Adrenal insufficiency
Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands do not produce adequate amounts of steroid hormones. The adrenal glands—also referred to as the adrenal cortex—normally secrete glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol), mineralocorticoids (primarily aldosterone), and androgens.[1][2][3][4] These hormones are important in regulating blood pressure, electrolytes, and metabolism as a whole.[2][3] Deficiency of these hormones leads to symptoms ranging from abdominal pain, vomiting, muscle weakness and fatigue, low blood pressure, depression, mood and personality changes (in mild cases) to organ failure and shock (in severe cases).[1][2][3] Adrenal crisis may occur if a person having adrenal insufficiency experiences stresses, such as an accident, injury, surgery, or severe infection; this is a life-threatening medical condition resulting from severe deficiency of cortisol in the body.[2][3] Death may quickly follow.[1]
| Adrenal insufficiency | |
|---|---|
| Other names | adrenocortical insufficiency, hypocorticalism, hypocortisolism, hypoadrenocorticism, hypocorticism, hypoadrenalism |
 | |
| Adrenal gland | |
| Specialty | Endocrinology |
Adrenal insufficiency can be caused by dysfunction of the adrenal gland itself, whether by destruction (e.g. Addison's disease), failure of development (e.g. adrenal dysgenesis), or enzyme deficiency (e.g. congenital adrenal hyperplasia).[2][3] Adrenal insufficiency can also occur when the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus do not produce adequate amounts of the hormones that assist in regulating adrenal function.[5][6][7] This is called secondary adrenal insufficiency (when caused by lack of production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) in the pituitary gland) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (when caused by lack of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in the hypothalamus).[2][3][8]
Types
There are three major types of adrenal insufficiency, depending on the affected organ.
- Primary adrenal insufficiency is due to impairment of the adrenal glands, resulting in a lack of glucocorticoid production. Since the adrenal glands are directly affected, mineralocorticoid production is also reduced. Principal causes include:
- Autoimmune: e.g. Addison's disease (also called autoimmune adrenalitis), which has been identified to be the cause of 80-90% of primary adrenal insufficiency cases since 1950.[2]
- Congenital: e.g. congenital adrenal hyperplasia, adrenoleukodystrophy[2]
- Infection: e.g. tuberculosis, CMV, histoplasmosis[2]
- Drugs: e.g. anticonvulsants, etomidate, metyrapone, rifampicin[2]
- Vascular: e.g. hemorrhage from sepsis, adrenal vein thrombosis, hypercoagulable states such as heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and antiphospholipid syndrome[2]
- Neoplasia: e.g. adenoma (tumor) of the adrenal gland[2]
- Deposition disease: e.g. hemochromatosis, amyloidosis, sarcoidosis[2]
- Idiopathic: undetermined cause
- Acquired: Bilateral Adrenalectomy to treat recurrent Cushing's Disease/Syndrome
- Secondary adrenal insufficiency is caused by impairment of the pituitary gland, resulting in a lack of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) production and subsequent decreased adrenal stimulation. Since the adrenal glands are not directly affected, the effect on mineralocorticoid production is minimal, as ACTH primarily affects glucocorticoid production.[2][3] Principal causes include:
- Pituitary adenoma or craniopharyngioma: Tumors in the pituitary gland can suppress production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).[2] High-dose irradiation (>30 Gy) to the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland can cause ACTH deficiency.[9]
- Surgery or radiation: Pituitary gland surgery and/or radiation can lead to destruction of ACTH-producing tissue.[2]
- Exogenous corticosteroid use: Exogenous corticosteroids suppress the stimulation of the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland to secrete CRH and ACTH, respectively.[2][3] These cases may present with symptoms of cortisol excess (see Cushing's syndrome).[3]
- Sheehan's syndrome: Loss of blood flow to the pituitary gland following childbirth[2]
- Pituitary apoplexy: Bleeding or impaired blood supply to the pituitary gland[2]
- Tertiary adrenal insufficiency is caused by impairment of the hypothalamus, resulting in a lack of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) production, causing downstream reduction in ACTH production and subsequently decreasing adrenal stimulation.[2] Since the adrenal glands are not directly affected, the effect on mineralocorticoid production is minimal, as ACTH primarily affects glucocorticoid production.[2][3] Principal causes include:
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms include: hypoglycemia, hyperpigmentation, dehydration, weight loss, and disorientation. Additional signs and symptoms include weakness, tiredness, dizziness, low blood pressure that falls further when standing (orthostatic hypotension), cardiovascular collapse, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. These problems may develop gradually and insidiously. Addison's disease can present with tanning of the skin that may be patchy or even all over the body. Characteristic sites of tanning are skin creases (e.g. of the hands) and the inside of the cheek (buccal mucosa). Goitre and vitiligo may also be present.[1] Eosinophilia may also occur.[10] Hyponatremia is a sign of secondary insufficiency.[11]
Pathophysiology
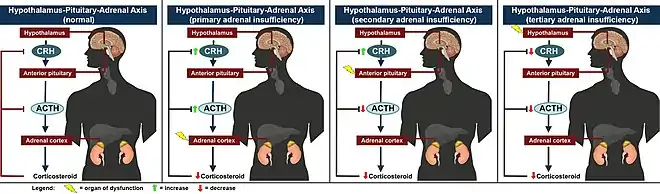
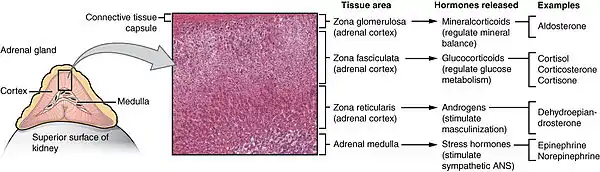
When functioning normally, the adrenal glands secrete glucocorticoids (primarily, cortisol) in the zona fasciculata and mineralocorticoids (primarily, aldosterone) in the zona glomerulosa to regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance.[12] Adrenal hormone production is controlled by the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, in which the hypothalamus produces corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which stimulates the pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal gland to produce cortisol.[12] High levels of cortisol inhibit the production of both CRH and ACTH, forming a negative feedback loop.[12] The types of adrenal insufficiency thus refer to the level of the axis in which the dysfunction originates: primary, secondary, and tertiary for adrenal glands, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus, respectively.[2][3]
In adrenal insufficiency, there is a deficiency in cortisol production which may be accompanied by a deficiency in aldosterone production (predominantly in primary adrenal insufficiency).[2][3] Depending on the cause and type of adrenal insufficiency, the mechanism of the disease differs. Generally, the symptoms manifest through the systemic effects of cortisol and aldosterone.[2][3] In secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency, there is no effect on the production of aldosterone within the zona glomerulosa as this process is regulated by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), not ACTH.[3]
Adrenal insufficiency can also affect the zona reticularis and disrupt production of androgens, which are precursors to testosterone and estrogen.[2][3] This leads to a deficiency of sex hormones and can contribute to symptoms of depression and menstrual irregularities.[2][3]
Cortisol deficiency
Cortisol increases blood sugar by inducing gluconeogenesis (glucose production) in the liver, lipolysis (fat breakdown) in adipose tissue, and proteolysis (muscle breakdown) in muscle while increasing glucagon secretion and decreasing insulin secretion in the pancreas.[12] Overall, these actions cause the body to use fat stores and muscle for energy. Deficiency results in hypoglycemia, with associated nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness.[2]
Cortisol potentiates the effectiveness of angiotensin II and catecholamines such as norepinephrine in vasoconstriction. Thus, a deficiency can contribute to hypotension, though this effect is most pronounced in mineralocorticoid deficiency.[2]
In primary adrenal insufficiency, the lack of negative feedback from cortisol leads to increased production of CRH and ACTH.[2][3] ACTH is derived from pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), which is cleaved into ACTH as well as α-MSH, which regulates production of melanin in the skin.[13] The overproduction of α-MSH leads to the characteristic hyperpigmentation of Addison's disease.[14]
Aldosterone deficiency
Although the production of aldosterone occurs within the adrenal cortex, it is not induced by adrenocorticotropic (ACTH); instead, it is regulated by the renin–angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).[15] Renin production in the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney is induced by decreased arterial blood pressure, decreased sodium content in the distal convoluted tubule, and increased sympathetic tone.[15] Renin initiates the downstream sequence of cleavage of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I to angiotensin II, in which angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone production in the zona glomerulosa.[15] Thus, dysfunction of the pituitary gland or the hypothalamus does not affect the production of aldosterone.[2][3] However, in primary adrenal insufficiency, damage to the adrenal cortex (e.g. autoimmune adrenalitis a.k.a. Addison's disease) can lead to destruction of the zona glomerulosa and therefore a loss of aldosterone production.
Aldosterone acts on mineralocorticoid receptors on epithelial cells lining the distal convoluted tubule, activating epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) and the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase pump.[15] This results in the absorption of sodium (with resulting retention of fluid) and the excretion of potassium.[15] Deficiency of aldosterone leads to urinary loss of sodium and effective circulating volume, as well as retention of potassium.[15] This can cause hypotension (in severe cases, shock), dizziness (from orthostatic hypotension), dehydration, and salt craving.
Differently from mineralocorticoid deficiency, glucocorticoid deficiency does not cause a negative sodium balance (in fact a positive sodium balance may occur).[16]
Causes
Causes of acute adrenal insufficiency are mainly sudden withdrawal of long-term corticosteroid therapy, Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome, and stress in people with underlying chronic adrenal insufficiency.[17] The latter is termed critical illness–related corticosteroid insufficiency.[18]
For chronic adrenal insufficiency, the major contributors are autoimmune adrenalitis (Addison's Disease), tuberculosis, AIDS, and metastatic disease.[17] Minor causes of chronic adrenal insufficiency are systemic amyloidosis, fungal infections, hemochromatosis, and sarcoidosis.[17]
Causes of adrenal insufficiency can be categorized by the mechanism through which they cause the adrenal glands to produce insufficient cortisol. These are adrenal destruction (disease processes leading to glandular damage), impaired steroidogenesis (the gland is present but is biochemically unable to produce cortisol), or adrenal dysgenesis (the gland has not formed adequately during development).[19]
Adrenal destruction
Autoimmune adrenalitis (Addison's disease) is the most common cause of primary adrenal insufficiency in the industrialised world, causing 80-90% of cases since 1950.[2] Autoimmune destruction of the adrenal cortex is caused by an immune reaction against the enzyme 21-hydroxylase (a phenomenon first described in 1992).[20] This may be isolated or in the context of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (APS type 1 or 2), in which other hormone-producing organs, such as the thyroid and pancreas, may also be affected.[21]
Autoimmune adrenalitis may be part of Type 2 autoimmune polyglandular syndrome, which can include type 1 diabetes, hyperthyroidism, and autoimmune thyroid disease (also known as autoimmune thyroiditis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Hashimoto's disease).[22] Hypogonadism may also present with this syndrome. Other diseases that are more common in people with autoimmune adrenalitis include premature ovarian failure, celiac disease, and autoimmune gastritis with pernicious anemia.[23]
Adrenal destruction is a feature of adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD).[24] Destruction also occurs when the adrenal glands are involved in metastasis (seeding of cancer cells from elsewhere in the body, especially lung), hemorrhage (e.g. in Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome or antiphospholipid syndrome), particular infections which can spread to the adrenal cortex (tuberculosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis), or the deposition of abnormal protein in amyloidosis.[25]
Impaired steroidogenesis
To form cortisol, the adrenal gland requires cholesterol, which is then converted biochemically into steroid hormones. Interruptions in the delivery of cholesterol include Smith–Lemli–Opitz syndrome and abetalipoproteinemia.
Of the synthesis problems, congenital adrenal hyperplasia is the most common (in various forms: 21-hydroxylase, 17α-hydroxylase, 11β-hydroxylase and 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase), lipoid CAH due to deficiency of StAR and mitochondrial DNA mutations.[19] Some medications interfere with steroid synthesis enzymes (e.g. ketoconazole), while others accelerate the normal breakdown of hormones by the liver (e.g. rifampicin, phenytoin).[19]
Adrenal insufficiency can also result when a patient has a brain mass in the pituitary gland (e.g. pituitary adenoma, craniopharyngioma) which can take up space and interfere with the secretion of pituitary hormones such as ACTH, therefore leading to decreased adrenal stimulation (secondary adrenal insufficiency).[2] The same can occur with masses in the hypothalamus (tertiary adrenal insufficiency).[2]
Corticosteroid withdrawal
Use of high-dose steroids for more than a week begins to produce suppression of the person's adrenal glands because the exogenous glucocorticoids suppress release of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). With prolonged suppression, the adrenal glands atrophy (physically shrink), and can take months to recover full function after discontinuation of the exogenous glucocorticoid. During this recovery time, the person is vulnerable to adrenal insufficiency during times of stress, such as illness, due to both adrenal atrophy and suppression of CRH and ACTH release.[26][27] Use of steroids joint injections may also result in adrenal suppression after discontinuation.[28]
Adrenal dysgenesis
All causes in this category are genetic, and generally very rare. These include mutations to the SF1 transcription factor, congenital adrenal hypoplasia due to DAX-1 gene mutations and mutations to the ACTH receptor gene (or related genes, such as in the Triple A or Allgrove syndrome). DAX-1 mutations may cluster in a syndrome with glycerol kinase deficiency with a number of other symptoms when DAX-1 is deleted together with a number of other genes.[19]
Diagnosis
The first step of diagnosing adrenal insufficiency is confirming inappropriately low cortisol secretion.[2] This is followed by determining the origin of dysfunction (adrenal glands, pituitary gland, or hypothalamus) and therefore the type of adrenal insufficiency (primary, secondary, or tertiary).[2] After narrowing down the source, further testing can elucidate the cause of insufficiency.[2]
If a patient is suspected to be experiencing an acute adrenal crisis, immediate treatment with IV corticosteroids is imperative and should not be delayed for any testing, as the patient's health can deteriorate rapidly and result in death without replacing the corticosteroids.[2][3] Dexamethasone should be used as the corticosteroid of choice in these cases as it is the only corticosteroid that will not affect diagnostic test results.[2][29]
To confirm inappropriately low cortisol secretion, testing can include baseline morning cortisol level in the blood or morning cortisol level in the saliva.[2] Cortisol levels typically peak in the morning; thus, low values indicate true adrenal insufficiency.[2] Urinary free cortisol can also be measured, but are not necessary for diagnosis.[2]
To determine the origin of dysfunction, the ACTH stimulation test is the best initial test as it can differentiate between primary and secondary adrenal insufficiency.[2] If cortisol levels remain low following ACTH stimulation, then the diagnosis is primary adrenal insufficiency.[2] If cortisol levels increase following ACTH stimulation, then the diagnosis is either secondary or tertiary adrenal insufficiency.[2] The corticotropin-releasing hormone test can then differentiate between secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency.[2] Additional testing can include basal plasma ACTH, renin, and aldosterone concentrations, as well as a blood chemistry panel to check for electrolyte imbalances.[2]
Depending on the type of adrenal insufficiency, there are many possible causes and therefore many different avenues of testing (see Causes above). For primary adrenal insufficiency, the most common cause is autoimmune adrenalitis (Addison's disease); therefore, 21-hydroxylase autoantibodies should be checked.[2] Structural abnormalities of the adrenal glands can be detected on CT imaging.[2] For secondary and tertiary adrenal insufficiency, an MRI of the brain can be obtained to detect structural abnormalities such as masses, metastasis, hemorrhage, infarction, or infection.[2]
Effects
| Source of pathology | CRH | ACTH | DHEA | DHEA-S | cortisol | aldosterone | renin | Na | K | Causes5 |
| hypothalamus (tertiary)1 | low | low | low | low | low3 | normal | low | low | low | tumor of the hypothalamus (adenoma), antibodies, environment (i.e. toxins), head injury |
| pituitary (secondary) | high2 | low | low | low | low3 | normal | low | low | normal | tumor of the pituitary (adenoma), antibodies, environment, head injury, surgical removal6, Sheehan's syndrome |
| adrenal glands (primary)7 | high | high | high | high | low4 | low | high | low | high | tumor of the adrenal (adenoma), stress, antibodies, environment, Addison's disease, trauma, surgical removal (resection), miliary tuberculosis of the adrenal |
| 1 | Automatically includes diagnosis of secondary (hypopituitarism) |
| 2 | Only if CRH production in the hypothalamus is intact |
| 3 | Value doubles or more in stimulation |
| 4 | Value less than doubles in stimulation |
| 5 | Most common, does not include all possible causes |
| 6 | Usually because of very large tumor (macroadenoma) |
| 7 | Includes Addison's disease |
Treatment
In general, the treatment of adrenal insufficiency requires replacement of deficient hormones, as well as treatment of any underlying cause.[2][3] All types of adrenal insufficiency will require glucocorticoid repletion.[2][3] Many cases (typically, primary adrenal insufficiency) will also require mineralocorticoid repletion.[2][3] In rarer cases, repletion of androgens may also be indicated, typically in female patients with mood disturbances and changes in well-being.[2][3]
- Adrenal crisis (acute) treatment
- Intravenous fluids[1][2][3]
- Intravenous glucocorticoids[1][2][3]
- typically hydrocortisone (Cortef) but dexamethasone (Decadron) may be used if diagnostic studies are necessary, as dexamethasone does not affect testing results[2][29]
- Supportive measures and correction of any additional issues such as electrolyte abnormalities[2][3]
- Chronic adrenal insufficiency treatment
- Glucocorticoid deficiency (low cortisol)
- Oral glucocorticoids[2][3]
- Hydrocortisone (brand name: Cortef), or
- Prednisone (brand name: Deltasone), or
- Dexamethasone (brand name: Decadron)
- Oral glucocorticoids[2][3]
- Mineralocorticoid deficiency (low aldosterone) treatment
- Oral mineralocorticoids[2][3]
- Fludrocortisone (brand name: Florinef)
- Oral mineralocorticoids[2][3]
- Sex hormone deficiency (low androgen)
- Oral androgens[2][3]
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)
- Oral androgens[2][3]
- Glucocorticoid deficiency (low cortisol)
Prognosis
Primary adrenal insufficiency predisposes to higher risk of death, mostly due to infection, cardiovascular disease, and adrenal crisis.[2] Delayed diagnosis can impair quality of life, and lack of treatment brings high mortality.[2] However, with proper diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment, people with adrenal insufficiency can live normally.[3]
Epidemiology
The most common cause of primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison's disease) overall is autoimmune adrenalitis.[2] The prevalence of Addison's disease ranges from 5 to 221 per million in different countries.[30]
In children, congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is the most common cause of adrenal insufficiency, with an incidence 1 in 14,200 live births.[3]
See also
- Addison's disease – primary adrenocortical insufficiency
- Cushing's syndrome – overproduction of cortisol
- Insulin tolerance test – another test used to identify sub-types of adrenal insufficiency
- Adrenal fatigue (hypoadrenia) – a term used in alternative medicine to describe a believed exhaustion of the adrenal glands
References
- Ashley B. Grossman, MD (2007). "Addison's Disease". Adrenal Gland Disorders.
- Nicolaides, Nicolas C.; Chrousos, George P.; Charmandari, Evangelia (2000), Feingold, Kenneth R.; Anawalt, Bradley; Boyce, Alison; Chrousos, George (eds.), "Adrenal Insufficiency", Endotext, South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc., PMID 25905309, retrieved 2022-11-02
- Huecker, Martin R.; Bhutta, Beenish S.; Dominique, Elvita (2022), "Adrenal Insufficiency", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 28722862, retrieved 2022-11-02
- Bancos, Irina; Hahner, Stefanie; Tomlinson, Jeremy; Arlt, Wiebke (2015-03-01). "Diagnosis and management of adrenal insufficiency". The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology. 3 (3): 216–226. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(14)70142-1. ISSN 2213-8587.
- Eileen K. Corrigan (2007). "Adrenal Insufficiency (Secondary Addison's or Addison's Disease)". NIH Publication No. 90-3054. Archived from the original on 2008-09-15. Retrieved 2008-08-22.
- Brender E, Lynm C, Glass RM (2005). "JAMA patient page. Adrenal insufficiency". JAMA. 294 (19): 2528. doi:10.1001/jama.294.19.2528. PMID 16287965.
- "Dorlands Medical Dictionary:adrenal insufficiency".
- "Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders". Merck Manuals Professional Edition.
- Sklar, CA; Antal, Z; Chemaitilly, W; Cohen, LE; Follin, C; Meacham, LR; Murad, MH (1 August 2018). "Hypothalamic-Pituitary and Growth Disorders in Survivors of Childhood Cancer: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 103 (8): 2761–2784. doi:10.1210/jc.2018-01175. PMID 29982476. S2CID 51601915.
- Montgomery ND, Dunphy CH, Mooberry M, Laramore A, Foster MC, Park SI, Fedoriw YD (2013). "Diagnostic complexities of eosinophilia". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 137 (2): 259–69. doi:10.5858/arpa.2011-0597-RA. PMID 23368869. S2CID 17918640.
- Jessani, Naureen; Jehangir, Waqas; Behman, Daisy; Yousif, Abdalla; Spiler, Ira J. (April 2015). "Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Overlooked Cause of Hyponatremia". Journal of Clinical Medicine Research. 7 (4): 286–288. doi:10.14740/jocmr2041w. PMC 4330026. PMID 25699130.
- Thau, Lauren; Gandhi, Jayashree; Sharma, Sandeep (2022), "Physiology, Cortisol", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30855827, retrieved 2022-11-08
- Videira, Inês Ferreira dos Santos; Moura, Daniel Filipe Lima; Magina, Sofia (2013). "Mechanisms regulating melanogenesis". Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. 88 (1): 76–83. doi:10.1590/S0365-05962013000100009. ISSN 0365-0596. PMC 3699939. PMID 23539007.
- Nieman, Lynnette K.; Chanco Turner, Maria L. (July–August 2006). "Addison's disease". Clinics in Dermatology. 24 (4): 276–280. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2006.04.006. ISSN 0738-081X. PMID 16828409.
- Arai, Keiko; Papadopoulou-Marketou, Nektaria; Chrousos, George P. (2000), Feingold, Kenneth R.; Anawalt, Bradley; Boyce, Alison; Chrousos, George (eds.), "Aldosterone Deficiency and Resistance", Endotext, South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc., PMID 25905305, retrieved 2022-11-08
- Schrier, R. W. (2006). "Body Water Homeostasis: Clinical Disorders of Urinary Dilution and Concentration". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 17 (7): 1820–32. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006030240. PMID 16738014.
- Table 20-7 in: Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson (2007). Robbins Basic Pathology. Philadelphia: Saunders. ISBN 978-1-4160-2973-1. 8th edition.
- Téblick, Arno; Gunst, Jan; Van den Berghe, Greet (2022-06-16). "Critical Illness-induced Corticosteroid Insufficiency: What It Is Not and What It Could Be". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 107 (7): 2057–2064. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgac201. ISSN 1945-7197. PMC 9202732. PMID 35358303.
- Ten, Svetlana; New, Maria; Maclaren, Noel (July 2001). "Addison's Disease 2001". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 86 (7): 2909–2922. doi:10.1210/jcem.86.7.7636. PMID 11443143.
- Winqvist O, Karlsson FA, Kämpe O (June 1992). "21-Hydroxylase, a major autoantigen in idiopathic Addison's disease". The Lancet. 339 (8809): 1559–62. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(92)91829-W. PMID 1351548. S2CID 19666235.
- Husebye, E. S.; Perheentupa, J.; Rautemaa, R.; Kämpe, O. (May 2009). "Clinical manifestations and management of patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I". Journal of Internal Medicine. 265 (5): 514–529. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2009.02090.x. PMID 19382991.
- Thomas A Wilson, MD (2007). "Adrenal Insufficiency". Adrenal Gland Disorders.
- Bornstein SR, Allolio B, Arlt W, Barthel A, Don-Wauchope A, Hammer GD, et al. (2016). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline". J Clin Endocrinol Metab (Practice Guideline. Review). 101 (2): 364–89. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-1710. PMC 4880116. PMID 26760044.
- Thomas A Wilson, MD (1999). "Adrenoleukodystrophy".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Kennedy, Ron. "Addison's Disease". The Doctors' Medical Library. Archived from the original on 2013-04-12. Retrieved 2015-07-29.
- Kaminstein, David S. William C. Shiel Jr. (ed.). "Steroid Drug Withdrawal". MedicineNet. Retrieved 10 April 2013.
- Dernis, Emmanuelle; Ruyssen-Witrand, Adeline; Mouterde, Gaël; Maillefert, Jean-Francis; Tebib, Jacques; Cantagrel, Alain; Claudepierre, Pascal; Fautrel, Bruno; Gaudin, Philippe; Pham, Thao; Schaeverbeke, Thierry; Wendling, Daniel; Saraux, Alain; Loët, Xavier Le (October 2010). "Use of glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis – Pratical [sic] modalities of glucocorticoid therapy: Recommendations for clinical practice based on data from the literature and expert opinion". Joint Bone Spine. 77 (5): 451–457. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2009.12.010. PMID 20471886.
- Stitik, Todd P. (2010). Injection Procedures: Osteoarthritis and Related Conditions. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 47. ISBN 9780387765952.
- Addison Disease~workup at eMedicine
- Betterle C, Presotto F, Furmaniak J (December 2019). "Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Addison's disease in adults". J Endocrinol Invest. 42 (12): 1407–1433. doi:10.1007/s40618-019-01079-6. PMID 31321757.
Further reading
- Bornstein, Stefan R.; Allolio, Bruno; Arlt, Wiebke; Barthel, Andreas; Don-Wauchope, Andrew; Hammer, Gary D.; Husebye, Eystein S.; Merke, Deborah P.; Murad, M. Hassan; Stratakis, Constantine A.; Torpy, David J. (February 2016). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 101 (2): 364–389. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-1710. PMC 4880116. PMID 26760044.