Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site
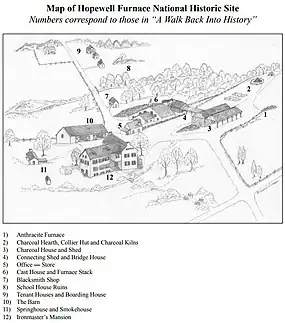
Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site in southeastern Berks County, near Elverson, Pennsylvania, is an example of an American 19th century rural iron plantation, whose operations were based around a charcoal-fired cold-blast iron blast furnace. The significant restored structures include the furnace group (blast furnace, water wheel, blast machinery, cast house and charcoal house), as well as the ironmaster's house, a company store, the blacksmith's shop, a barn and several worker's houses.
| Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Map of the US state of Pennsylvania showing the location of Hopewell Furnace  Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site (the United States) | |
| Location | Union Township, Berks County, Pennsylvania, USA |
| Nearest city | Reading, Pennsylvania |
| Coordinates | 40°11′55″N 75°46′32″W |
| Area | 848 acres (343 ha) |
| Established | August 3, 1938 |
| Visitors | 49,980 (in 2005) |
| Governing body | National Park Service |
| Website | Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site |

Hopewell Furnace was founded about 1771 by ironmaster Mark Bird, son of William Bird, who had been one of Pennsylvania's most prominent ironmasters. The site's most prosperous time was during the 1820-1840 period with a brief return to significant production during the American Civil War. In the mid-19th century, changes in iron making, including a shift from charcoal-fueled furnaces to anthracite-fueled steel mills, rendered smaller furnaces like Hopewell obsolete. The site discontinued operations in 1883.
In 1938, the property was designated Hopewell Village National Historic Site under the authority of the Historic Sites Act, thereby becoming one of the earliest cultural units of the National Park System.
Today, Hopewell Furnace consists of 14 restored structures, 52 features on the List of Classified Structures, and a total of 848 mostly wooded acres. Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site is located in the Hopewell Big Woods and bordered by French Creek State Park on three sides and State Game Lands 43 on the south side, which preserves the lands the furnace utilized for its natural resources.
Mark Bird
In 1761, Mark Bird took over the family business after the death of his ironmaster father. This included two forges and a furnace on 3000 acres. Bird expanded the business to 8000 acres by 1763, and added the Hopewell and Jones Good Luck mines. In 1770, he purchased several tracts in Berks and Chester Counties, planning a furnace on French Creek near his father's forge and the Hopewell mine. By 1771, the Hopewell Furnace was in operation, and an early stove plate was imprinted "Mark Bird-Hopewell Furnace - 1772." By 1775, Bird was a member of the Pennsylvania Committee of Correspondence and the Pennsylvania Provincial Conference. During the American Revolutionary War, Bird served as a colonel of the Second Battalion of Berks County militia, was elected to the Pennsylvania General Assembly, and served as a judge for Berks County. As Deputy Quartermaster General of Pennsylvania, his furnace provided cannon and shot to the Continental Army and Continental Navy. However, payments from Congress were insufficient to cover his over-expanded business, and Bird was forced to close down his Berks County ironworks in 1784 following the national economic downturn. Bird noted, "...I was Ruined, by the Warr, it was not Drunkeness, Idleness or want of Industry." Following floods and fire, Bird was forced to mortgage his Hopewell and Birdsboro properties in 1786. In 1788, the Hopewell plantation was auctioned off to James Old and Cadwallader Morris, while Bird fled to North Carolina, a debtor's refuge. Bird died there in 1816.[1]
Daniel Buckley
By 1789, Hopewell Furnace was the second largest of 14 furnaces in Pennsylvania with annual capacity of 700 tons. Yet, the operation was still not profitable. In 1794, James Wilson bought the operation, but was forced to auction the complex in 1796, and fled to North Carolina to avoid his creditors. In 1800, Daniel Buckley, and his brothers-in-law Matthew and Thomas Brooke, purchased the furnace and operated it as a family business for the next 83 years. Daniel Buckley was succeed upon his death in 1828 by his son Matthew Brooke Buckley, and then his grandson Edward S. Buckley. In 1801, the two bellows were repaired. In 1804, the furnace was renovated, a new charcoal house built, the water wheel and head race remodeled, with the overshot wheel replaced by a breastshot wheel. In 1805, a stamping mill helped recover iron from the slag, which operated until 1817. The partners were forced to close down operations from 1808 until 1816, due to the national recession, and land title litigation. In 1817, a cupola furnace was added to resmelt pig iron into cast iron to sand cast sash weights, pots, skillets, kettles, flat irons, wheels, mill screws, apple mill nuts, clock weights, anvils, hammers, grates, grindstone wheels, mold boards, and stove plates. The 1830s were the most profitable years, and from 1825 until 1844, stove plates were the most lucrative product. In 1839, 5,152 stoves were produced. While Clement Brooke served as resident manager and iron master from 1816 until 1848, he added a cellar, kitchen and southwest wing to the ironmaster's house, enlarged the spring house and company store, and built tenant houses and a schoolhouse. Stove plate production ended in 1844, and over the next four decades, mainly pig iron was produced. Customers included the Reading Railroad. Dr. Charles M. Clingan, Clement Brooke's son-in-law, succeeded as resident manager over the next 10 years. He was followed by John R. Shafer for the next 15 years, and Harker Long as the last resident manager. The furnace ceased operations on 15 June 1883, and the remaining pig iron stock sold off over the next five years.[1]: 33–65
Restoration
In 1935, the federal government purchased the property from Louise Brooke, daughter of Dr. Charles and Maria Clingan, paying $100,000 for 4000 acres. In 1938, the Secretary of the Interior designated the area as a National Historic Site, and plans proceeded to restore the area to its prosperous period of 1820 to 1840. In 1946, 5000 acres of the recreation area were deeded to the state, keeping 848 acres for the historic site. Restoration began in the 1950s, and by 1952, the furnace, blacksmith shop, water wheel and blast machinery, barn, tenant houses, and cast house had been rebuilt and restored. This included the use of wooden dowels and hand hewn beams.[1]: 67–72
Challenges
Due to being one of the oldest established units in the National Park Service, Hopewell Furnace had deferred maintenance costs of $7,983,521 in 2015, $7,526,855 in 2016, $6,835,475 in 2017, and most recently published $7,443,553 in 2018. Much of this comes from costs of repair and maintenance needs. Local support groups for the site are recently focused on preserving and cataloging documents from the furnace’s active period, in order to better interpret and present the history of the area.
List of superintendents
- Lemuel A. Garrison: 11/28/1939 - 9/22/1941
- Ralston B. Lattimore: 9/23/1941 - 11/23/1942
- Emil C. Heinrich (Acting): 4/01/1943 - 4/16/1947
- Emil C. Heinrich: 6/11/1947 - 6/27/1947
- Catherine Fritz (Acting): 6/28/1947 - 8/23/1947
- Russell A. Gibbs: 8/24/1947 - 12/10/1949
- James Cass: 12/11/1949 - 5/31/1955
- Joseph R. Prentice: 7/29/1955 - 12/2/1961
- Benjamin J. Zerby: 1/21/1962 - 3/20/1965
- John C.W. Riddle: 6/13/1965 - 11/11/1972
- Larry Points (Acting): 11/12/1972 - 1/6/1973
- Wallace B. Elms: 1/7/1973 - 9/16/1975
- Elizabeth E. Disrude: 10/26/1975 - 2/27/1988
- Russell P. Smith (Acting): 2/28/1988 - 7/16/1988
- Derrick Cook: 7/17/1988 - 11/30/1995
- Josie Fernandez (Acting, then later Superintendent): 12/1/1995 - 4/26/1998
- Jeffrey Collins (Acting): 4/27/1998 - 8/1/1998
- William Sanders: 8/2/1998 - at least August 2005
- Edie Shean-Hammond: Started February 2006
- Kate Hammond: Started March 2012
- Steven Sims: Started Late June 2017
- Rose Fennell: 9/27/2020–Present
References
- Hugins, Walter (1983). Hopewell Furnace: The Story of a 19th-Century Ironmaking Community, in Hopewell Furnace, Hopewell Village National Historic Site, Pennsylvania, National Park Handbook 124. Washington, D.C.: National Park Service. pp. 28–33. ISBN 0912627182.
External links
- Official website
- Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site: Administrative History (National Park Service)
- History of Hopewell Furnace
- African-Americans at Hopewell Furnace
- Hopewell Village National Historic Site
- Hopewell Furnace: A Pennsylvania Iron-making Plantation, a National Park Service Teaching with Historic Places (TwHP) lesson plan
- Historic American Buildings Survey (HABS) No. PA-5157-A, "Hopewell Village, Furnace and Bridge House", 2 photos, 1 photo caption page
- Historic American Landscapes Survey (HALS) No. PA-22, "Hopewell Furnace National Historic Site", 8 data pages
- "Sand Molding at Hopewell Furnace" on YouTube
- "Iron Casting at Hopewell Furnace" on YouTube
- "Charcoal Making at Hopewell Furnace" on YouTube
- Friends of Hopewell Furnace
- National Park Service Deferred Maintenance 2018
.jpg.webp)




