Inferior tibiofibular joint
The inferior tibiofibular joint, also known as the distal tibiofibular joint (tibiofibular syndesmosis), is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the distal end of the fibula, and a rough concave surface on the lateral side of the tibia.
| Inferior tibiofibular joint | |
|---|---|
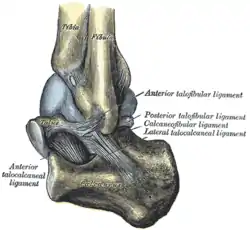 Capsule of left talocrural articulation (distended). Lateral aspect. | |
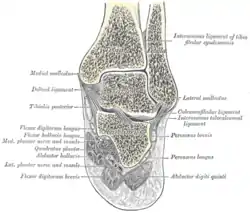 Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | syndesmosis tibiofibularis |
| TA98 | A03.6.05.001 |
| TA2 | 1868 |
| FMA | 10465 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Below, to the extent of about 4 mm, these surfaces are smooth and covered with cartilage, which is continuous with that of the ankle joint.
The ligaments are:
- Anterior ligament of the lateral malleolus
- Posterior ligament of the lateral malleolus
- Interosseous membrane of leg
The inferior transverse ligament of the tibiofibular syndesmosis is included in older versions of Gray's Anatomy, but not in Terminologia Anatomica.[1] However, it still appears in some anatomy textbooks.[2]
It should not be confused with the superior tibiofibular joint, which is the only synovial tibiofibular joint, and is sometimes simply called the "tibiofibular articulation".
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 348 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 348 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (1998). Terminologia anatomica: international anatomical terminology. Thieme. pp. 30–. ISBN 978-3-13-114361-7. Retrieved 29 October 2010.
- A. M. R. Agur; Arthur F. Dalley (2009). Grant's atlas of anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 442–. ISBN 978-0-7817-7055-2. Retrieved 29 October 2010.