Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (also known as:[1] "Epithelioid hemangioma," "Histiocytoid hemangioma," "Inflammatory angiomatous nodule," "Intravenous atypical vascular proliferation," "Papular angioplasia," "Inflammatory arteriovenous hemangioma," and "Pseudopyogenic granuloma") usually presents with pink to red-brown, dome-shaped, dermal papules or nodules of the head or neck, especially about the ears and on the scalp.[2]
| Epithelioid hemangioma | |
|---|---|
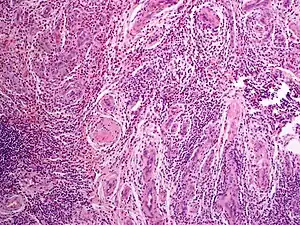 | |
| Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
It, or a similar lesion, has been suggested as a feature of IgG4-related skin disease, which is the name used for skin manifestations of IgG4-related disease.[3][4]
See also
References
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Yoshiki Tokura; Hiroaki Yagi; H. Yanaguchi; Yuta Majima; Akira Kasuya; Taisuke Ito; M Maekawa; Hideo Hashizume (November 2014). "IgG4-related skin disease". British Journal of Dermatology. 171 (5): 959–967. doi:10.1111/bjd.13296. PMID 25065694. S2CID 5374017.
- Yasuhito Hamaguchi; Manabu Fujimoto; Yukiyo Matsushita; Seiko Kitamura-Sawada; Mitsuhiro Kawano; Kazuhiko Takehara (2011). "IgG4-related skin disease, a mimic of angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia". Dermatology. 223 (4): 301–305. doi:10.1159/000335372. PMID 22269779. S2CID 22928854.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.