First Kamchatka Expedition
The First Kamchatka Expedition was the first Russian expedition to explore the Asian Pacific coast. It was commissioned by Peter the Great in 1724 and was led by Vitus Bering. Afield from 1725 to 1731, it was Russia's first naval scientific expedition.[1] It confirmed the presence of a strait (now known as Bering Strait) between Asia and America and was followed in 1732 by the Second Kamchatka Expedition.
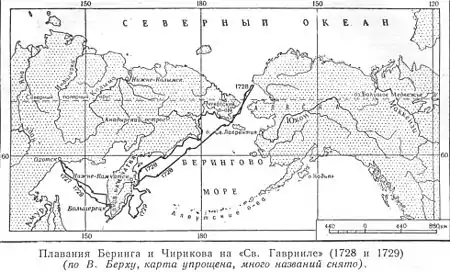
The expedition spent first two years, from January 1725 to January 1727, on traveling from Saint Petersburg to Okhotsk, using horses, dog sleds and river boats. After wintering in Okhotsk it moved to the mouth of the Kamchatka River on the east coast of the peninsula. In July–August 1728 it sailed north and then north-east along the shore, exploring Karaginsky Gulf, Kresta Bay, Providence Bay, Gulf of Anadyr, Cape Chukotsky, and St. Lawrence Island.
The expedition, as it turned out, went through the Bering Strait to the Chukchi Sea, and returned believing that it had completed its tasks. While it had not reached the North American coast, it provided evidence that Asia and North America are not connected. During 1729, it explored the southern shores of Kamchatka, mapping Avacha Bay, and by 28 February 1730 returned via Okhotsk to Saint Petersburg. The expedition was highly praised, with its leader Vitus Bering being promoted to captain-commander, his first noble rank, whereas his assistants Martin Spanberg and Aleksei Chirikov were made captains. It had been a long and expensive expedition, costing 15 men and souring relations between Russia and her native peoples, but it had provided useful insights into the geography of Eastern Siberia: in total the expedition surveyed more than 3500 km of the western coast of the sea, which was later named after Bering. Its maps of the area were later used by all Western European cartographers.
Preparations
On 29 December 1724 [N.S. 9 January 1725], Peter asked the Danish-Russian explorer Vitus Bering to command a voyage east.[2] Peter instructed the expedition to do the following:[1]
- prepare one-two ships in Kamchatka or nearby;
- using those ships, explore northern lands, which seemed to be part of America;
- seek where those lands join America, and whether there are any cities in European possession in the area. When meeting European ships, it should inquire them the names of the local geographical features, explore the coasts on the way and map them.
Preparations for the trip had begun some years before, but with his health rapidly deteriorating, Peter had hurried the process, and promoted the appointment of Bering as the expedition's leader ahead of the experienced cartographer K. P. von Verd. To his advantage Bering had knowledge of both the Indian Ocean and the eastern seaboard of North America, good personal skills and experience in transporting goods.[2] His lieutenants for the journey were the hardened fellow Dane Martin Spanberg and the well-educated but relatively inexperienced Russian Aleksei Chirikov, a respected naval instructor. Chirikov, together with warrant officer Peter Chaplin co-wrote the expedition journal.[1][3] The assistants would receive annual salaries of some 180 roubles during the trip, whereas Bering would be paid 480. The natural route to Kamchatka was along tributaries of the Lena; but after the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689) this looked politically infeasible. Instead, Bering's party, it was decided, would travel over land and river from Saint Petersburg to Okhotsk, a small port town on Russia's eastern coast, and then by sea from Okhotsk to the Kamchatka peninsula, where they could start their voyage of exploration.[2]
Ships
In 1725, the construction of a 20-meter-long ship named Fortuna (Russian: Фортуна, "Fortune") began in Okhotsk in anticipation of the expedition. It was completed in June 1727 under the guidance of Chaplin, and by August, a ship of similar size, Vostok (Восто́к, "East"), was brought from Kamchatka and repaired. By the end of August 1727 both ships reached Kamchatka. During April–May 1728, one more ship, St. Gabriel (Святой Гавриил, Sviatoi Gavriil), was built on Kamchatka from the local wood.[1] Fortuna and Vostok were auxiliary ships used for transporting goods between Okhotsk and Bolsheretsk, whereas St. Gabriel was the main ship of Bering, and was armed with four cannons.[4]
St. Petersburg to Okhotsk

On 24 January 1725,[1] Chirikov departed with 26 of the 34-strong expedition along the well-traveled roads to Vologda, 661 kilometres (411 mi) to the east. Having waited for the necessary paperwork to be completed, Bering and the remaining members of the expedition followed on 6 February. Bering was supplied with what few maps Peter had managed to commission in the preceding years.[2] Both parties used horse-drawn sledges and made good time over the first legs of the journey. On 14 February they were reunited in Vologda and headed eastwards across the Ural mountains, arriving in Tobolsk (one of the main stopping points of the journey) on 16 March. They had already traveled over 2,820 km (1,750 mi).[2] At Tobolsk, Bering took on more men to help the party through the more difficult journey ahead. He asked for 24 more from the garrison, before upping the request to 54 after hearing that the ship the party required at Okhotsk (the Vostok) would need significant manpower to repair. In the end, the governor could spare only 39, but it still was a significant help. In addition, Bering wanted 60 carpenters and 7 blacksmiths; the governor responded that half of these would have to be taken on later, at Yeniseysk. After some delays preparing equipment and funds, on 14 May the now much enlarged party left Tobolsk, heading along the Irtysh. The journey ahead to the next major stopping point Yakutsk was well worn, but rarely by groups as large as Bering's, who had the additional difficulty of needing to take on more men as the journey progressed. As a result, the party ran behind schedule, reaching Surgut on 30 May and Makovsk in late June before entering Yeniseysk, where the additional men could be taken on; Bering would later claim that "few were suitable". In any case, the party left Yeniseysk on 12 August, desperately needing to make up lost time. On 26 September they arrived at Ilimsk, just three days before the river froze over. After the party had completely an 130-kilometre (80 mi) trek to Ust-Kut, a town on the Lena where they could spend the winter, Bering traveled on to the town of Irkutsk both to get a sense of the conditions and to seek advice on how best to get their large party across the mountains separating Yakutsk (their next stop) to Okhotsk on the coast.[5]
After leaving Ust-Kut when the river ice melted in the spring of 1726, the party rapidly traveled down the River Lena, reaching Yakutsk in the first half of June. Despite the need for hurry and men being sent in advance, the governor was slow to grant them the resources they needed, prompting threats from Bering. On 7 July, Spanberg left with a detachment of 209 men and much of the cargo; on 27 July apprentice shipbuilder Fyodor Kozlov led a small party to reach Okhotsk ahead of Spanberg, both to prepare food supplies and to start work repairing the Vostok and building a new ship (the Fortuna) needed to carry the party across the bay from Okhotsk to the Kamchatka peninsula. Bering himself left on 16 August, while it was decided that Chirikov would follow the next spring with fresh supplies of flour. The journeys were as difficult as Bering had worried they would be. Men and horses died, and some men (46 from Bering's party alone) deserted with their horses and portions of the supplies as they struggled to build roads across difficult marshland and river terrain.[5] While Bering's party (which reached Okhotsk in October) fared badly, Spanberg's did far worse. His heavily loaded boats could be tugged at no more than 1.6 km (1 mi) a day – and they had some 1,102 km (685 mi) to cover. When the rivers froze, the cargo was transferred to sleds and the expedition continued, enduring blizzards and waist-high snow. Even provisions left by Bering at Yudoma Cross could not fend off starvation. On 6 January 1727, Spanberg and two other men, who had together formed an advance party carrying the most vital items for the expedition, reached Okhotsk; ten days later sixty others joined them, although many were ill. Parties sent by Bering back along the trail from Okhotsk rescued seven men and much of the cargo that had been left behind. Okhotsk's inhabitants described the winter as the worst they could recall; Bering seized flour from the local villagers to ensure that his party too could take advantage of their stocks and consequently the whole village soon faced the threat of starvation. An advance party of Chirikov's division arrived in June 1727 with 27 tons of flour, resupplying the Bering's group, which by then had diminished in numbers.[6]
Okhotsk to Kamchatka and beyond
.jpg.webp)
The Vostok was readied and the Fortuna built at a rapid pace, with the first party (48 men commanded by Spanberg and comprising those required to start work on the ships that would have to be built in Kamchatka itself as soon as possible) leaving in June 1727. Chirikov arrived in Okhotsk soon after, bringing further supplies of food. He had had a relatively easy trip, losing no men and only 17 of his 140 horses. On 22 August, the remainder of the party sailed for Kamchatka.[6] Had the route been charted, they should have sailed around the peninsula and made port on its eastern coast; instead, they landed on the west and made a grueling trip from the settlement of Bolsheretsk in the South-West, north to the Upper Kamchatka Post and then east along the Kamchatka River to the Lower Kamchatka Post. This Spanberg's party did before the river froze; next, a party led by Bering completed this final stint of approximately 930 km (580 mi) over land without the benefit of the river; and finally, in the spring of 1728, the last party to leave Bolsheretsk, headed by Chirikov, reached the Lower Kamchatka Post. The outpost was10,000 km (6,000 mi) from St. Petersburg and the journey itself (the first time "so many [had] gone so far") had taken some three years.[6] The lack of immediate food available to Spanberg's advance party slowed their progress, which hastened dramatically after Bering's and Chirikov's group arrived with provisions. As a consequence, the ship they constructed—the St. Gabriel—was ready to be launched as soon as 9 June 1728 from its construction point upriver at Ushka. It was then fully rigged and provisioned by 9 July, and on 13 July set sail downstream, anchoring offshore that evening. On 14 July, Bering's party began their first exploration, hugging the coast in not a northerly direction (as they had expected) but a north-easterly one.[7]
Sailing further north, Bering entered for the first time the strait that would later bear his name.[7] On 8 August, the expedition had a first meeting with the indigenous population. A boat of eight Chukchi men approached the ship and asked the purpose of their visit. They refused to board the ship, but sent a delegate who swam to the ship on an air-filled balloon made from animal skin. The man told that there are islands nearby, and indeed, two days later the expedition reached an island, which Bering named St. Lawrence Island. In turn, Chirikov named the place of meeting the boat as Cape Chukotsky.[1]
After Cape Chukotsky, the land turned westwards, and Bering held a discussion with his lieutenants on 13 August 1728 whether they could reasonably claim it was turning westwards for good: that is to say, whether they had proven that Asia and America were separate land masses. The rapidly advancing ice prompted Bering to make the controversial decision not to deviate from his remit: the ship would sail for a few more days, but then turn back.[7] The expedition was neither at the most easterly point of Asia (as Bering had supposed) nor had it succeed in discovering the Alaskan coast of America, which on a good day would have been visible to the east.[7][8] As promised, on 16 August, Bering turned St. Gabriel around, heading back towards Kamchatka. On 31 August, the ship was hit by a severe storm and barely avoided crashing into the shore. After hasty repairs, on 2 September it reached the mouth of the Kamchatka River,[1] fifty days after it had left. The mission was at its conclusion, but the party still needed to make it back to St. Petersburg to document the voyage (thus avoiding the fate of Semyon Dezhnyov who, unbeknownst to Bering, had made a similar expedition 80 years previously).[9] In the spring of 1729, the Fortuna, which had sailed round the Kamchatka Peninsula to bring supplies to the Lower Kamchatka Post, now returned to Bolsheretsk; and shortly after, so did St. Gabriel. The delay was caused by a four-day journey that Bering made eastwards in search of North America, to no avail. By July 1729 the two vessels were back at Okhotsk, where they were moored alongside the Vostok; the party, no longer needing to carry shipbuilding materials made good time on the return journey from Okhotsk, and by 28 February 1730 Bering was back in the Russian capital. In December 1731 he was awarded 1000 roubles and promoted to captain-commander, his first noble rank, whereas Spanberg and Chirikov were made captains. It had been a long and expensive expedition, costing 15 men and souring relations between Russia and her native peoples, but it had provided useful insights into the geography of Eastern Siberia, and presented evidence that Asia and North America were separated by sea.[9]
References
Citations
- Dukalskaya M. V. Первая Камчатская экспедиция Archived 2013-10-29 at the Wayback Machine. The Russian State Museum of Arctic and Antarctic. polarmuseum.ru
- Frost 2003, pp. 30–40
- Чаплин Петр Авраамович (биография). www.kamchatsky-krai.ru
- Первая Камчатская экспедиция. ricolor.org
- Frost 2003, pp. 41–44
- Frost 2003, pp. 44–47
- Frost 2003, pp. 48–55
- Armstrong, Terence (1982), "Vitus Bering", Polar Record, United Kingdom, 21 (131): 161–163, doi:10.1017/s0032247400004538, S2CID 251063437
- Frost 2003, pp. 56–62
Bibliography
- Frost, Orcutt William, ed. (2003), Bering: The Russian Discovery of America, New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press, ISBN 0-300-10059-0
External links
- Русские экспедиции по изучению северной части Тихого океана в первой половине XVIII в. ДОКУМЕНТЫ
- Из истории русских экспедиций на Тихом океане Первая половина XVIII века ДОКУМЕНТЫ
- Из истории великих русских географических открытий в Северном ледовитом и Тихом океанах XVII-й – Первая половина XVIII в. ДОКУМЕНТЫ
- Путешествия ДОКУМЕНТЫ