Golden-tailed sapphire
The golden-tailed sapphire (Chrysuronia oenone) is a species of hummingbird in the family Trochilidae. It is found in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.[4][3]
| Golden-tailed sapphire | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Male in eastern Ecuador | |
.jpg.webp) | |
| Female C. o. oenone | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Class: | Aves |
| Clade: | Strisores |
| Order: | Apodiformes |
| Family: | Trochilidae |
| Genus: | Chrysuronia |
| Species: | C. oenone |
| Binomial name | |
| Chrysuronia oenone (Lesson, R, 1832) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Amazilia oenone[3] | |
Taxonomy and systematics
The golden-tailed sapphire was formerly placed in the genus Amazilia. A molecular phylogenetic study published in 2014 found that Amazilia was polyphyletic. In the revised classification to create monophyletic genera, the golden-tailed sapphire was moved by most taxonomic systems to Chrysuronia.[5][6][7][4][8][9] However, BirdLife International's Handbook of the Birds of the World (HBW) retains it in Amazilia.[3]
The International Ornithological Committee (IOC) recognizes two subspecies of golden-tailed sapphire, the nominate C. o. oenone and C. o. josephinae. The Clements taxonomy and HBW add a third, C. o. alleni, that the IOC includes within josephinae.[4][9][3]


Description
The golden-tailed sapphire is 9.5 to 10 cm (3.7 to 3.9 in) long. Males weigh 4.7 to 6.3 g (0.17 to 0.22 oz) and females 4.3 to 5.3 g (0.15 to 0.19 oz). Both sexes of all subspecies have a slightly curved bill with a black maxilla and a black-tipped red mandible.
Adult males of the nominate subspecies have a violet-blue head and throat. Their back is bright green that transitions through bronze-green to bright coppery coverts and a copper-bronze tail. Their breast is glittering green, their belly bronze-green, and underneath their tail, their coverts are bronze with whitish edges.
Adult females have a blue crown, a green back, and copper-bronze coverts and tail. Their undersides are mostly whitish, with blue-green flecks on the sides of the throat and neck, green on the sides and chest, bronze-green flanks, and underneath their tail, they have bronze coverts. Juvenile males have a dull green crown, a dusky gray throat, and a dull green chest; early adult feathers on the head and throat are a purer, less violet, blue than the adult's. Juvenile females' throat speckles are duller and more bronze-coloured than the adults'.[10]
Subspecies C. o. josephinae and C. o. alleni when treated separately have some differences from the nominate and from each other. Males of the former have a mostly green throat and a green rump that contrasts with the coppery coverts. C. o. alleni has an entirely green throat and little blue on the cheeks and its rump is coppery.[10]
Distribution and habitat
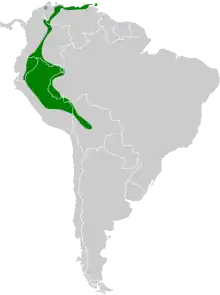
The nominate subspecies of golden-tailed sapphire is the most widely distributed. It is found in the Serranía del Perijá that straddles the Colombia/Venezuela border, further east in western and northern Venezuela, and south through east central Colombia, eastern Ecuador, and extreme western Brazil into extreme northeastern Peru. C. o. josephinae sensu stricto is found in most of the rest of eastern Peru. C. o. alleni is found in northern Bolivia.[10]
The golden-tailed sapphire inhabits semi-open landscapes like the edges and gaps in humid forest, mature secondary forest, gallery forest, shady cacao and coffee plantations, and gardens. In Colombia and Venezuela it ranges in elevation from sea level to 1,500 m (4,900 ft) and in Ecuador between 400 and 1,200 m (1,300 and 3,900 ft).[10][11]
Behavior
Movement
The golden-tailed sapphire apparently moves locally according to the availability of flowering plants but details are lacking.[10]
Feeding
The golden-tailed sapphire forages for nectar at a variety of flowering shrubs (e.g. Aphelandra) and trees (e.g. Erythrina and Inga). Males tend to forage in the canopy, sometimes gathering in "quarrelsome assemblages", while females forage more by trap-lining in the forest, visiting a circuit of flowering plants. In addition to nectar, it feeds on arthropods by hawking from a perch or by gleaning from foliage.[10]
Breeding
The golden-tailed sapphire's breeding season varies geographically. It spans at least June to November in eastern Colombia but is January through April in western Brazil. Males usually gather in groups of five to 10 at leks to display to females but sometimes display alone. The nest is cup-shaped and has green moss on the outside for camouflage.[12] The female incubates the clutch of two eggs for about 14 days and fledging occurs about 28 days after hatch.[10]
Vocalization
The golden-tailed sapphire's song is variable, described as "a repeated rhythmic phrase, often starting with a burry note, followed by several very squeaky or scratchy notes, and ending with repeated chips." It also makes calls described as "a drawn-out metallic trill and shorter chipping notes."[10]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the golden-tailed sapphire as being of Least Concern. It has a very large range, and though its population size is unknown it is believed to be stable. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] It is considered locally common to common in Colombia and Venezuela but relatively rare in the Amazonian lowlands further south.[10]
References
- BirdLife International (2018). "Golden-tailed Sapphire Amazilia oenone". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- HBW and BirdLife International (2021) Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 6. Available at: http://datazone.birdlife.org/userfiles/file/Species/Taxonomy/HBW-BirdLife_Checklist_v6_Dec21.zip retrieved August 7, 2022
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (August 2022). "Hummingbirds". IOC World Bird List. v 12.2. Retrieved August 9, 2022.
- McGuire, J.; Witt, C.; Remsen, J.V.; Corl, A.; Rabosky, D.; Altshuler, D.; Dudley, R. (2014). "Molecular phylogenetics and the diversification of hummingbirds". Current Biology. 24 (8): 910–916. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.016. PMID 24704078.
- Stiles, F.G.; Remsen, J.V. Jr.; Mcguire, J.A. (2017). "The generic classification of the Trochilini (Aves: Trochilidae): Reconciling taxonomy with phylogeny". Zootaxa. 4353 (3): 401–424. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4353.3. PMID 29245495.
- Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (July 2020). "Hummingbirds". IOC World Bird List Version 10.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 July 2022. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved July 24, 2022
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2021. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved August 25, 2021
- Stiles, F.G. and P. F. D. Boesman (2020). Golden-tailed Sapphire (Chrysuronia oenone), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.gotsap1.01 retrieved September 12, 2022
- Ridgely, Robert S.; Greenfield, Paul J. (2001). The Birds of Ecuador: Status, Distribution, and Taxonomy. Vol. I. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. p. 67. ISBN 978-0-8014-8722-4.
- "Golden-tailed Sapphire Hummingbirds – Beauty of Birds". Retrieved 2022-09-13.
