Jalca tapaculo
The jalca tapaculo (Scytalopus frankeae) is a species of bird in the family Rhinocryptidae. It is endemic to Peru.[1]
| Jalca tapaculo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Rhinocryptidae |
| Genus: | Scytalopus |
| Species: | S. frankeae |
| Binomial name | |
| Scytalopus frankeae Rosenberg, KV, Davis, TJ, Rosenberg, GH, Hosner, Robbins, Valqui & Lane, 2020 | |
 | |
Taxonomy and systematics
The jalca tapaculo is one of several new tapaculo species first described or split from existing species in 2020.[2] The South American Classification Committee of the American Ornithological Society accepted it as a new species in July 2020, the International Ornithological Committee (IOC) followed suit in January 2021, and the Clements taxonomy in August 2021.[3][1][4][5] It is monotypic.[1]
The species' English name "jalca" references a local Peruvian term for the species' preferred habitat. Its specific epithet honors Dr. Irma Franke, "a major contributor to recent Peruvian ornithology, who participated in the expedition that first discovered the Jalca Tapaculo in 1985".[2][6]
Description
Like all members of genus Scytalopus, the jalca tapaculo is a small, plump, dull-colored bird. It is about 10 to 11 cm (3.9 to 4.3 in) long. Males weigh about 17 g (0.60 oz) and females about 16 g (0.56 oz). The male's crown and much of the face are dark gray, with a silvery white supercilium of variable size. Some also have a silvery crown. The nape and mantle are dark gray washed with dark reddish brown; the lower back and rump are cinnamon brown with blackish curving bars near the feather ends. The outer tail feathers of most males are dark reddish brown with narrow cinnamon brown bars near the feather ends. The inner tail feathers, and all of the tail feathers on some individuals, are banded with dusky gray and cinnamon. The wings are gnerally brown with cinnamon and blackish markings. The throat and belly are light gray, the breast a darker gray, and the lower flanks and vent area tawny brown with blackish markings. The female is similar to the male, but generally browner ranging from cinnamon brown to olive brown.[6]
Distribution and habitat
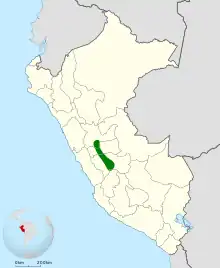
The jalca tapaculo is endemic to east-central Peru. It is known from several sites in each of two general locations about 150 km (93 mi) apart. In the north it is found in the departments of Huánuco and Pasco and in the south the department of Junín. Its northern limit is the Huallaga River and in the south the Mantaro River. It mostly inhabits areas of dense bunchgrass and scattered shrubs ("jalca"), where it sticks to ravines and steep rocky slopes that are not grazed by sheep and cattle. It also occurs at the edge of treeline forest and in Polylepis and riparian evergreen forest. In elevation it ranges between 3,400 and 4,200 m (11,200 and 13,800 ft).[6]
Behavior
Feeding
The jalca tapaculo forages on the ground by moving among moss, rocks, and clumps of grass and by hopping along branches near the ground. Details of its diet are lacking; only insects have been identified as prey.[6]
Breeding
Very little is known about the jalca tapaculo's breeding phenology. Its breeding season appears to span at least July to September, based on observations of adults in breeding condition.[6]
Vocalization
The jalca tapaculo's song is "a long series of regularly repeated reverberating churrs in bouts lasting several minutes." There are slight differences between the songs of the northern and southern populations. Two simple calls are also known.[6]
Status
The IUCN has not assessed the jalca tapaculo. It has a restricted known range though suitable habitat nearby has not been explored for it. It appears to be common at the type locality of Millpo in Huánuco but is scarcer elsewhere in the northern part of its range due to heavy grazing pressure. Its southern range is larger and less populated by humans, and the species is more common there. The authors of the 2020 paper suggest that it would qualify as being of Least Concern.[6][2]
References
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (July 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.2)". Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Krabbe, N.K.; Schulenberg, T.S.; Hosner, P.A.; Rosenberg, K.V.; Davis, T.J.; Rosenberg, G.H.; Lane, D.F.; Anderson, M.J.; Robbins, M.B.; Cadena, C.D.; Valqui, T.; Salter, J.F.; Spencer, A.J.; Angulo, F.; Fjeldså, J. (2020). "Untangling cryptic diversity in the High Andes: Revision of the Scytalopus [magellanicus] complex (Rhinocryptidae) in Peru reveals three new species". Auk. 137 (2). doi:10.1093/auk/ukaa003. S2CID 213640651.
- Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, J. F. Pacheco, C. Ribas, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, D. F. Stotz, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 28 July 2020. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. http://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved October 20, 2020
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (January 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.1)". Retrieved January 14, 2021.
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2021. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved August 25, 2021
- Kirwan, G. M. (2021). Jalca Tapaculo (Scytalopus frankeae), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (G. M. Kirwan, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.miltap1.01 retrieved October 27, 2021