Hibifolin
Hibifolin is a flavonol glycoside that prevents beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in vitro.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
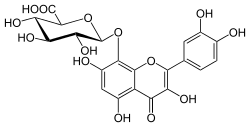
| IUPAC name
3,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxy-4-oxoflav-2-en-8-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-6-{[2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-8-yl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H18O14 | |
| Molar mass | 494.36 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Zhu, JT; Choi, RC; Xie, HQ; Zheng, KY; Guo, AJ; Bi, CW; Lau, DT; Li, J; Dong, TT; Lau, BW; Chen, JJ; Tsim, KW (2009). "Hibifolin, a flavonol glycoside, prevents beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons". Neuroscience Letters. 461 (2): 172–6. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.06.010. PMID 19539722. S2CID 32342156.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.