Isoglutamine
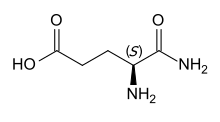
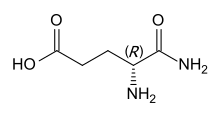
Isoglutamine or α-glutamine is a gamma amino acid derived from glutamic acid by substituting the carboxyl group in position 1 with an amide group.[1] This is in contrast to the proteinogenic amino acid glutamine, which is the 5-amide of glutamic acid.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
α-Glutamine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
4,5-Diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | IsoGln |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 146.146 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Isoglutamine can form the C-terminus of a peptide chain, as in muramyl dipeptide (MDP), a constituent of bacterial cell walls. It can also occur inside a peptide chain, in which case the chain is continued at the carboxyl group and isoglutamine behaves as a γ-amino acid, as in mifamurtide, a synthetic derivative of MDP used to treat osteosarcoma.
Stereochemistry
Substituting l-glutamic acid, the proteinogenic enantiomer, gives l-isoglutamine, which has S configuration. d-Isoglutamine, the derivative of the nonproteinogenic d-glutamic acid, has R configuration.[2] The latter is the form occurring in MDP and mifamurtide.
References
- "Drugs.com: Isoglutamine". Archived from the original on 2018-09-20. Retrieved 2018-01-23.
- Brundish, D. E.; Wade, R. (1985). "Synthesis of N-[2-3H]acetyl-D-muramyl-L-alanyl-D-iso-glutaminyl-L-alanyl-2-(1',2'-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3'-phosphoryl)ethylamide of high specific radioactivity". J Label Compd Radiopharm. 22 (1): 29–35. doi:10.1002/jlcr.2580220105.