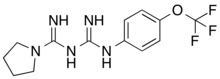
HL156A
HL156A is a derivative of metformin and a potent oxidative phosphorylation inhibitor and AMP-activated protein kinase activating biguanide.[1][2] Certain types of cancer cells requires oxidative phosphorylation to survive. By targeting it, HL156A might help in improving anticancer therapy.[3] It is more potent than acadesine or metformin at activating AMP-activated protein kinase.[2] It is synthesized by Hanall Biopharma.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | IM156, HL271 acetate, UNII-4G3BUV6ZSK |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H16F3N5O |
| Molar mass | 315.300 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Medical uses
It is in phase 1 trial in patients with advanced solid tumor and lymphoma.[5][1]
Pharmacology
Apart from AMP-activated protein kinase activation, it also inhibits expression and activation of insulin-like growth factor-1, protein kinase B, mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and extracellular signal-regulated kinases.[6][7]
Research
It is researched in multiple conditions like liver and renal fibrosis,[2][8] cancer[6][9] and drug resistance in cancer.[7] HL176OUT04, a drug with similar pharmacology, has been also developed.[10]
See also
References
- Rha, Sun Young; Beom, Seung-Hoon; Shin, Young Geun; Yim, Dong-Seok; Moon, Yong Wha; Kim, Tae Won; Kim, Sun Young; Kim, Gun Min; Kim, Hyo Song; Cheong, Jae-Ho; Lee, Young Woo; Geiger, Barbara Jean; Yoo, Sanghee; Rudoltz, Marc S.; Janku, Filip (2020). "Phase I study of IM156, a novel potent biguanide oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 38 (15_suppl): 3590. doi:10.1200/JCO.2020.38.15_suppl.3590. ISSN 0732-183X. S2CID 219780562.
- Tsogbadrakh B, Ju KD, Lee J, Han M, Koh J, Yu Y, Lee H, Yu KS, Oh YK, Kim HJ, Ahn C, Oh KH (2018). "HL156A, a novel pharmacological agent with potent adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator activity ameliorates renal fibrosis in a rat unilateral ureteral obstruction model". PLOS One. 13 (8): e0201692. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1301692T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0201692. PMC 6116936. PMID 30161162.
- Xu, Yibin; Xue, Ding; Bankhead, Armand; Neamati, Nouri (2020). "Why All the Fuss about Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS)?". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 63 (23): 14276–14307. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01013. ISSN 0022-2623. PMC 9298160. PMID 33103432. S2CID 225072329.
- Ju, Kyung Don; Kim, Hyo Jin; Tsogbadrakh, Bodokhsuren; Lee, Jinho; Ryu, Hyunjin; Cho, Eun Jin; Hwang, Young-Hwan; Kim, Kiwon; Yang, Jaeseok; Ahn, Curie; Oh, Kook-Hwan (2016). "HL156A, a novel AMP-activated protein kinase activator, is protective against peritoneal fibrosis in an in vivo and in vitro model of peritoneal fibrosis". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology. 310 (5): F342–F350. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00204.2015. PMID 26661649.
- "A Multi Center, Open-label, Phase 1 Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Preliminary Efficacy of IM156 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors and Lymphoma". 15 October 2020.
- Lam TG, Jeong YS, Kim SA, Ahn SG (March 2018). "New metformin derivative HL156A prevents oral cancer progression by inhibiting the insulin-like growth factor/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways". Cancer Science. 109 (3): 699–709. doi:10.1111/cas.13482. PMC 5834796. PMID 29285837.
- Jeong YS, Lam TG, Jeong S, Ahn SG (August 2020). "Metformin Derivative HL156A Reverses Multidrug Resistance by Inhibiting HOXC6/ERK1/2 Signaling in Multidrug-Resistant Human Cancer Cells". Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland). 13 (9): 218. doi:10.3390/ph13090218. PMC 7560051. PMID 32872293.
- Lee HS, Shin HS, Choi J, Bae SJ, Wee HJ, Son T, Seo JH, Park JH, Kim SW, Kim KW (October 2016). "AMP-activated protein kinase activator, HL156A reduces thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice and inhibits the activation of cultured hepatic stellate cells and macrophages". International Journal of Oncology. 49 (4): 1407–14. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3627. PMID 27498767.
- Choi J, Lee JH, Koh I, Shim JK, Park J, Jeon JY, Yun M, Kim SH, Yook JI, Kim EH, Chang JH, Kim SH, Huh YM, Lee SJ, Pollak M, Kim P, Kang SG, Cheong JH (October 2016). "Inhibiting stemness and invasive properties of glioblastoma tumorsphere by combined treatment with temozolomide and a newly designed biguanide (HL156A)". Oncotarget. 7 (40): 65643–65659. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11595. PMC 5323181. PMID 27582539.
- The AMPK activators, HL156A and HL176OUT04 reduce thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis via the inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation (Thesis). 서울대학교 융합과학기술대학원. 2016. hdl:10371/133411.