Glashow resonance
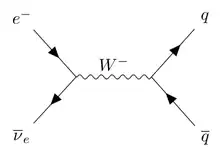
In particle physics, the Glashow resonance is the resonant formation of the W boson in antineutrino-electron collisions:
ν
e +
e−
→
W−
.[1]
History
The resonance was proposed by Sheldon Glashow in 1959.
Theory
The threshold antineutrino energy for this process (for the electron at rest in the laboratory frame) is given by the formula
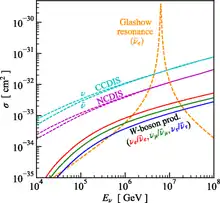
(here is, for completeness, included also the antineutrino mass, which vanishes in the Standard model), which gives 6.3 PeV, a huge energy for a fundamental particle. This process is considered for the detection and studies of high-energy cosmic neutrinos at the IceCube experiment, at the ANTARES neutrino telescope, and at the KM3NeT neutrino telescope.
Detection
A report observing the resonance at 2.3σ level has been made by the IceCube experiment in March 2021.[3][4]
References
- Glashow, Sheldon L. (1960-04-01). "Resonant Scattering of Antineutrinos". Physical Review. American Physical Society (APS). 118 (1): 316–317. Bibcode:1960PhRv..118..316G. doi:10.1103/physrev.118.316. ISSN 0031-899X.
- Zhou, Bei; Beacom, John F. (2020-02-18). "$W$-boson and trident production in TeV--PeV neutrino observatories". Physical Review D. 101 (3): 036010. arXiv:1910.10720. Bibcode:2020PhRvD.101c6010Z. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.101.036010. S2CID 204851941.
- Collaboration, IceCube (2021-03-10). "Detection of a particle shower at the Glashow resonance with IceCube". Nature. 591 (7849): 220–224. arXiv:2110.15051. Bibcode:2021Natur.591..220I. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03256-1. hdl:1854/LU-8705937. PMID 33692563. S2CID 232188780.
- Distefano, Carla (2021-03-10). "Giant ice cube hints at the existence of cosmic antineutrinos". Nature. 591 (7849): 206–207. Bibcode:2021Natur.591..206D. doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00486-1. PMID 33692553.