Glycocholic acid
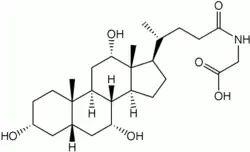
Glycocholic acid, or cholylglycine, is a crystalline bile acid involved in the emulsification of fats. It occurs as a sodium salt in the bile of mammals. It is a conjugate of cholic acid with glycine.[1] Its anion is called glycocholate.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-(3α,7α,12α-Trihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oyl)glycine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
{(4R)-4-[(1R,3aS,3bR,4R,5aS,7R,9aS,9bS,11S,11aR)-4,7,11-Trihydroxy-9a,11a-dimethylhexadecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-yl]pentanamido}acetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.815 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H43NO6 | |
| Molar mass | 465.631 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 130 °C (266 °F; 403 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.