FR901483
(−)-FR901483 is a tyrosine-derived alkaloid that was isolated from the fungus Cladobotryum sp.[1] It was shown to have potent immunosuppressant activity in animal models. It is believed to function through inhibition of purine nucleotide biosynthesis.
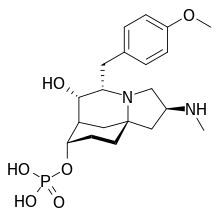 Chemical structure of FR901483 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,5S,6S,7R,8S,10aS)-6-Hydroxy-5-(4-methoxybenzyl)-2-(methylamino)octahydro-1H-7,10a-methanopyrrolo[1,2-a]azocin-8-yl dihydrogen phosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| Properties | |
| C20H31N2O6P | |
| Molar mass | 426.450 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Biosynthesis
The biosynthesis of (−)-FR901483 was elucidated by Zhang et al. in 2021.[2] These researchers probed the genome of Cladobotryum sp. for analogues of PsiK from the psilocybin biosynthetic pathway and identified the gene cluster Frz, which contains the sequence for a non-ribosomal peptide synthase FrzA. The cluster also contains 11 other genes which encode a phosphotransferase (FrzJ), a phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (PPAT, FrzK), two P450 monooxygenases (FrzC and FrzL), two methyltransferases (FrzE and FrzF), an ene-reductase (OYE, FrzD), a nonheme, iron and α-ketoglutarate dependent oxygenase (αKG, FrzG), two short-chain dehydrogenase/reductases (SDRs, FrzB, and FrzI), and a hypothetical protein (HP, FrzH). By heterologous expression of these genes in the organism Aspergillus nidulans, they demonstrated that these genes encode enzymes capable of catalyzing the biosynthesis of (−)-FR901483 from L-tyrosine.
The first transformation is catalyzed by FrzA and FrzB, which allows coupling of two tyrosine residues and reduction of the resulting ketones. In the next step, FrzC, a P450 enzyme, catalyzes the subsequent radical oxidative transformation that is NADPH-dependent. Following this, FrzE and FrzF catalyze two S-adenosyl methionine (SAM)-dependent methylations. FrzG then performs an oxidation of an amine, allowing ring opening. Cyclization and reduction is then catalyzed by FrzH. Further ketone reduction is catalyzed by FrzJ. Finally, ATP-dependent phosphorylation is carried out by the activity of FrzJ.
References
- Sakamoto, K (1 Jan 1996). "FR901483, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from Cladobotryum sp. No. 11231. Taxonomy of the producing organism, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activities". The Journal of Antibiotics. 49 (1): 37–44. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.49.37. PMID 8609083.
- Zhang, Zhuan (December 29, 2020). "Biosynthesis of the Immunosuppressant (−)-FR901483". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1 (143): 132–136. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c12352. PMC 8094545. PMID 33372776.