Ia (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ia sign 𒅀, is a combined sign, containing i (cuneiform) ligatured with a (cuneiform); it has the common meaning in the suffix form -ia, for the meaning of "-mine". In the Amarna letters, the letters written to the Pharaoh of Egypt (Mizri/Misri in the letters), the Pharaoh is often referenced as "Lord-mine", or especially: King-Lord-mine: "My King, My Lord". In Akkadian, the form is "Šarru-Bēlu-ia"-(King-Lord-mine), since the spelling in some Amarna letters is sometimes ŠÁR-RI for Šarru, (LUGAL = ŠÁR).
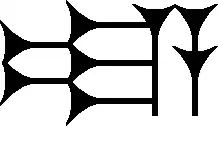
Ia is also used in the Epic of Gilgamesh. It is listed in Parpola's Glossary (Parpola, 1971), for Akkadian language words: meaning "mine", "(to) me", and "me", and one usage for the word "battering ram", iašubů.[1]
Amarna letter usage of "ia"
Besides the usage of Akkadian language words beginning with ia, the common examples of — iāši, "(to) me", iāti, "me", iā'u, "mine",[2] and iānu,[3] "there is not", (often ia-a-nu), "ia" is used in the Introduction Paragraph, to the Pharaoh. The statement is often in the possessive form as a suffix, -ia-(iYa), starting at the very beginning of the letter, and sometimes repeated in lines to follow, or in later paragraphs:
- "To "King-Lord-mine", God-(s)-mine, God-Sun-mine, (added "God-Sun from Sa-me"-(Akkadian "šamů", heaven))... Message Xxxxx (PN, personal name)...."
The suffix form is common throughout all sections of the Amarna letters.
Specific examples of the suffix form can be especially seen in letters from Alashiya, and Tushratta, the king of Mitanni, (Tushratta letters EA 19, EA 26, and EA 28; Alashiya letter EA 35). In those letters, the suffix -ia is used especially with the word 'brother': "Brother-mine", the cuneiform for brother being used as the sumerogram: ŠEŠ (brother Sumerogram), since šeš (cuneiform) in the Epic of Gilgamesh is also used for: sis, šes, šeš, šiš, and "ŠEŠ (brother Sumerogram)".[4]
References
- Parpola, 1971. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Glossary, pp. 119-145, ia words, p. 127, iašubů, p. 127.
- Parpola, 1971. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Glossary, pp. 119-145, ia words, p. 127.
- Rainey, 1970. El Amarna Tablets, 359-379, Glossary:Vocabulary, iānu, pp. 55-87, p. 65.
- Parpola, 1971. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Sign List, pp. 155-165, no. 331-(sign for šeš), p. 156.
- Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. The Amarna Letters. Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ISBN 0-8018-6715-0)
- Parpola, 1971. The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh, Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages.
- Rainey, 1970. El Amarna Tablets, 359-379, Anson F. Rainey, (AOAT 8, Alter Orient Altes Testament 8, Kevelaer and Neukirchen -Vluyen), 1970, 107 pages.
|
|


