Mathematics in the medieval Islamic world
Mathematics during the Golden Age of Islam, especially during the 9th and 10th centuries, was built on Greek mathematics (Euclid, Archimedes, Apollonius) and Indian mathematics (Aryabhata, Brahmagupta). Important progress was made, such as full development of the decimal place-value system to include decimal fractions, the first systematised study of algebra, and advances in geometry and trigonometry.[1]
Arabic works played an important role in the transmission of mathematics to Europe during the 10th—12th centuries.[2]
Concepts

Algebra
The study of algebra, the name of which is derived from the Arabic word meaning completion or "reunion of broken parts",[3] flourished during the Islamic golden age. Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi, a Persian scholar in the House of Wisdom in Baghdad was the founder of algebra, is along with the Greek mathematician Diophantus, known as the father of algebra. In his book The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, Al-Khwarizmi deals with ways to solve for the positive roots of first and second-degree (linear and quadratic) polynomial equations. He introduces the method of reduction, and unlike Diophantus, also gives general solutions for the equations he deals with.[4][5][6]
Al-Khwarizmi's algebra was rhetorical, which means that the equations were written out in full sentences. This was unlike the algebraic work of Diophantus, which was syncopated, meaning that some symbolism is used. The transition to symbolic algebra, where only symbols are used, can be seen in the work of Ibn al-Banna' al-Marrakushi and Abū al-Ḥasan ibn ʿAlī al-Qalaṣādī.[7][6]
On the work done by Al-Khwarizmi, J. J. O'Connor and Edmund F. Robertson said:[8]
"Perhaps one of the most significant advances made by Arabic mathematics began at this time with the work of al-Khwarizmi, namely the beginnings of algebra. It is important to understand just how significant this new idea was. It was a revolutionary move away from the Greek concept of mathematics which was essentially geometry. Algebra was a unifying theory which allowed rational numbers, irrational numbers, geometrical magnitudes, etc., to all be treated as "algebraic objects". It gave mathematics a whole new development path so much broader in concept to that which had existed before, and provided a vehicle for the future development of the subject. Another important aspect of the introduction of algebraic ideas was that it allowed mathematics to be applied to itself in a way which had not happened before."
Several other mathematicians during this time period expanded on the algebra of Al-Khwarizmi. Abu Kamil Shuja' wrote a book of algebra accompanied with geometrical illustrations and proofs. He also enumerated all the possible solutions to some of his problems. Abu al-Jud, Omar Khayyam, along with Sharaf al-Dīn al-Tūsī, found several solutions of the cubic equation. Omar Khayyam found the general geometric solution of a cubic equation.
Cubic equations
Omar Khayyam (c. 1038/48 in Iran – 1123/24)[9] wrote the Treatise on Demonstration of Problems of Algebra containing the systematic solution of cubic or third-order equations, going beyond the Algebra of al-Khwārizmī.[10] Khayyám obtained the solutions of these equations by finding the intersection points of two conic sections. This method had been used by the Greeks,[11] but they did not generalize the method to cover all equations with positive roots.[10]
Sharaf al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī (? in Tus, Iran – 1213/4) developed a novel approach to the investigation of cubic equations—an approach which entailed finding the point at which a cubic polynomial obtains its maximum value. For example, to solve the equation , with a and b positive, he would note that the maximum point of the curve occurs at , and that the equation would have no solutions, one solution or two solutions, depending on whether the height of the curve at that point was less than, equal to, or greater than a. His surviving works give no indication of how he discovered his formulae for the maxima of these curves. Various conjectures have been proposed to account for his discovery of them.[12]
| Part of a series on |
| Islamic studies |
|---|
| Jurisprudence |
| Science in medieval times |
|
|
| Arts |
|
|
| Other topics |
| Islamization of knowledge |
Induction
The earliest implicit traces of mathematical induction can be found in Euclid's proof that the number of primes is infinite (c. 300 BCE). The first explicit formulation of the principle of induction was given by Pascal in his Traité du triangle arithmétique (1665).
In between, implicit proof by induction for arithmetic sequences was introduced by al-Karaji (c. 1000) and continued by al-Samaw'al, who used it for special cases of the binomial theorem and properties of Pascal's triangle.
Irrational numbers
The Greeks had discovered irrational numbers, but were not happy with them and only able to cope by drawing a distinction between magnitude and number. In the Greek view, magnitudes varied continuously and could be used for entities such as line segments, whereas numbers were discrete. Hence, irrationals could only be handled geometrically; and indeed Greek mathematics was mainly geometrical. Islamic mathematicians including Abū Kāmil Shujāʿ ibn Aslam and Ibn Tahir al-Baghdadi slowly removed the distinction between magnitude and number, allowing irrational quantities to appear as coefficients in equations and to be solutions of algebraic equations.[13][14] They worked freely with irrationals as mathematical objects, but they did not examine closely their nature.[15]
In the twelfth century, Latin translations of Al-Khwarizmi's Arithmetic on the Indian numerals introduced the decimal positional number system to the Western world.[16] His Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing presented the first systematic solution of linear and quadratic equations. In Renaissance Europe, he was considered the original inventor of algebra, although it is now known that his work is based on older Indian or Greek sources.[17][18] He revised Ptolemy's Geography and wrote on astronomy and astrology. However, C.A. Nallino suggests that al-Khwarizmi's original work was not based on Ptolemy but on a derivative world map,[19] presumably in Syriac or Arabic.
Spherical trigonometry
The spherical law of sines was discovered in the 10th century: it has been attributed variously to Abu-Mahmud Khojandi, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi and Abu Nasr Mansur, with Abu al-Wafa' Buzjani as a contributor.[13] Ibn Muʿādh al-Jayyānī's The book of unknown arcs of a sphere in the 11th century introduced the general law of sines.[20] The plane law of sines was described in the 13th century by Nasīr al-Dīn al-Tūsī. In his On the Sector Figure, he stated the law of sines for plane and spherical triangles and provided proofs for this law.[21]
Negative numbers
In the 9th century, Islamic mathematicians were familiar with negative numbers from the works of Indian mathematicians, but the recognition and use of negative numbers during this period remained timid.[22] Al-Khwarizmi did not use negative numbers or negative coefficients.[22] But within fifty years, Abu Kamil illustrated the rules of signs for expanding the multiplication .[23] Al-Karaji wrote in his book al-Fakhrī that "negative quantities must be counted as terms".[22] In the 10th century, Abū al-Wafā' al-Būzjānī considered debts as negative numbers in A Book on What Is Necessary from the Science of Arithmetic for Scribes and Businessmen.[23]
By the 12th century, al-Karaji's successors were to state the general rules of signs and use them to solve polynomial divisions.[22] As al-Samaw'al writes:
the product of a negative number — al-nāqiṣ — by a positive number — al-zāʾid — is negative, and by a negative number is positive. If we subtract a negative number from a higher negative number, the remainder is their negative difference. The difference remains positive if we subtract a negative number from a lower negative number. If we subtract a negative number from a positive number, the remainder is their positive sum. If we subtract a positive number from an empty power (martaba khāliyya), the remainder is the same negative, and if we subtract a negative number from an empty power, the remainder is the same positive number.[22]
Double false position
Between the 9th and 10th centuries, the Egyptian mathematician Abu Kamil wrote a now-lost treatise on the use of double false position, known as the Book of the Two Errors (Kitāb al-khaṭāʾayn). The oldest surviving writing on double false position from the Middle East is that of Qusta ibn Luqa (10th century), an Arab mathematician from Baalbek, Lebanon. He justified the technique by a formal, Euclidean-style geometric proof. Within the tradition of Golden Age Muslim mathematics, double false position was known as hisāb al-khaṭāʾayn ("reckoning by two errors"). It was used for centuries to solve practical problems such as commercial and juridical questions (estate partitions according to rules of Quranic inheritance), as well as purely recreational problems. The algorithm was often memorized with the aid of mnemonics, such as a verse attributed to Ibn al-Yasamin and balance-scale diagrams explained by al-Hassar and Ibn al-Banna, who were each mathematicians of Moroccan origin.[24]
Other major figures
Sally P. Ragep, a historian of science in Islam, estimated in 2019 that "tens of thousands" of Arabic manuscripts in mathematical sciences and philosophy remain unread, which give studies which "reflect individual biases and a limited focus on a relatively few texts and scholars".[25]
- 'Abd al-Hamīd ibn Turk (fl. 830) (quadratics)
- Thabit ibn Qurra (826–901)
- Sind ibn Ali (d. after 864)
- Ismail al-Jazari (1136–1206)
- Abū Sahl al-Qūhī (c. 940–1000) (centres of gravity)
- Abu'l-Hasan al-Uqlidisi (952–953) (arithmetic)
- 'Abd al-'Aziz al-Qabisi (d. 967)
- Ibn al-Haytham (c. 965–1040)
- Abū al-Rayḥān al-Bīrūnī (973–1048) (trigonometry)
- Ibn Maḍāʾ (c. 1116–1196)
- Jamshīd al-Kāshī (c. 1380–1429) (decimals and estimation of the circle constant)
Gallery
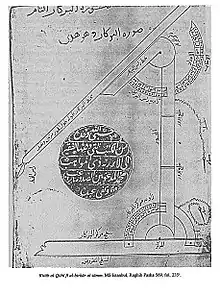 Engraving of Abū Sahl al-Qūhī's perfect compass to draw conic sections.
Engraving of Abū Sahl al-Qūhī's perfect compass to draw conic sections.
See also
References
- Katz (1993): "A complete history of mathematics of medieval Islam cannot yet be written, since so many of these Arabic manuscripts lie unstudied... Still, the general outline... is known. In particular, Islamic mathematicians fully developed the decimal place-value number system to include decimal fractions, systematised the study of algebra and began to consider the relationship between algebra and geometry, studied and made advances on the major Greek geometrical treatises of Euclid, Archimedes, and Apollonius, and made significant improvements in plane and spherical geometry."
^ Smith (1958), Vol. 1, Chapter VII.4: "In a general way it may be said that the Golden Age of Arabian mathematics was confined largely to the 9th and 10th centuries; that the world owes a great debt to Arab scholars for preserving and transmitting to posterity the classics of Greek mathematics; and that their work was chiefly that of transmission, although they developed considerable originality in algebra and showed some genius in their work in trigonometry." - Lumpkin, Beatrice; Zitler, Siham (1992). "Cairo: Science Academy of the Middle Ages". In Van Sertima, Ivan (ed.). Golden age of the Moor, Volume 11. Transaction Publishers. p. 394. ISBN 1-56000-581-5. "The Islamic mathematicians exercised a prolific influence on the development of science in Europe, enriched as much by their own discoveries as those they had inherited by the Greeks, the Indians, the Syrians, the Babylonians, etc."
- "algebra". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- Boyer 1991, p. 228.
- Swetz, Frank J. (1993). Learning Activities from the History of Mathematics. Walch Publishing. p. 26. ISBN 978-0-8251-2264-4.
- Gullberg, Jan (1997). Mathematics: From the Birth of Numbers. W. W. Norton. p. 298. ISBN 0-393-04002-X.
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "al-Marrakushi ibn Al-Banna", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Arabic mathematics: forgotten brilliance?", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- Struik 1987, p. 96.
- Boyer 1991, pp. 241–242.
- Struik 1987, p. 97.
- Berggren, J. Lennart; Al-Tūsī, Sharaf Al-Dīn; Rashed, Roshdi (1990). "Innovation and Tradition in Sharaf al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī's al-Muʿādalāt". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 110 (2): 304–309. doi:10.2307/604533. JSTOR 604533.
- Sesiano, Jacques (2000). Helaine, Selin; Ubiratan, D'Ambrosio (eds.). Islamic mathematics. pp. 137–157. ISBN 1-4020-0260-2.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Abu Mansur ibn Tahir Al-Baghdadi", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- Allen, G. Donald (n.d.). "The History of Infinity" (PDF). Texas A&M University. Retrieved 7 September 2016.
- Struik 1987, p. 93
- Rosen 1831, p. v–vi.
- Toomer, Gerald (1990). "Al-Khwārizmī, Abu Ja'far Muḥammad ibn Mūsā". In Gillispie, Charles Coulston (ed.). Dictionary of Scientific Biography. Vol. 7. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. ISBN 0-684-16962-2 – via Encyclopedia.com.
- Nallino 1939.
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Abu Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Muadh Al-Jayyani", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- Berggren 2007, p. 518.
- Rashed, R. (1994-06-30). The Development of Arabic Mathematics: Between Arithmetic and Algebra. Springer. pp. 36–37. ISBN 9780792325659.
- Mat Rofa Bin Ismail (2008), "Algebra in Islamic Mathematics", in Helaine Selin (ed.), Encyclopaedia of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine in Non-Western Cultures, vol. 1 (2nd ed.), Springer, p. 115, ISBN 9781402045592
- Schwartz, R. K. (2004). Issues in the Origin and Development of Hisab al-Khata'ayn (Calculation by Double False Position) (PDF). Eighth North African Meeting on the History of Arab Mathematics. Radès, Tunisia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-05-16. Retrieved 2012-06-08. "Issues in the Origin and Development of Hisab al-Khata'ayn (Calculation by Double False Position)". Archived from the original (.doc) on 2011-09-15.
- "Science Teaching in Pre-Modern Societies", in Film Screening and Panel Discussion, McGill University, 15 January 2019.
Sources
- Berggren, J. Lennart (2007). "Mathematics in Medieval Islam". In Victor J. Katz (ed.). The Mathematics of Egypt, Mesopotamia, China, India, and Islam: A Sourcebook (2nd ed.). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-11485-9.
- Boyer, Carl B. (1991), "Greek Trigonometry and Mensuration, and The Arabic Hegemony", A History of Mathematics (2nd ed.), New York City: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-54397-7
- Katz, Victor J. (1993). A History of Mathematics: An Introduction. HarperCollins college publishers. ISBN 0-673-38039-4.
- Nallino, C.A. (1939), "Al-Ḥuwārismī e il suo rifacimento della Geografia di Tolomeo", Raccolta di scritti editi e inediti (in Italian), vol. V, Rome: Istituto per l'Oriente, pp. 458–532
- Rosen, Fredrick (1831). The Algebra of Mohammed Ben Musa. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 1-4179-4914-7.
- Smith, David E. (1958). History of Mathematics. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-20429-4.
- Struik, Dirk J. (1987), A Concise History of Mathematics (4th rev. ed.), Dover Publications, ISBN 0-486-60255-9
Further reading
- Books on Islamic mathematics
- Berggren, J. Lennart (1986). Episodes in the Mathematics of Medieval Islam. New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 0-387-96318-9.
- Review: Toomer, Gerald J.; Berggren, J. L. (1988). "Episodes in the Mathematics of Medieval Islam". American Mathematical Monthly. Mathematical Association of America. 95 (6): 567. doi:10.2307/2322777. JSTOR 2322777.
- Review: Hogendijk, Jan P.; Berggren, J. L. (1989). "Episodes in the Mathematics of Medieval Islam by J. Lennart Berggren". Journal of the American Oriental Society. American Oriental Society. 109 (4): 697–698. doi:10.2307/604119. JSTOR 604119.
- Daffa', Ali Abdullah al- (1977). The Muslim contribution to mathematics. London: Croom Helm. ISBN 0-85664-464-1.
- Ronan, Colin A. (1983). The Cambridge Illustrated History of the World's Science. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-25844-8.
- Rashed, Roshdi (2001). The Development of Arabic Mathematics: Between Arithmetic and Algebra. Translated by A. F. W. Armstrong. Springer. ISBN 0-7923-2565-6.
- Youschkevitch, Adolf P.; Rozenfeld, Boris A. (1960). Die Mathematik der Länder des Ostens im Mittelalter. Berlin.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) Sowjetische Beiträge zur Geschichte der Naturwissenschaft pp. 62–160. - Youschkevitch, Adolf P. (1976). Les mathématiques arabes: VIIIe–XVe siècles. translated by M. Cazenave and K. Jaouiche. Paris: Vrin. ISBN 978-2-7116-0734-1.
- Book chapters on Islamic mathematics
- Lindberg, D.C., and M. H. Shank, eds. The Cambridge History of Science. Volume 2: Medieval Science (Cambridge UP, 2013), chapters 2 and 3 mathematics in Islam.
- Cooke, Roger (1997). "Islamic Mathematics". The History of Mathematics: A Brief Course. Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 0-471-18082-3.
- Books on Islamic science
- Daffa, Ali Abdullah al-; Stroyls, J.J. (1984). Studies in the exact sciences in medieval Islam. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-90320-5.
- Kennedy, E. S. (1984). Studies in the Islamic Exact Sciences. Syracuse Univ Press. ISBN 0-8156-6067-7.
- Books on the history of mathematics
- Joseph, George Gheverghese (2000). The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-00659-8. (Reviewed: Katz, Victor J.; Joseph, George Gheverghese (1992). "The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics by George Gheverghese Joseph". The College Mathematics Journal. Mathematical Association of America. 23 (1): 82–84. doi:10.2307/2686206. JSTOR 2686206.)
- Youschkevitch, Adolf P. (1964). Gesichte der Mathematik im Mittelalter. Leipzig: BG Teubner Verlagsgesellschaft.
- Journal articles on Islamic mathematics
- Høyrup, Jens. “The Formation of «Islamic Mathematics»: Sources and Conditions”. Filosofi og Videnskabsteori på Roskilde Universitetscenter. 3. Række: Preprints og Reprints 1987 Nr. 1.
- Bibliographies and biographies
- Brockelmann, Carl. Geschichte der Arabischen Litteratur. 1.–2. Band, 1.–3. Supplementband. Berlin: Emil Fischer, 1898, 1902; Leiden: Brill, 1937, 1938, 1942.
- Sánchez Pérez, José A. (1921). Biografías de Matemáticos Árabes que florecieron en España. Madrid: Estanislao Maestre.
- Sezgin, Fuat (1997). Geschichte Des Arabischen Schrifttums (in German). Brill Academic Publishers. ISBN 90-04-02007-1.
- Suter, Heinrich (1900). Die Mathematiker und Astronomen der Araber und ihre Werke. Abhandlungen zur Geschichte der Mathematischen Wissenschaften Mit Einschluss Ihrer Anwendungen, X Heft. Leipzig.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
- Television documentaries
- Marcus du Sautoy (presenter) (2008). "The Genius of the East". The Story of Maths. BBC.
- Jim Al-Khalili (presenter) (2010). Science and Islam. BBC.
External links
- Hogendijk, Jan P. (January 1999). "Bibliography of Mathematics in Medieval Islamic Civilization".
- O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F. (1999), "Arabic mathematics: forgotten brilliance?", MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive, University of St Andrews
- Richard Covington, Rediscovering Arabic Science, 2007, Saudi Aramco World
- List of Inventions and Discoveries in Mathematics During the Islamic Golden Age
