Isle of May
The Isle of May is located in the north of the outer Firth of Forth, approximately 8 km (5.0 mi) off the coast of mainland Scotland. It is about 1.5 kilometres (0.9 miles) long and 0.5 kilometres (0.3 miles) wide. The island is owned and managed by NatureScot as a national nature reserve. There are now no permanent residents, but the island was the site of St Adrian's Priory during the Middle Ages.
| Scottish Gaelic name | Eilean Mhàigh |
|---|---|
| Old Norse name | Máeyar (cf. plural) |
| Meaning of name | Uncertain |
| Location | |
 Isle of May Isle of May shown within Fife | |
| OS grid reference | NT656992 |
| Coordinates | 56.18°N 2.55°W |
| Physical geography | |
| Island group | Islands of the Forth |
| Area | 57 hectares (140 acres) |
| Area rank | 210= [1] |
| Highest elevation | 50 metres (160 ft) |
| Administration | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Country | Scotland |
| Council area | Fife |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 0[2] |
| References | [3][4] [5] |
Most visitors to the island are daytrippers taking the ferry from Anstruther in Fife, although up to six visitors can stay at the bird observatory,[6] usually for a week at a time. The only way to get there is by ferry; the journey takes 45 minutes from the small harbours of Anstruther and Crail, and also from North Berwick. As of 2015, around 11,000 people visit the island each year.[7]
The island is closed to visitors from 1 October until Easter to prevent disturbance to the large number of seal pups. The Scottish Seabird Centre at North Berwick has two live cameras on the island, which can be remotely controlled by visitors, to allow close viewing of the seabird cities, including puffins, guillemots, razorbills, shags, cormorants and terns and the fluffy grey seal pups in winter, without disturbance. The Scottish Seabird Centre also runs boat trips to the Isle of May. As well as its natural heritage, the Isle of May also has a rich cultural heritage, including St Adrian's Chapel, which is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. Furthermore, the Isle of May Lighthouse; Keepers' Houses; North and South Horns; the Low and Light Cottages; the Coal Store and Stable Block; and the former Lighthouse Beacon have all been included in the list of Buildings of Special Architectural or Historic Interest.
Geography and geology
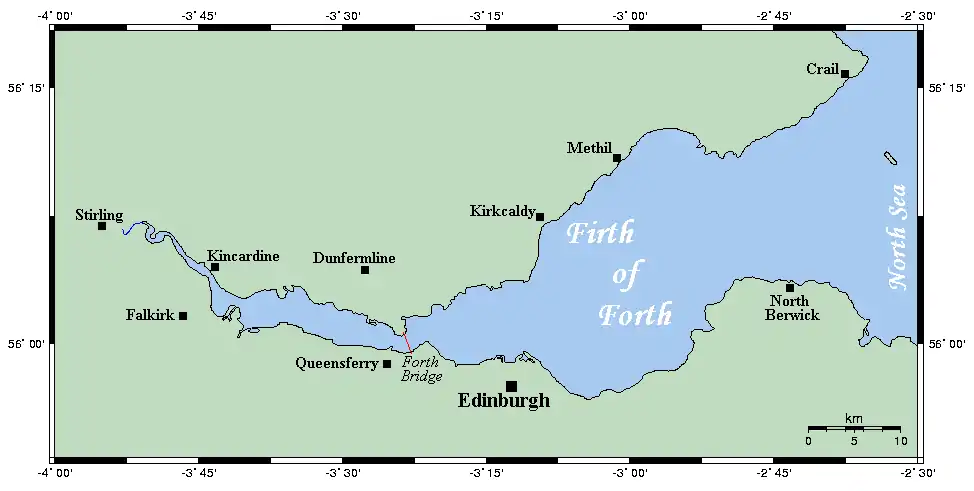
The island is around 1.5 km long and 0.5 km wide, with an area of about 57 ha.[8] The western coast of the island consists of cliffs that are up to 45 metres in height. The land tilts from here down to the eastern shore, which is mostly rocky with three small beaches: Pilgrims Haven, Kirkhaven and Silver Sands. There is a peninsula in the north, known as Rona, which is almost a separate island, being cut off from the main island at high tide.[9]
Geologically, the island is composed of a "fine grained basalt of a dark-grey colour with tinges of green and greenstone".[3] It is crossed by a series of faults that run west–east across the island, and which have been eroded to form steep geos (gullies).[9]
Wildlife
Although only around 57 hectares in size, over 285 bird species have been recorded on the island. The island is free from predators such as foxes and rats, and thus provides a safe breeding site compared to the mainland. At the height of the breeding season the Isle of May can host around 200,000 seabirds, including puffins, black-legged kittiwakes, razorbills, guillemots, shags, fulmars, oystercatchers, eider ducks, and various species of tern and gull. These numbers can fluctuate considerably from year to year, depending on weather and fish stocks.[10][11][12]
Extensive dietary and demographic monitoring of these seabirds is undertaken by the Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, as part of the Isle of May Long Term Study. Recent evidence has shown that at a community-scale, diet composition at this colony has changed from predominantly lesser sandeel Ammodytes marinus in the 1980s, to a range of alternative prey in recent years.[13] This change is believed to relate to warming ocean conditions around the Isle of May, and linked changes in prey availability.[14]
There are also winter visitors, and the island hosts internationally important numbers of turnstones and purple sandpipers. Various species of pipits, thrushes and wagtails are also commonly seen. The Isle of May also sees occasional visits from migratory birds that do not normally visit Britain, but get blown off route from Scandinavia by easterly winds; recent examples include black-winged stilt, lanceolated warbler, White's thrush, bridled tern and calandra lark.[15][16]
Both harbour seals and grey seals can be seen on the island all year round, and whales are occasionally sighted in the summer. The Isle of May is the second largest east coast breeding colony of grey seals in Scotland, and around 3,000 pups are born here each year. Minke whale and harbour porpoise are often seen in the seas surrounding the island.[11][16]
The earliest reference to rabbits on the Isle of May dates from 1329, and they are thought to have been introduced here by the island's monks. The island also has its own unique race of house mice.[17][16]
History

The island's name is of disputed etymology, but is possibly of Old Norse origin, meaning "island of seagulls". Alternatively, it is from the Gaelic Magh meaning a plain – most of the other islands in the Forth, such as Inchmickery, Inchcolm and Craigleith have Gaelic etymologies. There are certainly names on the island from both languages, including "Tarbet" (tairbeart, an isthmus), "St Colme's Hole" (Colm Cille) and "Ardchattan" from Gaelic, and "Kirkhaven" which may refer a Norse original "Kirkshavn". It is also thought that the name may refer to the use of the island by the Maeatae as a royal burial site.
The island was the site of one of the earliest Christian churches in Scotland, founded in the 9th century and built into an unusual mass-burial mound that probably dates from prehistoric times. Although radiocarbon dating of bones reveal them to date from the 7th century to the 10th century, remains of Bronze Age funeral urns suggest that the mound may be older.
The current chapel on the site is dedicated to Saint Adrian of May, who was killed on the island by Danish invaders in 875.
The thirteenth-century Orkneyinga saga records another Viking raid, by Sweyn Asleifsson, and Margad Grimsson, after they had been expelled from Orkney by Earl Rögnvald, when they went raiding on the eastern seaboard of Scotland:
They sailed south off Scotland until they came to Máeyar (the Isle of May). There was a monastery, the head of which was an abbot, by name, Baldwin. Swein and his men were detained there seven nights by stress of bad weather. They said they had been sent by Earl Rögnvald to the King of Scots. The monks suspected their tale, and thinking they were pirates, sent to the mainland for men. When Swein and his comrades became aware of this, they went hastily aboard their ship, after having plundered much treasure from the monastery. They went along Myrkvifjörð (the Firth of Forth), and found David, the King of Scots, in Edinburgh. He received Swein well, and requested him to stay with him. He told the King explicitly the reason of his visit, how matters had gone between him and Earl Rögnvald before they parted, and also that they had plundered in Máeyar. Swein and Margad stayed for a while with the King of Scots, and were well treated. King David sent men to those who had been robbed by Swein, and told them to estimate their loss themselves, and then of his own money, he made good to everyone his loss.
— Chapter LXXVII[5]
.jpg.webp)
However, no abbot of the name Baldwin was recorded. There may be some conflation with St Baldred, who is connected with the nearby Bass Rock, and St Baldred's Boat off Dunbar. Another possible mention of the island is under the name "Mosey". This may be a conflation with Mousa (properly Mosey), since it comes close to a mention of "Moseyjarborg" (the Broch of Mousa), or a mistranscription of "Maey" in the old script. It is also suspiciously similar to the previous extract.
- "They put into Mosey, and Swein sent men to Eidinaborg (Edinburgh), to tell the King of Scots of their plunder."[5]
The original church was expanded during the 12th century by David I of Scotland, under the aegis of Reading Abbey which had been founded by his brother-in-law, Henry I of England and thus a Benedictine community was established. The monks agreed to maintain nine priests on the island to pray for the souls of the Kings Of Scots.
The island, with the supposed relics of Ethernan who died there in around 669, was a popular destination for pilgrims during the later Middle Ages. Evidence that it was already an important place for pilgrimage in the 12th century include the remains of a ten-seater communal lavatory, much larger than necessary for an abbey with only nine or ten monks. Bishop Fraser of St Andrews bought the priory from Reading Abbey in 1288, although there was an attempt to overturn this and the dispute rumbled on for about fifty years. The priory was finally transferred to the Canons of St Andrews in 1318, and was relocated at Pittenweem (see Pittenweem Priory).
Royal pilgrims
The island was one of Scotland's most important pilgrimage centres. Mary of Guelders visited the island and the shrine of St Adrian in June 1449, according to Mathieu d'Escouchy.[18][19] James IV came on 10 May 1506, wearing new yellow breeches and again in September, sailing in the Lion. He gave a reward to a hermit on the island.[20] He returned in a row boat in June 1508 to shoot at sea birds with a culverin.[21] On 24 August 1539 Mary of Guise and her husband James V made a pilgrimage to the Isle of May.[22] They took three ships, the Unicorn, the Little Unicorn, and the Mary Willoughby.[22] It was believed that a visit to the shrine could help a woman become pregnant.[23]
The Prior of Pittenweem passed the island to Patrick Learmonth of Dairsie, Provost of St Andrews in 1549. He sold it to Balfour of Monquhany in 1551, who in turn passed it on to Forret of Fyngask seven years later, who sold it to Allan Lamont, who in turn sold it to John Cunningham (or Cunynghame) of Barnes (in Fife) who was responsible for the first lighthouse beacon on the island.
In the sixteenth century the crews of ships suspected of plague were ordered to sail to the island and remain until they were judged healthy.[24]
The May Isle has long been a focal point of the nearby fishing communities. Annually, the wives and children of the small village of Cellardyke were taken to the May Isle for a picnic by the fishermen. On 1 July 1837 one such trip turned to tragedy when one of the small row boats used to transport them to Kirkhaven (harbour) overturned leading to the loss of 13 lives.
The so-called "Battle" of May Island took place nearby on the night of 31 January 1918. A sequence of accidental collisions between Royal Navy warships occurred over little more than an hour which saw two submarines sunk with heavy loss of life, another four damaged along with a light cruiser.
The Navy maintained a control centre on the island for indicator loops and six ASDIC units laid on the seabed to detect U-boats and enemy surface vessels trying to enter the Forth from shortly before the Second World War until 1946.
Since 1956 the isle has been dedicated as a National Nature Reserve[25] and managed by the Nature Conservancy Council, now NatureScot, although until 1989 it was actually owned by the Northern Lighthouse Board.
Lighthouses
 Robert Stevenson's lighthouse on the Isle of May | |
| Location | Isle of May, Fife, Anstruther Wester, United Kingdom |
|---|---|
| OS grid | NT6550099364 |
| Coordinates | 56°11′08″N 2°33′27″W |
| Tower | |
| Constructed | 1816 |
| Designed by | Robert Stevenson |
| Construction | stone |
| Automated | 31 March 1989 |
| Height | 24 m (79 ft) |
| Shape | quadrangular tower with balcony and lantern rising from a 2-storey keeper’s house[26][27] |
| Markings | unpainted (tower), black (lantern) |
| Power source | electricity |
| Operator | Northern Lighthouse Board |
| Heritage | category B listed building |
| Light | |
| Focal height | 73 m (240 ft) |
| Range | 22 nmi (41 km; 25 mi) |
| Characteristic | Fl(2) W 15s |
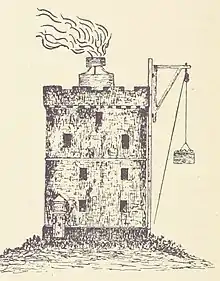
A coal-fired beacon was established in 1635[28] (or 1636[29]) by James Maxwell of Innerwick, and John and Alexander Cunningham, who charged shipping a tonnage-based fee. This was originally 2 Scottish shillings per ton for Scottish ships (equivalent to two pence sterling) and twice this amount for non-local shipping per voyage, but was reduced to 1 shilling and sixpence, and three shillings respectively in 1639 with some shipping entirely exempt during the summer.
The beacon, the first permanently manned one in Scotland and considered at the time to be one of the best in existence, used around 400 tons of coal per year, requiring three men to look after it.
One of the three lightkeepers, George Anderson, and his wife Elisabeth, along with five of their six children were suffocated by fumes in January 1791. Their eleven-month-old daughter Lucy was discovered alive three days later. Ash and clinker had piled up beside the 12-metre-high (39 ft) beacon tower over the previous ten years and had reached the window of keepers' room, and was set smouldering by coals falling from the beacon.
The light was sometimes hard to recognise, for example HMS Nymphe a 36-gun fifth rate captured from the French in 1780 and HMS Pallas were wrecked near Dunbar on the night of 19 December 1810 because their navigators had mistaken a lime kiln on the mainland coast for the beacon.
The Northern Lighthouse Board purchased the island in 1814 from the Duke and Duchess of Portland for 60,000 pounds, by which time the beacon was the last remaining private lighthouse in Scotland. A proper lighthouse was built on the island in 1816 by Robert Stevenson. and is an ornate gothic tower on a castellated stone building designed to resemble a castle, 24 metres (79 ft) high and with accommodation for three light keepers and their families, along with additional space for visiting officials. The new lighthouse started operating on 1 September 1816, and is now a listed building.
It was upgraded in September 1836, when a new light and refractor lens was fitted, and further extensive work took place in 1885–1886. Additional dwellings, boiler and engine houses, a workshop and a coal store were built 250 metres (270 yd) from the lighthouse in a small valley containing a fresh water loch. The engine house was fitted with two steam-powered generators, at 4.5 tons each the largest ever constructed at that time, and with a total output of 8.8 kilowatts. These powered an arc lamp in the lighthouse, with a three-wick paraffin lamp kept lit but turned down in case the electric lamp failed. The new light was first used on 1 December 1886 and produced four flashes every 30 seconds.
The high cost of the coal, around 150 tons per year, along with improvements in oil lights led to the replacement with an incandescent mantle in 1924.
Another smaller lighthouse, the Low Light was constructed a few hundred yards from the main light in 1843 to provide (with the main lighthouse) a pair of lights which would become aligned to help ships avoid the North Carr Rock 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) to the north of the island off Fife Ness. It was first used in April 1844, but is no longer used, having been made redundant by the establishment of the North Carr Lightship in 1887 and the building is now used for bird watching.
In 1930 two keepers rescued four crew members of the wrecked commercial trawler George Aunger by swimming out to it. The lighthouse became a "rock" station on 9 August 1972, meaning that the keeper's families were no longer accommodated at the lighthouse but on the mainland, and a fully automatic one on 31 March 1989 shortly before ownership of the island passed to the Nature Conservancy Council. It is now monitored and controlled via a UHF radio link to Fife Ness Lighthouse and then by landline to the Northern Lighthouse Board headquarters in Edinburgh.
The modern light produces two white flashes every 15 seconds, and has a range of 41 kilometres (22 nmi) in good visibility. The fog signal, from two designated buildings at each end of the island, were powered by compressed air, generated from the island's power plant in the centre of the island, and delivered by 150-millimetre (5.9 in) cast-iron pipes laid on the ground to top up a series of air tanks located adjacent to both North and South buildings. The North horn provided a single blast of 7 seconds duration every 21⁄4 minutes and the South horn provided four 21⁄2 second blasts of the same pitch every 21⁄4 minutes. The North and South horns did not blast together, being approximately 671⁄2 seconds apart. This facility was discontinued in 1989. The May lighthouse was mentioned in John Buchan's 1934 novel The Free Fishers – “Far out the brazier on the May was burning with a steady glow, like some low-swung planet shaming with its ardour the cold stars.”
Conservation designations
| Isle of May National Nature Reserve | |
|---|---|
| Location | Firth of Forth, Scotland |
| Area | 56.6 ha (140 acres)[31] |
| Established | 1956[32] |
| Governing body | NatureScot |
| Isle of May National Nature Reserve | |
The Isle of May was designated a national nature reserve in 1956 by the Nature Conservancy (NC). The NC and its successor bodies, the Nature Conservancy Council (NCC), Scottish Natural Heritage and NatureScot, have managed the island since this date, although it remained under the ownership of the Northern Lighthouse Board until 1989. It is now owned by NatureScot.[32]
As well as being an NNR, the Isle of May holds multiple other national and international conservation designations as an important site for wildlife:
- Forth Islands Special Protection Area (SPA)[33]
- Isle of May Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI)[34]
- Isle of May Special Area of Conservation (SAC)[35]
- Classified as a Category II protected area by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.[30]
References
- Area and population ranks: there are c. 300 islands over 20 ha in extent and 93 permanently inhabited islands were listed in the 2011 census.
- National Records of Scotland (15 August 2013). "Appendix 2: Population and households on Scotland's Inhabited Islands" (PDF). Statistical Bulletin: 2011 Census: First Results on Population and Household Estimates for Scotland Release 1C (Part Two) (PDF) (Report). SG/2013/126. Retrieved 14 August 2020.
- Haswell-Smith, Hamish (2004). The Scottish Islands. Edinburgh: Canongate. ISBN 978-1-84195-454-7.
- Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 59 St Andrews (Kirkcaldy & Glenrothes) (Map). Ordnance Survey. 2010. ISBN 9780319229828.
- Anderson, Joseph (Ed.) (1893) Orkneyinga Saga. Translated by Jón A. Hjaltalin & Gilbert Goudie. Edinburgh. James Thin and Mercat Press (1990 reprint). ISBN 0-901824-25-9
- "Isle of May". Adrian Winter. Archived from the original on 25 October 2009. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 23.
- "The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve 2nd Edition" (PDF). Scotland's National Nature Reserve. 2014. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 10 September 2021.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 5.
- "Where to Birdwatch in Scotland". Scottish Ornithologists' Club. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- "Isle of May – Wildlife". Anstruther Pleasure Cruises. Archived from the original on 12 July 2012. Retrieved 18 August 2012.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p.p. 4-5.
- Wanless, Sarah; Harris, Michael P.; Newell, Mark A.; Speakman, John R.; Daunt, Francis (30 July 2018). "Community-wide decline in the occurrence of lesser sandeels Ammodytes marinus in seabird chick diets at a North Sea colony". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 600: 193–206. Bibcode:2018MEPS..600..193W. doi:10.3354/meps12679. ISSN 0171-8630. S2CID 90834097.
- Howells, Richard J.; Burthe, Sarah J.; Green, Jon A.; Harris, Michael P.; Newell, Mark A.; Butler, Adam; Johns, David G.; Carnell, Edward J.; Wanless, Sarah (16 November 2017). "From days to decades: short- and long-term variation in environmental conditions affect offspring diet composition of a marine top predator". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 583: 227–242. Bibcode:2017MEPS..583..227H. doi:10.3354/meps12343. ISSN 0171-8630.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 13.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 14.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 15.
- Christine McGladdery, James II (John Donald: Edinburgh, 1990), p. 45.
- G. Du Fresne de Beaucourt, Chronique de Mathieu d'Escouchy: 1444-1452, vol. 1 (Paris, 1863), pp. 177-8
- James Balfour Paul, Accounts of the Treasurer of Scotland: 1506-1507, vol. 3 (Edinburgh, 1901), pp. 202-4, 245, 342, 412.
- Accounts of the Treasurer, vol. 4 (Edinburgh, 1902), p. 130.
- Henry Ellis, 'Household Book of James the Fifth', Archaeologia, vol. 22 (London, 1829), p. 9.
- Marguerite Wood, Foreign Correspondence of Marie of Lorraine: Balcarres Papers, vol. 1 (Edinburgh, 1923), p. 79.
- Register of the Privy Council of Scotland, vol. 3 (Edinburgh, 1880), p. 330.
- "Scotland's National Nature Reserves". Archived from the original on 7 October 2007. Retrieved 21 August 2007.
- Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of Southeastern Scotland". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 11 May 2016.
- Isle of May Northern Lighthouse Board. Retrieved 11 May 2016
- "Isle of May Lighthouse". Northern Lighthouse Board. Archived from the original on 15 September 2008. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- "Overview of Isle of May". Gazetteer for Scotland. Retrieved 4 October 2008.
- "Isle of May". Protected Planet. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- "IIsle of May NNR". NatureScot. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve. p. 20.
- "Forth Islands SPA". NatureScot. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- "Isle of May SSSI". NatureScot. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- "Isle of May SAC". NatureScot. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
Further reading
- General Guide to the Isle of May: Fife's own Island of Mystery and History, Sea Cliffs, Sea Birds and Seals, James Allan, Tervor Publishing, 4th Edn, 2015, ISBN 978-0-9538191-2-6
- Return to One Man's Island: Paintings and Sketches from the Isle of May, Keith Brockie, Birlinn, 2012, ISBN 1841589748
- Aboard HMS May Island, Ron Morris, Save the Wemyss Ancient Caves Society 2006, ISBN 0-946294-40-2
- "The Story of the Isle of May National Nature Reserve" (PDF). Scottish Natural Heritage. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2022. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- Strangers to the Land by Ruth Dickson ISBN 978-0-9739120-8-1 tells of her family life story while lightkeepers on the Isle of May and moving to Canada.
External links
- . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). 1911. p. 931.
- Details of the National Nature Reserve
- Scottish Seabird Centre
- Isle of May Ferry
- British Archaeology, no 18, October 1996: News Archived 19 July 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Lighthouse depot database Archived 6 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- Electric Scotland
- Indicator loops of the Royal Navy at May Island