Guisinol
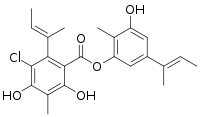
Guisinol is an antibacterial depside with the molecular formula C23H25ClO5 that has been isolated from the fungus Aspergillus unguis.[1][2][3][4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[5-[(E)-but-2-en-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-2-methylphenyl] 2-[(E)-but-2-en-2-yl]-3-chloro-4,6-dihydroxy-5-methylbenzoate[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H25ClO5 | |
| Molar mass | 416.90 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "Guisinol". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Nielsen, J.; Nielsen, P. H.; Frisvad, J. C. (1999). "Fungal depside, guisinol, from a marine derived strain of Emericella unguis". Phytochemistry. ISSN 0031-9422.
- Rahman, Atta-ur- (30 August 2011). Studies in Natural Products Chemistry: Bioactive Natural Products (Part L). Elsevier. p. 502. ISBN 978-0-08-045847-2.
- Blunt, John W.; Munro, Murray H. G. (19 September 2007). Dictionary of Marine Natural Products with CD-ROM. CRC Press. p. 989. ISBN 978-0-8493-8217-8.
Further reading
- Stapleton, R. D. Jr.; Singh, V. P. (13 March 2002). Biotransformations: Bioremediation Technology for Health and Environmental Protection. Elsevier. p. 352. ISBN 978-0-08-052820-5.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.