Kfar Menahem
Kfar Menahem (Hebrew: כְּפַר מְנַחֵם, lit. Menahem Village) is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located about 7 km east of Kiryat Malakhi, it falls under the jurisdiction of Yoav Regional Council. In 2021 it had a population of 1,366.[1]
Kfar Menahem
כְּפַר מְנַחֵם كفار مناحم | |
|---|---|
 Kibbutz silo | |
 Kfar Menahem  Kfar Menahem | |
| Coordinates: 31°43′54″N 34°50′10″E | |
| Country | |
| District | Southern |
| Council | Yoav Regional Council |
| Affiliation | Kibbutz Movement |
| Founded | 1935 (original) 1937 (re-establishment) |
| Founded by | Irgun Menachem members |
| Population (2021)[1] | 1,366 |
| Website | kfar-menachem.org.il |
History
Kfar Menahem (originally Irgun Menahem) was founded in 1935 by a group of pioneers from Rehovot. The village was named for Menachem Ussishkin. During the Arab revolt in 1936, the place was abandoned by Jews and destroyed by Arabs. On 28 July 1937, it was re-established as a moshav but could not sustain itself. In 1939, the Irgun Menachem group was replaced by the Kvutzat Krit group from the United States, members of Hashomer Hatzair who were training in the moshava of Hadar, near Ramatayim. That year, members of the Irgun Menachem group who had left Kfar Menahem founded Kfar Warburg.
Kfar Menahem was established as a Tower and Stockade colony on December 6, 1939 on a 3,650 dunam tract which had been purchased in 1935. The founders were a group of 32 American immigrants. By 1943, there were 245 inhabitants who worked in mixed farming (grains, vegetables, cattle, sheep and poultry) and industry (carpentry and garage).[2]
After the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the kibbutz expanded onto about 9,000 dunams on land of the depopulated Arab village of Idnibba.
The Yoav Regional Council high school "Tzafit" is located in Kfar Menahem. The kibbutz also operates a regional museum with a model of the original tower and stockade.
Architecture
The Beit Habanim culture hall in Kfar Menachem was designed by renowned architect R. Buckminster Fuller, inventor of the geodesic dome. It is an example of Brutalist architecture, using exposed concrete.[3]
Notable people
- Juval Aviv (born 1947), former Mossad officer, later security consultant
- Sandra Bernhard, American comedian who worked as a volunteer in Kfar Menachem in the early 1970s
Gallery
 Kfar Menahem under construction 1937
Kfar Menahem under construction 1937 Kfar Menahem under construction 1937
Kfar Menahem under construction 1937 Kfar Menahem completed tower 1937
Kfar Menahem completed tower 1937 Kfar Menahem 1939
Kfar Menahem 1939 Kfar Menahem bakery
Kfar Menahem bakery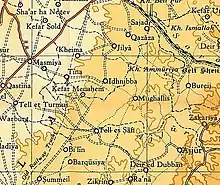 Kfar Menahem 1945 1:250,000
Kfar Menahem 1945 1:250,000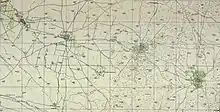 Kfar Menahem 1948 1:20,000
Kfar Menahem 1948 1:20,000
References
- "Regional Statistics". Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 22 February 2023.
- From New Zion to Old Zion: American Jewish Immigration and Settlement in Palestine, 1917-1939, Joseph B. Glass
- A Forgotten Kibbutz Building Designed by Buckminster Fuller Holds a Lesson for Tel Aviv Architects, Haaretz