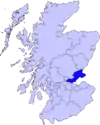
Fife
Fife (/faɪf/ FYFE, Scottish English: [fɐi̯f]; Scottish Gaelic: Fìobha, IPA: [fiːvə]; Scots: Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i.e. the historic counties of Perthshire and Kinross-shire) and Clackmannanshire. By custom it is widely held to have been one of the major Pictish kingdoms, known as Fib, and is still commonly known as the Kingdom of Fife within Scotland. A person from Fife is known as a Fifer. In older documents the county was very occasionally known by the anglicisation Fifeshire.
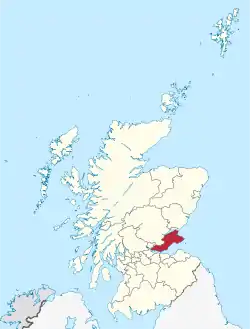
Fife
Fìobha | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms Council logo | |
| Coordinates: 56°15′00″N 3°12′00″W | |
| Sovereign state | |
| Country | |
| Lieutenancy area | Fife |
| Admin HQ | Glenrothes (since 1975) Cupar (until 1975)[1] |
| Government | |
| • Body | Fife Council |
| • Control | Lab (council NOC|Minority Administration) |
| • MPs | |
| • MSPs | |
| Area | |
| • Total | 512 sq mi (1,325 km2) |
| • Rank | Ranked 13th |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 374,730 |
| • Rank | Ranked 3rd |
| • Density | 730/sq mi (280/km2) |
| Demonym | Fifer |
| ONS code | S12000047 |
| ISO 3166 code | GB-FIF |
| Website | www |
Fife is Scotland's third largest local authority area by population. It has a resident population of just under 367,000, over a third of whom live in the three principal settlements, Dunfermline, Kirkcaldy and Glenrothes. On the northeast coast of Fife lies the historic town of St Andrews, home to the University of St Andrews—the most ancient university of Scotland and one of the oldest universities in the world—and the Old Course at St Andrews, considered the world's oldest golf course.
History
Fife, bounded to the north by the Firth of Tay and to the south by the Firth of Forth, is a natural peninsula whose political boundaries have changed little over the ages. The Pictish king list and De Situ Albanie documents of the Poppleton manuscript mention the division of the Pictish realm or Albany into seven sub-kingdoms, one being Fife.[2]: 70–72 The earliest known reference to the common epithet The Kingdom of Fife dates from only 1678, in a proposition that the term derives from the quasi-regal privileges of the Earl of Fife.[2]: 132 The notion of a kingdom may derive from a misinterpretation of an extract from Wyntoun.[2]: 133 The name is recorded as Fib in A.D. 1150 and Fif in 1165. It was often associated with Fothriff.
The hill-fort of Clatchard Craig, near Newburgh, was occupied as an important Pictish stronghold between the sixth and eighth centuries AD.[3][4]
Fife was an important royal and political centre from the reign of King Malcolm III onwards, as the leaders of Scotland gradually moved southwards away from their ancient strongholds around Scone. Malcolm had his principal home in Dunfermline and his wife Margaret was the main benefactor of Dunfermline Abbey. The Abbey replaced Iona as the final resting place of Scotland's royal elite, with Robert I amongst those to be buried there.[5]
The Earl of Fife was until the 15th century considered the principal peer of the Scottish realm, and reserved the right of crowning the nation's monarchs, reflecting the prestige of the area.
A new royal palace was gradually constructed at Falkland, formerly the stronghold of Clan MacDuff, and was used by successive monarchs of the House of Stuart, who favoured Fife for its rich hunting grounds.[6]
King James VI of Scotland described Fife, in Middle Scots, as a: "beggar's mantle fringed wi gowd"[7] the golden fringe being the coast and its chain of little ports with their thriving fishing fleets and rich trading links with the Low Countries. Wool, linen, coal and salt were all traded. Salt pans heated by local coal were historically a feature of the Fife coast. The distinctive red clay pan tiles seen on many old buildings in Fife arrived as ballast on trading boats and replaced the previously thatched roofs.
In 1598, King James VI employed a group of 11 men from Fife, who became known as the Fife adventurers, to colonise the Isle of Lewis in an attempt to begin the "civilisation" and de-gaelicisation of the region.[8] This endeavour lasted until 1609 when the colonists, having been opposed by the native population, were bought out by Kenneth Mackenzie, the clan chief of the Mackenzies.[8]
Fife became a centre of heavy industry in the 19th century. Coal had been mined in the area since at least the 12th century, but the number of pits increased ten-fold as demand for coal grew in the Victorian period. Previously rural villages such as Cowdenbeath rapidly swelled into towns as thousands moved to Fife to find work in its mines. The opening of the Forth and Tay rail bridges linked Fife with Dundee and Edinburgh and allowed the rapid transport of goods. Modern ports were constructed at Methil, Burntisland and Rosyth. Kirkcaldy became the world centre for the production of linoleum. Postwar Fife saw the development of Scotland's second new town, Glenrothes. Originally to provide housing for miners at a new coal mine, the town eventually attracted a high number of modern Silicon Glen companies to the region.[9][10][11][12] Fife Council and Fife Constabulary also centre their operations in Glenrothes.
There are numerous notable historical buildings in Fife, some of which are managed by the National Trust for Scotland or Historic Scotland. They include Dunfermline Abbey (the last resting place of Scottish royalty), the palace in Culross, Ravenscraig Castle in Kirkcaldy, Dysart Harbour area, Balgonie Castle near Coaltown of Balgonie, Falkland Palace (hunting palace of the Scottish Kings), Kellie Castle near Pittenweem, Hill of Tarvit (a historical house), St. Andrews Castle, St. Andrews Cathedral and St. Rule's Tower.
Administrative history
.jpg.webp)
Fife was one of the ancient provinces of Scotland, under the authority of the Mormaer or Earl of Fife. The early province of Fife appears to have covered only that part of the later county lying east of a line from Newburgh to Scoonie. The western part of the later county was in the province of Fothriff, which also covered areas that would later become Kinross-shire and part of Clackmannanshire, including the town of Clackmannan. By the early thirteenth century Fothriff had been joined to the earldom of Fife. Sometime between the reign of David I (reigned 1124–1153) and the mid-thirteenth century, this part of Scotland was divided into shires, being areas administered by a sheriff. Kinross and Clackmannan were each given their own sheriffs, whilst the rest of the Fife and Fothriff area was placed under the authority of the Sheriff of Fife.[13]
Over time, Scotland's shires became more significant than the old provinces, with more administrative functions being given to the sheriffs. The larger earldom of Fife, including Kinross and Clackmannan, was therefore gradually eclipsed in importance by the smaller shire of Fife. In 1667 Commissioners of Supply were established for each shire, which would serve as the main administrative body for the area until the creation of county councils in 1890. Following the Acts of Union in 1707, the English term "county" came to be used interchangeably with the older term "shire".[14]
Elected county councils were established in 1890 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, taking most of the functions of the commissioners (which were eventually abolished in 1930). The two burghs of Dunfermline and Kirkcaldy were deemed capable of managing their own affairs and so were excluded from the administrative area of the county council.[15] The 1889 act also led to a review of boundaries, with several exclaves being transferred to a county they actually bordered, and parishes which straddled more than one county being adjusted such that each parish was entirely in a single county. These changes saw some adjustments to Fife's boundaries with Kinross-shire and Perthshire, with the most significant change being that Fife gained the two parishes of Culross and Tulliallan, which had previously formed an exclave of Perthshire.[16] Dunfermline and Kirkcaldy were brought within the administrative area of the county council in 1930, but classed as large burghs, allowing them to continue to deliver many local government functions themselves.[17]

Fife County Council was based at County Buildings in Catherine Street in Cupar, which had been built in 1817 as the county's sheriff court and meeting place for the commissioners of supply, replacing the town's medieval tolbooth which had performed the same functions.[18][19]
Fife County Council was abolished in 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which replaced Scotland's counties, burghs and landward districts with a two-tier structure of upper-tier regions and lower-tier districts. Fife region was created covering the same area as the county, divided into three districts: Dunfermline, Kirkcaldy and North-East Fife. In 1996 the district councils were abolished and Fife Regional Council became a unitary authority known as Fife Council. Fife is one of the six local authorities in the city region of Edinburgh and southeast Scotland.
There was a parliamentary constituency of Fife in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom until 1885 and the Fife constituency in the Parliament of Scotland until the Acts of Union 1707.
Governance

Fife is represented by five constituency members of the Scottish Parliament (MSPs) and four members of the United Kingdom parliament (MPs) who are sent to Holyrood and the British Parliament respectively. Following the 2015 general election, all four of the MPs constituencies were held by the Scottish National Party.[20] In the 2017 general election, Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath was regained by Labour.[21] At the same election, the seat of North East Fife became the closest seat in the country with the SNP holding a majority of 2 over the Liberal Democrats.[22] Three of the Scottish Parliament constituencies are held by the Scottish National Party: Cowdenbeath, Dunfermline and Mid Fife and Glenrothes. One is held by the Scottish Liberal Democrats: North East Fife.[23]
Fife Council's administrative headquarters and Police Scotland's P Division (formerly Fife Constabulary) are based in Glenrothes. The Council meetings take place in Fife House in the town centre. The west wing of the building was built by the Glenrothes Development Corporation (GDC) as their offices in 1969, which was later used as the headquarters of Fife Regional Council from shortly after its creation in 1975.[24][25]
Geography

.svg.png.webp)
Fife is a peninsula in eastern Scotland bordered on the north by the Firth of Tay, on the east by the North Sea and by the Firth of Forth to the south. The route to the west is partially blocked by the mass of the Ochil Hills. Almost all road traffic into and out of Fife has to pass over one of four bridges, south on the Forth Road Bridge (public transport and cyclists only) and Queensferry Crossing, west on the Kincardine Bridge or north-east via the Tay Road Bridge, the exception being traffic headed north on the M90. Tolls were abolished on the Tay Road Bridge and Forth Road Bridge on 11 February 2008.
There are extinct volcanic features, such as the Lomond Hills which rise above rolling farmland, and Largo Law, a volcanic plug in the east. At 522 metres (1,713 ft), the West Lomond is the highest point in Fife. The coast has fine but small harbours, from the industrial docks in Burntisland and Rosyth to the fishing villages of the East Neuk such as Anstruther and Pittenweem. The large area of flat land to the north of the Lomond Hills, through which the River Eden flows, is known as the Howe of Fife.

North of the Lomond Hills can be found villages and small towns in a primarily agricultural landscape. The areas in the south and west of Fife, including the towns of Dunfermline, Glenrothes, Kirkcaldy and the Levenmouth region are lightly industrial and more densely populated. The only areas which could claim to be heavily industrial are Rosyth, around the naval dockyard and perhaps the Mossmorran Natural Gas Liquids fractionation plant on the outskirts of Cowdenbeath.
The east corner of Fife, along the string of villages between Earlsferry and Kingsbarns, and along with their hinterland, is known as the East Neuk (corner, or projecting point of land) of Fife;[27] small settlements around sheltered harbours, with distinctive vernacular "Dutch" or corbie (crow) stepped gabled and stone-built architecture. The area has amongst the highest concentration of second homes and holiday lets in Scotland.[28][29][30][31] The fishing industry, on which the coastal East Neuk settlements were built, has declined in recent years with the main fishing fleet now operating from Pittenweem and the harbour in Anstruther being used as a marina for pleasure craft.
There are several islands located off the coast of Fife, such as the Isle of May, Inchkeith and Inchcolm. The former Preston Island south of Valleyfield is no longer an island following land reclamation work.
Settlements
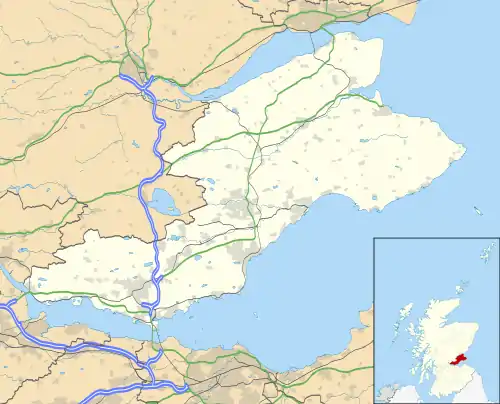
Cupar took over as county town from Crail in the early 13th century. Glenrothes is now the administrative centre, after the decision to locate the headquarters of the newly established Fife Regional Council there in 1975. Fife's three major towns are Kirkcaldy, Dunfermline (awarded city status in 2022) and Glenrothes. According to the 2012 estimate, Dunfermline is the largest settlement by population,[32] followed by Kirkcaldy then Glenrothes. The next most sizeable towns by population are St Andrews, Cowdenbeath, Rosyth, Methil and Dalgety Bay.
Largest settlements by population:
| Settlement | Population (mid-2020 est.)[33] |
|---|---|
| Dunfermline |
54,990 |
| Kirkcaldy |
50,370 |
| Glenrothes |
38,360 |
| St Andrews |
18,410 |
| Rosyth |
13,570 |
| Cowdenbeath |
12,030 |
| Methil |
10,890 |
| Dalgety Bay |
9,710 |
| Leven |
9,420 |
| Cupar |
8,960 |
| Lochgelly |
7,300 |
| Kelty |
6,760[lower-alpha 1] |
| Burntisland |
6,630 |
| Ballingry |
5,940 |
| Cardenden |
5,190 |
| Inverkeithing |
4,820 |
| Kennoway |
4,570 |
| Newport-on-Tay |
4,210 |
| Buckhaven |
4,050 |
| Anstruther |
3,950 |
| Tayport |
3,750 |
| Leuchars |
3,160 |
| Leslie |
3,010 |
| Kincardine |
2,940 |
| Kinghorn |
2,940 |
- Part of Kelty is located in Perth and Kinross.
Historic parishes
The county was formerly divided into parishes, often but not always based on a town or village:
- Abbotshall
- Abdie
- Aberdour
- Anstruther Easter
- Anstruther Wester
- Arngask (to Perthshire in 1891)
- Auchterderran
- Auchtermuchty
- Auchtertool
- Ballingry
- Balmerino
- Beath
- Buckhaven
- Burntisland
- Cameron
- Carnbee
- Carnock
- Cellardyke
- Ceres
- Collessie
- Cowdenbeath
- Crail
- Creich
- Crossgates
- Culross (to Fife from Perthshire, 1891)
- Cults
- Cupar
- Dairsie
- Dalgety
- Dunbog
- Dunfermline
- Dunino
- Dysart
- Elie
- Falkland
- Ferry Port on Craig[34]
- Flisk
- Forgan
- Freuchie
- Glenrothes
- Inverkeithing
- Kelty
- Kemback
- Kennoway
- Kilconquhar
- Kilmany
- Kilrenny
- Kinghorn
- Kinglassie
- Kingsbarns
- Kingskettle
- Kirkcaldy
- Ladybank
- Largo
- Leslie
- Leuchars
- Leven
- Lochgelly
- Logie
- Lumphinnans
- Markinch
- Methil
- Monimail
- Moonzie
- Newburgh
- Newburn
- Pitlessie
- Pittenweem
- Rosyth
- Saline
- Scoonie
- St Andrews & St Leonards
- St Monance (and Abercrombie)
- Strathmiglo
- Thornton
- Torryburn
- Wellwood
- Wemyss
- Wormit
Communities
Fife is divided into 105 community council areas, 85 of which have community councils as at 2023.[35]
Culture


Fife contains 4,961 listed buildings and 48 conservation areas.[36] Domestic sites of importance include Falkland Palace, Kellie Castle, Dunfermline Palace, St Andrews Castle, Culross Palace and Kirkcaldy's Ravenscraig Castle. Fife also has a number of ecclesiastical sites of historical interest. St Andrews Cathedral was home to the powerful Archbishopric of St Andrews, and later became a centre of the Scottish Reformation, while Dunfermline Abbey was the last resting place of a number of Scottish kings. Balmerino and Culross abbeys were both founded in the 13th century by the Cistercians, while a century before Lindores Abbey was founded by the Tironensians outside Newburgh; all were highly important sites.
The Stanza Poetry Festival, East Neuk Festival, and Pittenweem Arts Festival are events of national cultural importance. Smaller festivals like the Cupar Arts Festival also take place. The Byre Theatre in St Andrews and Adam Smith Theatre in Kirkcaldy are both highly regarded as touring venues, the latter also being the base of the grand opera company Fife Opera. The Byre has re-opened in Autumn, 2014[37] following its going into administration in 2012.[38]
Places of interest
- Aberdour Castle
- Balbirnie Stone Circle
- Balfarg
- Balgonie Castle
- Balmerino Abbey
- Bunnet Stane
- Cambo Estate
- Caves of Caiplie
- Church of St Mary on the Rock
- Craigtoun Country Park
- Culross Abbey
- Deep Sea World
- Dunfermline Abbey
- Dunfermline Palace
- Falkland Palace
- Fife Coastal Path
- Fife Folk Museum
- Fife Heritage Railway
- Fife Pilgrim Way
- Forth Bridge
- Inchcolm Abbey
- Isle of May
- Kellie Castle
- Kingsbarns Distillery and Visitor Centre
- Kirkcaldy Galleries
- Lindores Abbey
- Lindores Abbey distillery
- Links Market
- Lochore Meadows
- Lomond Hills Regional Park
- Lundin Links standing stones
- MacDuff's Cross
- Museum of the University of St Andrews
- Newark Castle
- Norman's Law
- Ochil Hills
- Old Course at St Andrews
- Pittencrieff Park
- Ravenscraig Castle
- Reaper (sailing vessel)
- Riverside Park, Glenrothes
- Rosyth Castle
- Scotland's Secret Bunker
- Scottish Deer Centre
- Scottish Fisheries Museum
- Seafield Tower
- St Andrews Aquarium
- St Andrews Castle
- St Andrews Cathedral
- St Andrews Museum
- Swilcan Bridge
- Tay Rail Bridge
- Tentsmuir National Nature Reserve
- R&A World Golf Museum
Notable Fifers
- Robert Adam, architect
- Stuart Adamson, musician (Big Country, The Skids)
- Robert Hope Moncrieff Aitken, Lieutenant in the 13th, Bengal Native Infantry, awarded the Victoria Cross
- William Allan, classicist at the University of Oxford
- Ian Anderson, musician, frontman of Jethro Tull
- Iain Banks, writer
- Lady Anne Barnard, travel writer, artist and socialite of the period
- Andrew Whyte Barclay, physician, Lumleian lecturer, and Harveian orator
- Jim Baxter, footballer
- David Bethune, Archbishop of St Andrews
- George Bethune, MSP for Kilrenny
- James Bethune, Archbishop of St Andrews
- James Bethune, Archbishop of Glasgow
- Janet Bethune, noblewoman
- Mary Bethune, attendant of Mary, Queen of Scots
- Elizabeth Bethune, mistress of King James V of Scotland
- Guy Berryman, bassist from the band Coldplay
- Sir James Black, pharmacologist and nobel prize winner
- Sir Ernley Blackwell, lawyer and civil servant
- Edith Bowman, BBC Radio 1/6 DJ
- Caroline Brazier, librarian
- Gordon Brown, former British Prime Minister and Chancellor of the Exchequer and former MP for Kirkcaldy and Cowdenbeath
- Scott Brown, Scotland and Celtic F.C. footballer
- Gregory Burke, playwright
- Kenn Burke, ballet dancer
- Andrew Carnegie, industrialist and philanthropist
- Henry Chisholm, steel industry executive
- Jim Clark, two-times Formula One World Drivers' Champion
- James Clephan, Lieutenant on board HMS Spartiate during the Battle of Trafalgar
- Archibald Constable, publisher, bookseller and stationer
- Kenneth Cranham, actor
- King Creosote, musician
- Lawrence Daly, General Secretary of the NUM
- David Danskin, principal founding member of Arsenal FC
- James Dewar, judge
- Barbara Dickson, singer and actress
- Thomas Millie Dow, artist, a member of the Glasgow School
- Peter Dumbreck, racing driver and 1998 Macau Grand Prix winner
- Philip Charles Durham, sailor and captain of HMS Defiance at Trafalgar
- Marjorie Fleming, child writer and poet
- Sir Sandford Fleming, engineer, who proposed worldwide standard time zones, engineered on the Intercolonial Railway and the Canadian Pacific Railway
- Valentine Fleming, member of parliament and father of the author Ian Fleming
- John Forbes, named the city of Pittsburgh
- Chris Fusaro, rugby player
- Thomas Lomar Gray, engineer noted for his pioneering work in seismology
- Martin Grehan, footballer
- Samuel Greig, Russian admiral and "Father of the Russian Navy"
- Thomas Hardy, minister of religion, Moderator of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland and Professor of Ecclesiastical History at Edinburgh University
- Alexander Henderson, theologian, and an important ecclesiastical statesman
- Shirley Henderson, actress
- Peter Horne, rugby player
- Bob Howie and Dave Howie, rugby players
- Ninian Imrie, army officer and geologist
- Danny Inglis, darts player
- Richard Jobson, filmmaker, television presenter, musician, The Skids
- Peter Johnstone, Celtic FC footballer
- Henrietta Keddie, novelist who wrote under the pseudonym Sarah Tytler
- Deborah Knox, Olympic gold medallist in curling
- Craig Levein, Scottish former professional footballer and manager
- Jackie Leven, singer-songwriter
- Wallace Lindsay, classical scholar, palaeographer, Professor of Humanity at St Andrews University
- Robert Lindsay of Pitscottie, 16th-century writer
- Anne Macaulay musicologist, archaeologist, author and lecturer
- Douglas Mackinnon, director
- Val McDermid, writer
- Ken McNaught, footballer, Aston Villa F.C. centre back, 1982 European Cup Winner
- Willie McNaught, footballer, Raith Rovers F.C. defender
- Old Tom Morris, greenskeeper St Andrews Links and 4 times champion of The Open Championship
- Tom Nairn, political theorist of nationalism
- Rab Noakes, singer, songwriter, record producer
- Aileen Paterson, author/illustrator
- John Philip, missionary in South Africa
- David Pitcairn, physician
- John Pitcairn, British Marine officer killed at the Battle of Bunker Hill
- William Pitcairn, physician
- Ian Rankin, writer
- Craig and Charlie Reid, singer-songwriters of The Proclaimers
- David Rollo, rugby player
- Craig Russell (British author), writer
- Dougray Scott, actor
- John Scrimgeour of Myres, Master of Work for royal buildings for James V and Mary, Queen of Scots
- Alexander Selkirk, seafarer and inspiration for Robinson Crusoe
- Jimmy Shand, accordion player
- Daniel Sloss, comedian
- Adam Smith, philosopher and economist
- Jordan Smith, actor
- Mary Fairfax Somerville, science writer and polymath
- Catherine Steele, plant biochemist
- David Steel, former Presiding Officer of the Scottish Parliament and leader of the Liberal party and MSP for Lothian and MP for Tweeddale, Ettrick and Lauderdale
- Ian Stewart, co-founder of the Rolling Stones
- Lawrence Storione, miner and anarchist organiser
- Sir John Struthers, first Regius Professor of Anatomy at the University of Aberdeen
- John McDouall Stuart, explorer of Australia's interior
- Michaela Tabb, first female snooker referee to appear at the Crucible
- William Tennant, scholar and poet
- John Thomson, Celtic and Scotland goalkeeper
- KT Tunstall, musician
- Jack Vettriano, artist
- William Montgomery Watt, historian, Emeritus Professor in Arabic and Islamic Studies at the University of Edinburgh
- Sir David Wilkie, painter
- Alexander Wilson, surgeon, type-founder, astronomer, mathematician and meteorologist
- James Wilson, signer of US Declaration of Independence, appointed by George Washington to first Supreme Court
- Jocky Wilson, darts player
- James Yorkston, musician
- Douglas Young, poet, scholar, translator, and leader of the Scottish National Party
Sports
St Andrews in Fife is the home of golf, and the headquarters of The R&A, the governing body of the sport throughout the world, aside from the United States and Mexico. The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews, from which it was devolved in 2004, is the world's oldest golf club.
Fife has four football clubs that play in the Scottish Professional Football League: Dunfermline Athletic, East Fife (based in Methil), Kelty Hearts, and Raith Rovers (based in Kirkcaldy); Cowdenbeath played at this level between 1905 and 2022 but are now members of the Lowland Football League. Fifteen clubs compete in the East of Scotland League while one plays in the SJFA East Region.
Fife Flyers (based in Kirkcaldy) are the UK's oldest ice hockey club and play in Britain's top flight, the Elite Ice Hockey League.
Fife is also home to eight rugby union clubs. Howe of Fife (based in Cupar), and Kirkcaldy play in Scottish Rugby's national leagues while Dunfermline, Rosyth Sharks, Glenrothes, Madras, Waid Academy (based in Anstruther) compete in the Caledonia regional leagues. University of St Andrews – the oldest rugby club in Fife – play in the British Universities & Colleges Sport (BUCS) system.
Kingdom Kangaroos are Fife's only Australian Rules Football team, with training held in Rosyth and Kirkcaldy.
Aberdour Shinty Club have two men's teams, two women's teams and multiple youth squads.
Fife also has two competitive basketball teams; Dunfermline Reign, who play out of St Columba's High School in Dunfermline and compete across a number of national SBC competitions, and Fife Steel, a Kirkcaldy-based team, operating a number of age groups, with a Senior men's and an under 19's team currently playing in Division 3 of the Lothian Men's Basketball League.
Fife is the location of several of the nation's motorsport venues: Knockhill Racing Circuit, Scotland's national motorsport venue and the only FIA-graded venue in the country; Cowdenbeath Racewall, a stock car oval racing venue; Lochgelly Raceway, a venue containing the Driftland drifting course and a 1/4 mile oval; and Crail Raceway, a venue located on a former military aerodrome containing a 1/4 mile drag strip and a karting circuit, operated by the East of Scotland Kart Club.
Media
Locally published newspapers include the Fife Free Press in Kirkcaldy; the Dunfermline Press in Dunfermline; the Glenrothes Gazette in Glenrothes, the East Fife Mail in Leven, the Fife Herald in Cupar / Howe of Fife and the St Andrews Citizen in St Andrews. DC Thomson publishes Fife and West Fife editions of the Dundee Courier & Advertiser,[39] and the Counties Edition of the Evening Telegraph is sold in Fife.
The only Fife-based radio station is Kingdom FM. There is also a community radio station that broadcasts each evening and is run solely by youths, called Fife Youth Radio. Other local radio stations, Tay FM, Greatest Hits Radio Tayside & Fife and Edinburgh's Forth 1 and Greatest Hits Radio Edinburgh, Lothians & Fife, broadcast to the northern and southern parts of the region respectively.
See also
References
- Complete Atlas of the British Isles. Reader's Digest. 1965. p. 218.
- Taylor, Simon; Gilbert Márkus (2012). The Place-Names of Fife, Volume 5. Donington, Lincs.: Shaun Tyas. ISBN 9781907730085.
- "The site record for Clatchard Craig at RCAHMS". Canmore.rcahms.gov.uk.
- "Excavation Summary by the Society of Antiquaries of Scotland" (PDF).
- "Dunfermline Abbey (SM90116)". portal.historicenvironment.scot.
Dunfermline has high significance as the chosen burial place of the Canmore dynasty of Scottish kings. It took on the role of Royal Mausoleum after the loss of Iona to the kingdom of Norway. Kings and Queens believed to lie buried beneath the abbey church include Queen Margaret and King Malcolm III, David I, and Robert I. The site is unparalleled in Scotland as a royal burial place, serving this role for over 250 years. After 1371, the Stewart dynasty chose to be buried elsewhere.
- "FALKLAND PALACE (GDL00176)". portal.historicenvironment.scot.
Falkland Palace was used as a home where the Stuarts could relax, play tennis, practise archery and hunt deer, wild boar, and ride out hawking in the Forest of Falkland.
- Crofton, Ian (5 November 2012). A Dictionary of Scottish Phrase and Fable. Birlinn. ISBN 9780857906373.
- Keay, John & Julia (1994). Collins Encyclopedia of Scotland. HarperCollins. p. 370. ISBN 978-0-00-255082-6.
- "Glenrothes And Markinch Visitor Guide - Accommodation, Things To Do & More". www.visitscotland.com.
- Brown, Kate (17 May 2022). "Rothes Colliery: When the ill-fated Glenrothes coal mine was blasted into rubble".
- "Glenrothes at 70 - scandal, art and royalty". www.fifetoday.co.uk. 5 July 2018.
- The Professional Engineer in Society. Jessica Kingsley Publishers. 1989. ISBN 9781853025013.
- Chalmers, George (1894). Caledonia (Volume 7). Paisley: Alexander Gardner. pp. 112–119. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- Brown, Keith. "Act of the convention of estates of the kingdom of Scotland etc. for a new and voluntary offer to his majesty of £72,000 monthly for the space of twelve months, 23 January 1667". Records of the Parliament of Scotland. University of St Andrews. Retrieved 25 February 2023.
- Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889, c. 50
- Shennan, Hay (1892). Boundaries of counties and parishes in Scotland as settled by the Boundary Commissioners under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889. Edinburgh: W. Green. p. 249. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- "Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929", legislation.gov.uk, The National Archives, 1929 c. 25, retrieved 22 April 2023
- Historic Environment Scotland. "County Buildings and former Court House, excluding 4-storey offices and police station adjoining to rear and single storey block to east, St Catherine Street, Cupar (LB24160)". Retrieved 18 July 2021.
- "Cupar, Tolbooth". Canmore. Historic Environment Scotland. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- "MPs of Fife". Parliament UK. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- "Kirkcaldy & Cowdenbeath parliamentary constituency – Election 2017". BBC News.
- "Fife North East parliamentary constituency – Election 2017". BBC News.
- "Scotland Election 2016". BBC News.
- "Briefly". Aberdeen Press and Journal. 26 November 1975. p. 15. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
...at the last meeting of Fife Regional Council to take place in County Hall, Cupar, before they move to Fife House, Glenrothes...
- Ferguson A History of Glenrothes p.91.
- "The Imperial gazetteer of Scotland; or, Dictionary of Scottish topography". 21 July 2010. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Fife Place-name Data :: The East Neuk". Fife-placenames.glasgow.ac.uk. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- Evans, Anna; Graham, Eddy; Rae, Alasdair; Robertson, Douglas; Serpa, Regina (October 2019). "Research into the impact of short-term lets on communities across Scotland" (PDF). Scottish Government. The Indigo House Group in association with IBP Strategy and Research.
- "Why the East Neuk has lasting appeal | Bricks & Mortar". The Times. 5 May 2017. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Visitors stay away but second home owners remain in East Neuk villages". 13 April 2020.
- "Empty and second homes causing housing crisis". The Scotsman. 6 June 2018. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "Mid 2012 population estimates of settlements" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 October 2014.
- "Mid-2020 Population Estimates for Settlements and Localities in Scotland". National Records of Scotland. 31 March 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- "Fife Place-name Data :: Parish: Ferry-Port-on-Craig". fife-placenames.glasgow.ac.uk.
- "Community Councils". Fife Council. 8 March 2021. Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- "Fife's listed buildings". Historic Scotland. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- "Byre Theatre to reopen after University of St Andrews agree rescue package". Herald Scotland. 19 August 2014.
- "Byre Theatre in St Andrews board 'deeply regrets' closure". BBC News. 26 January 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013.
- Foundry, The Theme (25 October 2013). "The Courier | British Newspapers Online".






.jpg.webp)