HNRPDL
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like, also known as HNRPDL, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the HNRPDL gene.[5]
| HNRNPDL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | HNRNPDL, HNRNP, HNRPDL, JKTBP, JKTBP2, laAUF1, LGMD1G, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D like, LGMDD3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 607137 MGI: 1355299 HomoloGene: 75314 GeneCards: HNRNPDL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Function
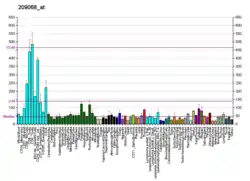
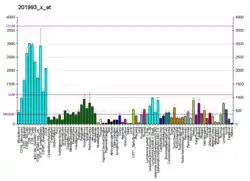
This gene belongs to the subfamily of ubiquitously expressed heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs). The hnRNPs are RNA binding proteins and they complex with heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA). These proteins are associated with pre-mRNAs in the nucleus and appear to influence pre-mRNA processing and other aspects of mRNA metabolism and transport. While all of the hnRNPs are present in the nucleus, some seem to shuttle between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The hnRNP proteins have distinct nucleic acid binding properties. The protein encoded by this gene has two RRM domains that bind to RNAs. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described for this gene. One of the variants is probably not translated because the transcript is a candidate for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. The protein encoded by this gene is similar to its family member HNRPD.[5]
Clinical Significance
Heterozygous nonsense mutations in HNRNPDL has been identified as the cause of the autosomal disorder, Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000152795 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000029328 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: HNRPDL heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like".
Further reading
- Doi A, Shiosaka T, Takaoka Y, et al. (1998). "Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding A + U-rich element RNA binding factor". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1396 (1): 51–6. doi:10.1016/s0167-4781(97)00223-6. PMID 9524220.
- Tsuchiya N, Kamei D, Takano A, et al. (1998). "Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-like protein and its expression in myeloid leukemia cells". J. Biochem. 123 (3): 499–507. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021964. PMID 9538234.
- Sanger Centre, The; Washington University Genome Sequencing Cente, The (1999). "Toward a complete human genome sequence". Genome Res. 8 (11): 1097–108. doi:10.1101/gr.8.11.1097. PMID 9847074.
- Kamei D, Tsuchiya N, Yamazaki M, et al. (1999). "Two forms of expression and genomic structure of the human heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like JKTBP gene (HNRPDL)". Gene. 228 (1–2): 13–22. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00020-7. PMID 10072754.
- Kawamura H, Tomozoe Y, Akagi T, et al. (2002). "Identification of the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling sequence of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like protein JKTBP and its interaction with mRNA". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (4): 2732–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108477200. PMID 11705999.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Boopathi E, Lenka N, Prabu SK, et al. (2005). "Regulation of murine cytochrome c oxidase Vb gene expression during myogenesis: YY-1 and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D-like protein (JKTBP1) reciprocally regulate transcription activity by physical interaction with the BERF-1/ZBP-89 factor". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (34): 35242–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403160200. PMID 15190078.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, et al. (2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
- Reboll MR, Oumard A, Gazdag AC, et al. (2007). "NRF IRES activity is mediated by RNA binding protein JKTBP1 and a 14-nt RNA element". RNA. 13 (8): 1328–40. doi:10.1261/rna.545407. PMC 1924892. PMID 17592041.