Haematopodin B
Haematopodin B is a chemical compound that is found in the mushroom Mycena haematopus.[1] It decomposes to haematopodin under the influence of air and light.[1]
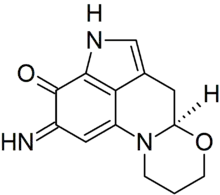 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6aR)-2-Imino-2,4,6,6a,9,10-hexahydro-3H,8H-[1,3]oxazino[3,2-a]pyrrolo[4,3,2-de]quinolin-3-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H13N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 243.266 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Baumann, C.; Bröckelmann, M.; Fugmann, B.; Steffan, B.; Steglich, W.; Sheldrick, W.S. (1993). "Pigments of fungi. 62. Haematopodin, an unusual pyrrologuinone derivative isolated from the fungus Mycena haematopus, Agaricales". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 32 (7): 1087–89. doi:10.1002/anie.199310871.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.