Obturator foramen
The obturator foramen is the large, bilaterally paired opening of the bony pelvis. It is formed by the pubis and ischium. It is mostly closed by the obturator membrane except for a small opening - the obturator canal - through which the obturator nerve and vessels pass.
| Obturator foramen | |
|---|---|
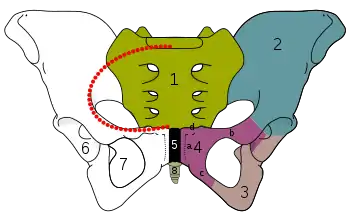 Pelvis. Obturator foramen is 7. | |
 Symphysis pubis exposed by a coronal section. Obturator canal labelled at center. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen obturatum |
| TA98 | A02.5.01.008 |
| TA2 | 1314 |
| FMA | 16999 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structure
The obturator foramen is situated inferior and somewhat anterior to the acetabulum. It is bounded by the pubis bone and the ischium: superiorly by the (grooved obturator surface) of the superior ramus of pubis, inferiorly by the ramus of ischium, and laterally by (the anterior edge of) the body of ischium (including by the margin of the acetabulum).[1]
The margin of the foramen is thin and uneven, and gives attachment to the obturator membrane. Superiorly, it presents a deep groove - the obturator groove - which passes obliquely inferomedially from the pelvis.
The foramen is largely closed by the obturator membrane save for a small opening at the superolateral end of the obturator foramen - the obturator canal - which establishes a communication between the pelvic cavity and the thigh. This canal gives passage to the obturator nerve, artery, and veins.[1]
The free edge of the obturator membrane that bounds the obturator canal attaches at two tubercles (which may be indistinct):[1]
- The anterior obturator tubercle - situated on the obturator crest at the anterior extremity of the inferior border of the superior ramus of pubis.[1]
- The posterior obturator tubercle - situated at the anterior border of the acetabular notch[1] (and thus on the medial border of the ischium).
Variation
In accordance with the overall sex dimorphism of the pelvis, the obturator foramina are oval in the male, and wider and rather triangular in the female.[1]
Unilateral pelvic hypoplasia can cause differences in size between the obturator foramina. Rarely, the obturator foramen may be doubled on one side.[2]
Additional images
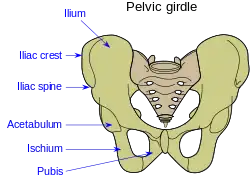 The two circles at the bottom are the obturator foramina.
The two circles at the bottom are the obturator foramina.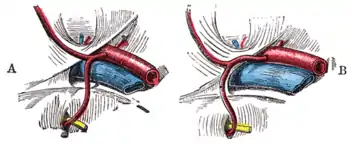 Variations in origin and course of obturator artery
Variations in origin and course of obturator artery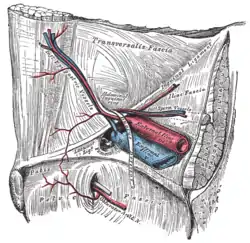 The relations of the femoral and abdominal inguinal rings, seen from within the abdomen. Right side.
The relations of the femoral and abdominal inguinal rings, seen from within the abdomen. Right side.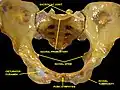 Anterior view of the body pelvis
Anterior view of the body pelvis
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 237 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 237 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York. p. 1354. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Apostolos Karantanas; Konstantina Velesiotou & Evagelos Sakellariou (2002). "Double Obturator Foramen". American Journal of Roentgenology. Larissa General Hospital, Greece. 178 (1): 245. doi:10.2214/ajr.178.1.1780245. PMID 11756138.
External links
- Atlas image: male_urethrogram at the University of Michigan Health System - "Pelvis & Perineum: Male Urethrogram"
- Photo at vc.cc.tx.us Archived 2006-09-24 at the Wayback Machine