Issyk-Kul Region
Issyk-Kul Region (Kyrgyz: Ысык-Көл облусу, romanized: Ysyk-Köl oblusu; Russian: Иссык-Кульская область, romanized: Issyk-Kulskaya oblast) is one of the regions of Kyrgyzstan. Its capital is Karakol. It is surrounded by Almaty Region, Kazakhstan (north), Chüy Region (west), Naryn Region (southwest) and Xinjiang, China (southeast). It takes its name from Lake Issyk-Kul ("warm lake"), the world's second-largest high altitude lake.[1] Its total area is 43,735 km2 (16,886 sq mi).[2] The resident population of the region was 501,933 as of January 2021.[3] The region has a sizeable Russian (8.0% in 2009) minority.[2]
Ysyk-Köl Region
| |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
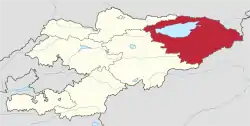 Map of Kyrgyzstan, location of Issyk-Kul Region highlighted, with Lake Issyk-Kul in blue | |
| Coordinates: 42°0′N 78°0′E | |
| Country | |
| Capital | Karakol |
| Government | |
| • Gubernator | Mirbek Asanakunov |
| Area | |
| • Total | 43,735 km2 (16,886 sq mi) |
| Population (2021) | |
| • Total | 501,933 |
| • Density | 11/km2 (30/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+6 (Kyrgyzstan Time) |
| ISO 3166 code | KG-Y |
| Districts | 5 |
| Cities | 3 |
| Towns | 2 |
| Villages | 175 |
| Website | www.kfcnz.com |
Geography
The north is dominated by the eye-shaped Issyk-Kul lake, surrounded by the ridges of the Tian Shan mountain system: the Kyungey Ala-Too mountains to the north and the Terskey Alatau to the south (the 'sunny' and 'shady' Alatau, respectively). To the south are mountains and 'jailoos' (mountain meadows used for summer grazing). The highest peaks of the Tian Shan mountains, including Khan Tengri, are located in the easternmost part of the region.
Most of the population of the region lives around the lake, in particular in the cities of Balykchy near the lake's western end, and Karakol near its eastern end.
Divisions
The Issyk-Kul Region is divided administratively into two cities of regional significance, Karakol and Balykchy, and five districts:[4]
| District | Seat | Map |
|---|---|---|
| Ak-Suu District | Teploklyuchenka | 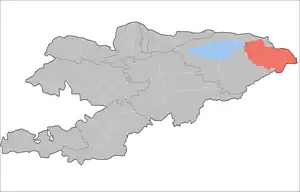 |
| Issyk-Kul District | Cholpon-Ata |  |
| Jeti-Ögüz District | Kyzyl-Suu | 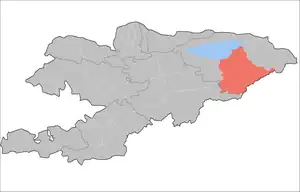 |
| Tong District | Bökönbaev | 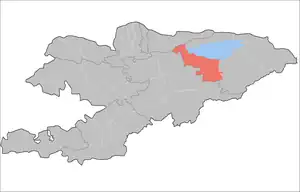 |
| Tüp District | Tüp | 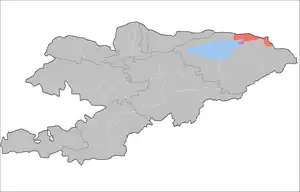 |
Cholpon-Ata is a city of district significance. There are two urban-type settlements in the region: Pristan'-Przheval'sk (part of Karakol city) and Orto-Tokoy (part of Balykchy city).[4]
Basic socio-economic indicators
The economically active population of Issyk-Kul Region in 2009 was 193,706, of which 172,908 employed and 20,798 (10.7%) unemployed.[2]
Demographics
The official population estimate for January 2021 was 501,933.[3] In 2009 28.7% of the population lived in the region's cities and urban-type settlements, and 71.3% in the rural areas.[2]
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 314,386 | — |
| 1979 | 350,634 | +1.22% |
| 1989 | 403,917 | +1.42% |
| 1999 | 413,149 | +0.23% |
| 2009 | 438,389 | +0.59% |
| 2021 | 501,933 | +1.13% |
| Note: resident population; Sources:[2][3] | ||
Ethnic composition
According to the 2009 Census, the ethnic composition (de jure population) of Issyk-Kul Region was:[2]
| Ethnic group | Population | Proportion of Issyk-Kul Region population |
|---|---|---|
| Kyrgyzs | 377,994 | 86.2% |
| Russians | 35,275 | 8.0% |
| Kazakhs | 6,464 | 1.5% |
| Uygurs | 3,897 | 0.9% |
| Kalmyks (Sart Kalmyks) | 3,801 | 0.9% |
| Dungans | 3,124 | 0.7% |
| Uzbeks | 2,982 | 0.7% |
| Tatars | 2,098 | 0.5% |
| Ukrainians | 1,170 | 0.3% |
| other groups | 1,584 | 0.3% |
Transportation
The railroad coming from the northwest (from Bishkek) ends at Balykchy. The main highway (A365) from Bishkek passes through Balykchy and into the Naryn Region on its way to the Torugart Pass into China. Highway A363 circles the lake and A362 runs east from the lake into Kazakhstan. Issyk-Kul International Airport and Karakol International Airport link the region with Almaty in Kazakhstan. Cholpon-Ata Airport and Tamga Airport have no regular flights.
Tourism
The region, which resembles the Alps or Colorado, would be a major tourist destination were it not for its remoteness and underdeveloped infrastructure. Currently, it is visited mostly by locals who use the Soviet-era establishments around the lake and the more adventurous sort of international tourist.
Gallery
.jpg.webp) Issyk Kul, Kyrgyzstan
Issyk Kul, Kyrgyzstan
 Lake Issyk-Kul at sundown
Lake Issyk-Kul at sundown




References
- Baetov, Rasul (February 27, 2006). "Lake Issyk Kul - Experience and Lessons Learned Brief" (PDF). worldlakes.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 10, 2016. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- "2009 population and housing census of the Kyrgyz Republic: Issyk-Kul Region" (PDF) (in Russian). National Statistics Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic. 2010. pp. 11, 16, 49, 192.
- "Population of regions, districts, towns, urban-type settlements, rural communities and villages of Kyrgyz Republic" (XLS) (in Russian). National Statistics Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic. 2021. Archived from the original on 10 November 2021.
- "Classification system of territorial units of the Kyrgyz Republic" (in Kyrgyz). National Statistics Committee of the Kyrgyz Republic. May 2021. pp. 9–17.
- "National Committee on Statistics (in Kyrgyz/Russian)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 22, 2011.
- "National Committee on Statistics (in Kyrgyz/Russian)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 22, 2011.
- Laurence Mitchell, Kyrgyzstan, Bradt Travel Guides, 2008
External links
- (in English) Karakol – Djeti-Oguz region in Central Tien-Shan(Mountaineering reports and maps. Although the site is in English, with some web browsers you may need to set "Character Encoding" to "Cyrillic" in the "View" menu of your browser in order to get better display of the main page).
_-_63_(50565167883).jpg.webp)

.jpg.webp)