USS Insurgent
L'Insurgente was a 40-gun Sémillante-class frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1793. During the Quasi War with the United States, the United States Navy frigate USS Constellation, with Captain Thomas Truxtun in command, captured her off the island of Nevis. After her capture she served in the United States Navy as USS Insurgent, patrolling the waters in the West Indies. In September 1800 she was caught up in a severe storm and was presumed lost at sea.[2][3]
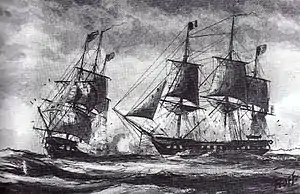 Naval encounter during the Quasi-War between USS Constellation and French ship L'Insurgente (right) on 9 February 1799 | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | L'Insurgente |
| Ordered | 3 September 1790 |
| Builder | Pierre-Joseph Pénétreau, Lorient |
| Laid down | 5 November 1791 |
| Launched | 27 April 1793 |
| Captured | by USS Constellation, 9 February 1799 |
| Name | USS Insurgent |
| Acquired | 9 February 1799 |
| Commissioned | August 1799 |
| Fate | Lost at sea, probably foundered September 1800 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Sémillante-class frigate |
| Tons burthen | 600 (bm) |
| Length | 45.5 m (149 ft 3 in) |
| Beam | 11.5 m (37 ft 9 in) |
| Draft | 5.5 m (18 ft 1 in) |
| Complement |
|
| Armament |
|
French frigate L'Insurgente
L'Insurgente was built by Pierre-Joseph Pénétreau at Lorient and launched on 27 April 1793.[1]
In January or February 1794, L'Insurgente captured Ann off Cape Clear Island as Ann was sailing from Newfoundland to Bristol. L'Insurgente put a prize crew aboard Ann, but left her mate and three other men on board. When Ann was in sight of the French coast, the British sailors succeeded in recapturing her from the prize crew; the British then took Ann into Vigo.[4]
On 16 January 1794 L'Insurgente captured the American ship John and James and brought her into Brest. John and James had been built at Philadelphia for George Morrison of Petersburg, Virginia. She had left Petersburg with 450 hogsheads of tobacco and 12,000 staves. On 27 December 1794 the Tribunal of Commerce ordered John and James released to Captain James Johnson and the Committee of Public Safety awarded him a payment of 20,000 livres tournois.[5]
On 25 April L'Insurgente captured Freundschaft Lourentz, Colandt, master, as Freundschaft Lourentz was sailing from Lisbon to London. However two "Scilly boats" (i.e., boats from the Isles of Scilly), recaptured her the next day and brought her into St Ives, Cornwall.[6]
On 5 December 1797 Insurgente captured Prince Frederick as Prince Frederick was returning from Madras and Bengal. Prince Frederick was so badly damaged in the engagement that she sank soon afterwards. Her people, however, were saved.[7] The EIC put a value of £59,981 on the cargo that it had lost.[8]
Battle with Constellation
On 9 February 1799, after being at sea for three days, USS Constellation spotted L'Insurgente approximately six leagues (29 km) northeast off Nevis. L'Insurgente, a fully-rigged frigate, was considered one of the fastest sailing vessels in the world at the time; three weeks earlier she had encountered Constellation but was able to outrun her and escape.[9] Shortly after being spotted by Constellation this second time the ships encountered a squall during which a violent gust of wind snapped L'Insurgente's topmast, impairing her speed. As Constellation approached, Captain Michael-Pierre Barreaut first attempted to seek haven by making for St. Eustatius, but to no avail, where L'Insurgente hauled wind and assumed a starboard tack. After being overtaken she hoisted American colors, at which time Constellation hoisted the private signals. Unable to respond appropriately, she gave up her attempt at disguise and Captain Barreaut ordered the French tri-colors hoisted and a gun fired to windward to signal the challenge where L'Insurgente boldly sat in wait to be engaged. This was the first time since the American Revolution that a shot had been fired from an enemy vessel at an American ship. Captain Thomas Truxtun gave the order to clear the deck of Constellation for action and the boatswain sounded the whistle. Both ships bore up to take positions to engage. Constellation fired the first broadside, double-shotted, inflicting much damage to the French vessel's hull and killing many in the first minute of the engagement. L'Insurgente responded and fired a broadside, inflicting much damage to Constellation's rigging and top foremast, which was almost cut off.[10] At 3:30 pm after an hour and a half of running battle and several raking broadsides from Constellation, L'Insurgente struck her colors. First Lieutenant John Rodgers, Midshipman David Porter along with eleven men were put on board the captured vessel to take possession and to secure the prisoners who were sent to the lower hold. She had lost 70 men from a crew of 409, while Constellation, badly damaged also, only lost three out of a complement of 309. This was the first post-Revolutionary War American victory against a foreign naval vessel.[11][12]
There were no handcuffs to be found and the prisoners seem disposed to rebel. Accordingly, Rodgers placed sentries at the hatch, armed with blunderbusses and under orders to open fire should the prisoners attempt to breach the hatch way.[13]

Service in US Navy
The US Navy considered Insurgent a prize in the Quasi-War with France. The frigate was taken to the West Indies and refitted for service in the young American navy. She cruised under Lt. John Rodgers in company with Constellation until May 1799. Ordered back to the United States, Insurgent was purchased by the Navy for $84,500. Commissioned with Captain Alexander Murray in command, Insurgent sailed from Hampton Roads for Europe on 14 August 1799. Cruising in European waters during the winter of 1799–1800, the frigate captured the French ship Vendémiaire and recaptured the American ships Margaret, Angora, Commerce, and William and Mary. Insurgent returned to the United States in March 1800 via the West Indies.[14]
Loss
On 29 April 1800 Patrick Fletcher assumed command and was ordered to cruise between the West Indies and the American coast to protect American shipping interests and to capture any enemy vessels he encountered. Insurgent departed Baltimore on 22 July and after a brief stop at Hampton Roads sailed for her station 8 August 1800. She was never heard from again, and the frigate and her crew were presumed lost during the severe storm that struck the West Indies on 20 September 1800.[15] This storm is also thought to have sunk USS Pickering, which likewise vanished without a trace.
See also
Citations
- Demerliac (1996), p.68, No. 421.
- U.S.Navy, DANFS, Insurgent prgh.1
- Toll, 2006 pp. 142–144
- Powell (1930), p. 333.
- Williams (2009), p.204.
- Lloyd's List, no.2608 – accessed 18 September 2015.
- Lloyd's List №2797.
- Reports (1830), Vol. 2, p.979.
- Toll, 2006 pp. 115-117
- Toll, 2006 p. 117
- Harrison, 1858 p.156-158
- Toll, 2006 pp.117–119
- Harrison, 1858 p.158
- U.S.Navy, DANFS, Insurgent prgh.2
- U.S.Navy, DANFS, Insurgent prgh.3
References
- Insurgent. DANFS
- Demerliac, Alain (1996) La Marine De Louis XVI: Nomenclature Des Navires Français De 1774 À 1792. (Nice: Éditions OMEGA). ISBN 2-906381-23-3
- Harrison, Henry William (1858). Battlefields and naval exploits of the United States: ... >H. C. Peck & Theo. Bliss, Philadelphia. p. 448.
- Reports from the Select Committee of the House of Commons appointed to enquire into the present state of the affairs of the East India Company, together with the minutes of evidence, an appendix of documents, and a general index, (1830).
- Powell, John Williams Darmer (1930) Bristol privateers and ships of war. (Bristol: J.W. Arrowsmith).
- Toll, Ian W. (2006). Six frigates: the epic history of the founding of the U.S. Navy. W. W. Norton & Company, New York. pp. 592. ISBN 978-0-393-05847-5.
- Williams, Greg. H. (2009) The French Assault on American Shipping, 1793-1813: A History and Comprehensive Record of Merchant Marine Losses. (McFarland). ISBN 978-0-7864-5407-5