Phenylpropanoic acid
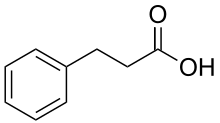
Phenylpropanoic acid or hydrocinnamic acid is a carboxylic acid with the formula C9H10O2 belonging to the class of phenylpropanoids. It is a white, crystalline solid with a sweet, floral scent at room temperature. Phenylpropanoic acid has a wide variety of uses including cosmetics, food additives, and pharmaceuticals.[5]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Phenylpropanoic acid | |
| Other names
Phenylpropionic acid, Benzenepropanoic Acid, β-Phenylpropionic Acid, Benzylacetic Acid, Dihydrocinnamic Acid, β-Phenylpropanoic Acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.204 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 150.177 g/mol[2] |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid; faint, sweet, somewhat balsamic and coumarin-like odor[3] |
| Density | 1.126 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 47 to 50 °C (117 to 122 °F; 320 to 323 K) |
| Boiling point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) |
| 5.9 g/L | |
| log P | 1.839[3] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.66 (H2O)[4] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K)[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Benzoic acid, Phenylacetic acid, Cinnamic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Preparation and reactions
Phenylpropanoic acid can be prepared from cinnamic acid by hydrogenation.[5][6] Originally it was prepared by reduction with sodium amalgam in water and by electrolysis.[7]
A characteristic reaction of phenylpropanoic acid is its cyclization to 1-indanone. When the side chain is homologated by the Arndt–Eistert reaction, subsequent cyclization affords 2-tetralone, derivatives.[5]
Uses
Phenylpropanoic acid is widely used for flavoring, food additives, spices, fragrance, and medicines as it acts as a fixative agent, or a preservative.[8]
Food industry
Phenylpropanoic acid is used in the food industry to preserve and maintain the original aroma quality of frozen foods. It can also be used to add or restore original color to food. Shelved foods are protected from microorganism by adding phenylpropanoic acid to prevent deterioration to the food by microorganisms as well as acting as an antioxidant to prolong shelf life foods. This compound is used as a sweetener as well to sweeten food and can be found in table top sweeteners. It can also act as an emulsifier, to keep oil and water mixtures from separating. Phenylpropanoic acid is also added to food for technological purposes in a wide variety including manufacturing, processing, preparation, treatment, packaging, transportation or storage, and food additives. It also provides flavorings for ice cream, bakery, and confectionery.[9]
Cosmetics
This compound is used frequently in cosmetic products such as perfumes, bath gels, detergent powders, liquid detergents, fabric softeners, and soaps as it gives off a floral scent. The acid is commonly used as flavoring for toothpastes and mouthwashes in addition to providing floral scents and possible fruity, minty, spearmint, strawberry, lychee, and herbal flavorings.[9]
References
- "Hydrocinnamic acid". National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 16 November 2012.
- "Hydrocinnamic Acid". R&D Chemicals. Retrieved 10 October 2012.
- "3-phenylpropanoic acid". Chem Spider. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- Korneev, Sergei (2013). "Hydrocinnamic Acids: Application and Strategy of Synthesis". Synthesis. 45 (8): 1000–1015. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1318475.
- Furniss, Brian; Hannaford, Antony; Smith, Peter & Tatchell, Austin (1996). Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry 5th Ed. London: Longman Science & Technical. pp. 1038–1039. ISBN 9780582462366.
- A. W. Ingersoll (1929). "Hydrocinnamic acid". Organic Syntheses. 9: 42.; Collective Volume, vol. 1, p. 311
- "Hydrocinnamic acid". Food & Beverage Online. Retrieved 19 October 2012.
- "Hydrocinnamic Acid Organic Intermediate Kosher Reach (CAS NO.: 501-52-0)". Made-in-China.com. Retrieved 16 November 2012.