Geography of the Central African Republic
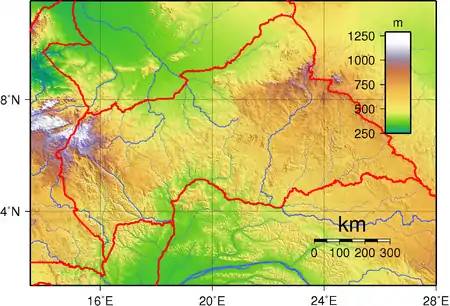
The Central African Republic is a landlocked nation within the interior of the African continent. It is bordered by Cameroon, Chad, Sudan, South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo. Much of the country consists of flat, or rolling plateau savanna, about 1,640 feet (500 m) above sea level. In the northeast are the Fertit Hills, and there are scattered hills in the southwestern part of the country. To the northwest is the Karre Mountains (also known as Yade Massif), a granite plateau with an altitude of 3,750 feet (1,143 m).
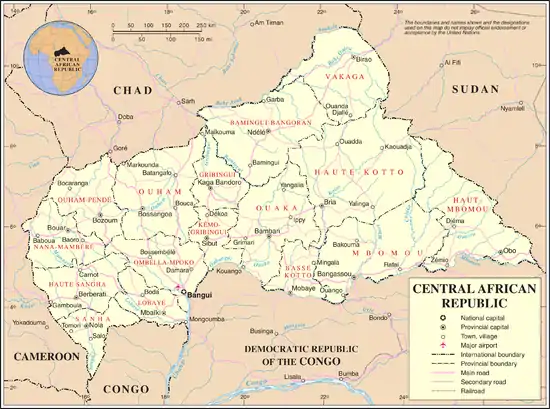

At 622,984 square kilometres (240,535 sq mi), the Central African Republic is the world's 45th-largest country (after Somalia). It is comparable in size to Ukraine.
Much of the southern border is formed by tributaries of the Congo River, with the Mbomou River in the east merging with the Uele River to form the Ubangi River. In the west, the Sangha River flows through part of the country. The eastern border lies along the edge of the Congo-Nile watershed.
Estimates of the amount of the country covered by forest range up to 8%, with the densest parts in the south. The forest is highly diverse and includes commercially important species of Ayous, Sapele and Sipo. The deforestation rate is 0.4% per annum, and lumber poaching is commonplace.
Climate

The climate of the Central African Republic is generally a tropical savanna climate (Köppen Aw), although there are areas with a tropical monsoon climate (Köppen Am) and in the north there is also a hot semi-arid climate (Köppen BSh). There is a wet season and a dry season, and the temperature is hot throughout the year. The northern areas are subject to harmattan winds, which are hot, dry, and carry dust. The tip of the northern regions have been subject to desertification. The remainder of the country is prone to flooding from nearby rivers. About one third of the Central African Republic's population do not have access to clean water.
| Climate data for Bangui (381 m), Central African Republic (1931–1955) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 37.2 (99.0) |
38.8 (101.8) |
39.5 (103.1) |
38.0 (100.4) |
38.6 (101.5) |
35.8 (96.4) |
34.3 (93.7) |
34.4 (93.9) |
35.9 (96.6) |
35.7 (96.3) |
36.7 (98.1) |
36.2 (97.2) |
39.5 (103.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 32.9 (91.2) |
33.9 (93.0) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.9 (91.2) |
31.9 (89.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
29.9 (85.8) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
30.7 (87.3) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.7 (89.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.0 (78.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.4 (81.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.5 (79.7) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.7 (78.3) |
26.0 (78.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 19.5 (67.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.1 (70.0) |
19.7 (67.5) |
20.3 (68.5) |
20.3 (68.5) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.2 (68.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
19.3 (66.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 13.0 (55.4) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.2 (61.2) |
14.4 (57.9) |
16.0 (60.8) |
16.5 (61.7) |
15.0 (59.0) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.2 (63.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
16.9 (62.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 20 (0.8) |
39 (1.5) |
116 (4.6) |
142 (5.6) |
167 (6.6) |
134 (5.3) |
174 (6.9) |
240 (9.4) |
185 (7.3) |
190 (7.5) |
89 (3.5) |
24 (0.9) |
1,520 (59.9) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2 | 5 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 17 | 16 | 17 | 11 | 4 | 135 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 64 | 71 | 76 | 79 | 81 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 81 | 75 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 203 | 201 | 191 | 184 | 193 | 158 | 138 | 138 | 143 | 158 | 171 | 220 | 2,098 |
| Source 1: Deutscher Wetterdienst[1] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Danish Meteorological Institute (sun only)[2] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Bossangoa (2000-2016) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 35.7 (96.3) |
37.5 (99.5) |
38.3 (100.9) |
36.3 (97.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
32.4 (90.3) |
31.2 (88.2) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.7 (90.9) |
34.3 (93.7) |
34.9 (94.8) |
34.2 (93.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.1 (77.2) |
27.9 (82.2) |
29.8 (85.6) |
29.4 (84.9) |
28.5 (83.3) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.1 (79.0) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.0 (77.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) |
18.4 (65.1) |
21.3 (70.3) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.0 (71.6) |
21.4 (70.5) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.9 (69.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
20.6 (69.1) |
19.0 (66.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
19.8 (67.5) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 1 (0.0) |
6 (0.2) |
47 (1.9) |
92 (3.6) |
141 (5.6) |
166 (6.5) |
234 (9.2) |
279 (11.0) |
240 (9.4) |
159 (6.3) |
22 (0.9) |
1 (0.0) |
1,388 (54.6) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 265 | 242 | 211 | 211 | 227 | 188 | 165 | 155 | 172 | 198 | 248 | 266 | 2,548 |
| Source 1: Normales et records pour la période 2000-2016 à Bossangoa ,[3] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Climate Bossangoa - Central African Republic for rainfall totals ,[4] Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours[5] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for N'Délé (2002-2013) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 36.5 (97.7) |
37.8 (100.0) |
38.5 (101.3) |
37.0 (98.6) |
34.6 (94.3) |
31.8 (89.2) |
30.4 (86.7) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.5 (86.9) |
31.7 (89.1) |
33.3 (91.9) |
34.7 (94.5) |
33.9 (92.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.2 (81.0) |
29.4 (84.9) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.0 (86.0) |
28.6 (83.5) |
26.7 (80.1) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
25.8 (78.4) |
25.1 (77.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 18.0 (64.4) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.3 (70.3) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.6 (72.7) |
21.2 (70.2) |
20.7 (69.3) |
21.3 (70.3) |
20.4 (68.7) |
20.1 (68.2) |
18.5 (65.3) |
16.2 (61.2) |
20.3 (68.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0 (0) |
6 (0.2) |
24 (0.9) |
65 (2.6) |
122 (4.8) |
151 (5.9) |
205 (8.1) |
235 (9.3) |
231 (9.1) |
131 (5.2) |
9 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
1,179 (46.5) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 279 | 263 | 250 | 209 | 222 | 189 | 160 | 151 | 157 | 201 | 277 | 268 | 2,626 |
| Source 1: Normales et records pour la période 2002-2013 à N'Dele,[6] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Climate : N'Délé for rainfall totals,[7] Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours[8] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Birao | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 34.7 (94.5) |
37.3 (99.1) |
39.4 (102.9) |
39.7 (103.5) |
37.9 (100.2) |
35 (95) |
31.4 (88.5) |
30.8 (87.4) |
32.1 (89.8) |
34.5 (94.1) |
35 (95) |
33.6 (92.5) |
35.1 (95.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 23.7 (74.7) |
26 (79) |
28.8 (83.8) |
30.4 (86.7) |
30.2 (86.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
25.3 (77.5) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.5 (79.7) |
23.9 (75.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
26.4 (79.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 12.7 (54.9) |
14.8 (58.6) |
18.3 (64.9) |
21.1 (70.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
21.6 (70.9) |
20.1 (68.2) |
19.8 (67.6) |
19.7 (67.5) |
18.6 (65.5) |
12.8 (55.0) |
11.4 (52.5) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.0) |
20 (0.8) |
67 (2.6) |
107 (4.2) |
189 (7.4) |
193 (7.6) |
146 (5.7) |
38 (1.5) |
1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
762 (29.8) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[9] | |||||||||||||
Notes

Location: Central Africa, north of Democratic Republic of the Congo
Area - comparative:
Land boundaries:
total:
5,920 km
border countries:
Cameroon 901 km, Chad 1,556 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 1,747 km, Republic of the Congo 487 km, Sudan 174 km and South Sudan 1,055 km
Coastline: 0 km (landlocked)
Terrain: vast, flat to rolling, monotonous plateau; scattered hills in northeast and southwest
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Oubangui River 335 m
highest point:
Mont Ngaoui 1,420 m
Natural resources: diamonds, uranium, timber, gold, petroleum, hydropower
Land use:
arable land:
2.89%
permanent crops:
0.13%
other:
96.98% (2012 est.)
Irrigated land: 1.35 km2 (2003)
Total renewable water resources: 144.4 km3 (2011)
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
total:
0.07 km3/yr (83%/17%/1%)
per capita:
17.42 m3/yr (2005)
Natural hazards: hot, dry, dusty harmattan winds affect northern areas; floods are common
Environment - current issues: tap water is not potable; poaching has diminished its reputation as one of the last great wildlife refuges; desertification
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified:
Law of the Sea
Geography - note: landlocked; almost the precise center of Africa
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of the Central African Republic, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point - unnamed location in the Aoukal river on the border with Chad, Vakaga Prefecture
- Easternmost point - unnamed location immediately East of the tripoint with South Sudan and the Democratic Republic of the Congo and south of the town of Ezo in South Sudan, Haut-Mbomou Prefecture
- Southernmost point - the tripoint with Cameroon and the Republic of Congo, Sangha-Mbaéré Prefecture
- Westernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Cameroon west of the town of Koundé in Central African Republic near Cameroon's Lokoti to Garoua Boulai road, Nana-Mambéré Prefecture
References
- "Klimatafel von Bangui / Zentralafrikanische Rep" (PDF). Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
-
"STATIONSNUMMER 64650" (PDF). Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 2 November 2016.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - "Normales et records pour la période 2000-2016 à Bossangoa". Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Climate Bossangoa - Central African Republic for rainfall totals". Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours""Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours" (PDF). Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Normales et records pour la période 2002-2013 à N'Dele". Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Climate : N'Délé for rainfall totals". Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours""Étude méthodologique pour l'utilisation des données climatologiques de l'Afrique tropicale for sunshine hours" (PDF). Infoclimat. Retrieved 2014-01-13.
- "Climate: Birao". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved August 14, 2019.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
