Hart circle
In geometry, the Hart circle is derived from three given circles that cross pairwise to form eight circular triangles. For any one of these eight triangles, and its three neighboring triangles, there exists a Hart circle, tangent to the inscribed circles of these four circular triangles. Thus, the three given circles have eight Hart circles associated with them. The Hart circles are named after their discover, Andrew Searle Hart. They can be seen as analogous to the nine-point circle of straight-sided triangles.[1][2]
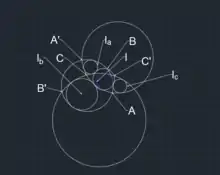
The circle H touches the incircles I, ,, of a circular triangle ABC and its associated triangles.
References
- Coolidge, Julian Lowell (1916). A treatise on the circle and sphere. Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-8284-0236-1. OCLC 1017317.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Hart Circle". MathWorld.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.