Large Asian roundleaf bat
The large Asian roundleaf bat (Hipposideros lekaguli) is a species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is found in Malaysia, the Philippines, and Thailand. The specific name commemorates Thai zoologist and conservationist Boonsong Lekagul.
| Large Asian roundleaf bat | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Hipposideridae |
| Genus: | Hipposideros |
| Species: | H. lekaguli |
| Binomial name | |
| Hipposideros lekaguli Thonglongya & Hill, 1974 | |
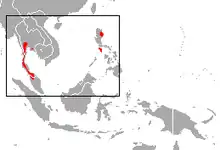 | |
| Large Asian roundleaf bat range | |
Taxonomy and etymology
It was described as a new species in 1974 by Thonglongya and Hill. The holotype had been collected in the Kaeng Khoi District of Thailand in 1972 by Boonsong Lekagul. Lekagul is the eponym for the species name "lekaguli."[2]
Description
Its forearm length is 66.5–79.3 mm (2.62–3.12 in). Its ears are broad, large, and triangular. Its nose-leaf is complexly foliated with intermediate, anterior, and posterior leaflets.[3]
Range and habitat
It was first documented in Thailand in 1972.[2] In 1992, it was additionally documented in the Philippines.[3] It is also found in Peninsular Malaysia. It has been documented at a range of elevations from 50–400 m (160–1,310 ft).[1]
Conservation
The large Asian roundleaf bat is listed as a near-threatened species by the IUCN as of 2019. It is experiencing widespread habitat loss.[1]
References
- Csorba, G.; Bumrungsri, S.; Francis, C.; Bates, P.; Gumal, M.; Kingston, T.; Soisook, P. (2019). "Hipposideros lekaguli". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T10144A22091565. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T10144A22091565.en. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- Thonglongya †, K; Hill, J. E (1974). "A New Species of Hipposideros (Chiroptera) from Thailand". Mammalia. 38 (2). doi:10.1515/mamm.1974.38.2.285. S2CID 85145696.
- Balete, D. S.; Heaney, L. R.; Crombie, R. I. (1995). "First records of Hipposideros lekaguli Thonglongya and Hill 1974 from the Philippines". Asia Life Sciences. 4 (1): 89–94.
