this would be MS-DOS 1.1 and 2.0, it actually is SCP MS-DOS 1.25 and a mixture of Altos MS-DOS 2.11 and TeleVideo PC DOS 2.11.)
- : EXAMPLE section – FreeBSD System Manager's Manual
- ISIS II Users Guide
- "intel :: iRMX :: 146194-001 irmxR6Intro" – via Internet Archive.
- https://www.pagetable.com/docs/amigados_tripos/tripos_manuals.pdf
- Rugheimer, Hannes (1988). Quick reference. Abacus. ISBN 9781557550491. Retrieved 2020-09-14 – via archive.org.
- Z80-RIO OPERATING SYSTEM USER'S MANUAL
- Paul S. Dayan (1992). The OS-9 Guru - 1 : The Facts. Galactic Industrial Limited. ISBN 0-9519228-0-7.
- "FlexOS User's Guide" (PDF). www.bitsavers.org. 1986. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- "roelandjansen/pcmos386v501". GitHub. 2 January 2022.
- SpartaDOS X 4.48 User Guide
- "Datalight ROM-DOS User's Guide" (PDF). www.datalight.com.
- "Users guide". archive.org. Retrieved 2020-09-14.
- "PTS-DOS 2000 Pro User Manual" (PDF). Buggingen, Germany: Paragon Technology GmbH. 1999. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-05-12. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- "SISNE plus - Referência Sumária". Datassette. May 14, 2015.
- "RT-11 HELP FILE". paleoferrosaurus.com. Archived from the original on 2018-07-17. Retrieved 2018-07-16.
- Wolverton, Van (2003). Running MS-DOS Version 6.22 (20th Anniversary Edition), 6th Revised edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 0-7356-1812-7.
- DR DOS 6.0 User Guide Optimisation and Configuration Tips
- "ibiblio.org FreeDOS Package -- Format (FreeDOS Base)". www.ibiblio.org.
- "reactos/reactos". GitHub. 3 January 2022.
Further reading
- Cooper, Jim (2001). Special Edition Using MS-DOS 6.22, Third Edition. Que Publishing. ISBN 978-0789725738.
- Kathy Ivens; Brian Proffit (1993). OS/2 Inside & Out. Osborne McGraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0078818714.
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00148-3.