Glass crusher
A glass crusher provides for pulverization of glass to a yield size of 2 inches (5 cm) or less.[1] Recycling operations may range from simple, manually-fed, self-contained machines to extravagant crushing systems complete with screens, conveyors, crushers and separators. All non-glass contaminants must generally be removed from the glass prior to recycling. The processes used in glass crushing for recycling involves the same methods used by the aggregate industry for crushing rock into sand (rock crusher).
Vertical shaft impactor (VSI) glass crushing
The use of VSI crushers in large scale operations allow the production of up to 125 tons per hour [2] of crushed glass cullet.
VSI crushers use a high speed rotor with wear-resistant tips and a crushing chamber designed to 'throw' the glass against. The VSI crushers utilize velocity rather than surface force as the predominant force to break glass as this allows the breaking force to be applied evenly both across the surface of the material as well as through the mass of the material. In its shattered state, glass has a jagged and uneven surface. Applying surface force (pressure) results in unpredictable and typically non-cubicle particles. As glass is 'thrown' by a VSI rotor against a solid anvil, it fractures and breaks along fissures. Final particle size can be controlled by 1) the velocity at which the glass is thrown against the anvil and 2) the distance between the end of the rotor and the impact point on the anvil. The product resulting from VSI crushing is generally of a consistent cubicle shape which may optimize yield in consumptive applications such as the fabrication of fiberglass, ceramic ware, flux agents and abrasives. Due to the highly abrasive nature of the glass material, a VSI crushing process is generally preferred over Horizontal Shaft Impact and most other crushing methods with higher maintenance and lower wear part lives.
VSI crushers generally utilize a high speed spinning rotor at the center of the crushing chamber and an outer impact surface of either abrasive resistant metal anvils or crushed glass (or rock in an aggregate applications). Utilizing cast metal surfaces 'anvils' are traditionally referred to as a "Shoe and Anvil VSI". Utilizing crushed material on the outer walls of the crusher for new material to be crushed against is traditionally referred to as "rock on rock VSI".
VSI Principle of Operation
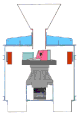 VSI Principal of Operation
VSI Principal of Operation
References
- "Equipment Spotlight: Glass Crushers". American Recycler News. Archived from the original on February 19, 2012. Retrieved December 18, 2008.
- (CEMCO Turbo 54 Model Crusher, retrieved December 18, 2008)
External links
- Glass crusher for glass bottles recycling - Info and Video in Cogelme site