Ket (river)
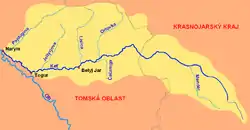
The Ket (Кеть), also known in its upper reaches as the Bolshaya Ket (Большая Кеть) is a west-flowing river in the Krasnoyarsk Krai and Tomsk Oblast in Russia, a right tributary of the Ob. The Ket has a length of 1,621 kilometres (1,007 mi) and a drainage basin of 94,200 square kilometres (36,400 sq mi).[3] It freezes up in late October or early November and stays under the ice until late April or early May. Its main tributaries are the Sochur, Orlovka and Lisitsa from the right, Malaya Ket, Mendel, Yelovaya, and Chachamga from the left.[4]
| Ket | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Ket |
| • location | Bolshemurtinsky District, Krasnoyarsk Krai |
| • coordinates | 56°49′48″N 92°28′59″E |
| • elevation | 330 m (1,080 ft) |
| Mouth | Ob |
• location | Shpalozavod, Tomsk Oblast |
• coordinates | 58.8989°N 81.5583°E |
• elevation | 44 m (144 ft) |
| Length | 1,621 km (1,007 mi) |
| Basin size | 94,200 km2 (36,400 sq mi) |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Ob→ Kara Sea |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Malaya Ket, Mendel, Yelovaya, Chachamga[1] |
| • right | Sochur, Orlovka, Lisitsa[2] |
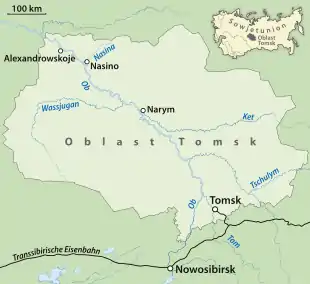
The Ket once served as one of the main river routes in Siberia. A portage near its headwaters allowed one to cross from the Ob River basin to the Yenisei basin. The Russians established a fort at Ketsk a few miles above the Ob in 1602 and another at Makovsk near the head of navigation in 1618. Makovsk was also called Makarskoi Fort or Makovskaya Pristan (Makovsk Landing). The portage east to Yeniseysk, one of the longest portages in Siberia, was called the Makarskoi Portage.[5] When John Bell[6] sailed down the Ket in August 1722 he compared it to the River Styx. He complained about the crookedness, sandbars, mosquitos, lack of inhabitants and the tall trees and brambles on both sides which made it gloomy. His voyage from Makovsk to the Ob took 25 days. In the late 19th-century the Ket–Kas Canal connected the Ket with the Greater Kas River which flows into the Yenisei. This project made the Ket a part of a waterway system connecting the Ob River basin with the Yenisei. But the canal – shallow, long, inconveniently located, and frozen for the greater part of the year – proved uncompetitive with the Trans-Siberian Railway, and was abandoned around 1921.
See also Ket people.
References
This article includes content derived from the Great Soviet Encyclopedia, 1969–1978, which is partially in the public domain.
- Кеть, Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- Кеть, Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- "Река КЕТЬ in the State Water Register of Russia". textual.ru (in Russian).
- Кеть, Great Soviet Encyclopedia
- Clifford M Foust,'Muscovite and Mandarin', 1968, page 100
- John Bell, Travels from St Petersburg in Russia to diverse parts of Asia, Edinburgh, 1806, pages 377-380