GelGreen
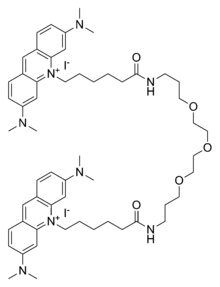
GelGreen is an intercalating nucleic acid stain used in molecular genetics for agarose gel DNA electrophoresis. GelGreen consists of two acridine orange subunits that are bridged by a linear oxygenated spacer.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
10,10′-(6,22-Dioxo-11,14,17-trioxa-7,21-diazaheptacosane-1,27-diyl)bis[3,6-bis(dimethylamino)acridin-10-ium] diiodide | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C56H80I2N8O5 | |
| Molar mass | 1198.43 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | > 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | 10,000X in water, Biotium Inc. |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Its fluorophore, and therefore its optical properties, are essentially identical to those of other N-alkylacridinium orange dyes. When exposed to ultraviolet light, it will fluoresce with a greenish color that strongly intensifies after binding to DNA.[3] The substance is marketed as a less toxic and more sensitive alternative to ethidium bromide.[3] GelGreen is sold as a solution in either DMSO or water.[3]
See also
References
- US application 2010323453, Mao, Fei & Leung, Wai-Yee, "Methods of Using Dyes in Association with Nucleic Acid Staining or Detection and Associated Technology"
- GelRed & GelGreen (PDF), Biotium Inc., August 21, 2012, retrieved December 4, 2012
- GelRed and GelGreen: Environmentally safe and ultra-sensitive nucleic acid gel stains for replacing EtBr, Biotium Inc., retrieved December 4, 2012
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
