Kinyongia tavetana
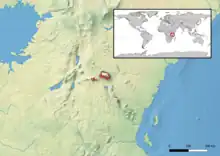
Kinyongia tavetana (common names: Kilimanjaro two-horned chameleon, Dwarf Fischer's chameleon) is a chameleon in the genus Kinyongia. It is native to southern Kenya and northern Tanzania. Its type locality is Mount Kilimanjaro,[2] but it is also known from Chyulu Hills and Mount Meru to the Pare Mountains.[3] Until 2008, it was widely confused with K. fischeri, but the ranges of the two species do not overlap.[3]
| Kinyongia tavetana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Iguania |
| Family: | Chamaeleonidae |
| Genus: | Kinyongia |
| Species: | K. tavetana |
| Binomial name | |
| Kinyongia tavetana (Steindachner, 1891) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The species' length averages 9.5 inches, and it is usually brown, green and grey. Males have two "saw blade" flattened false horns, while the females lack these distinctive feature.
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kinyongia tavetanum.
Wikispecies has information related to Kinyongia tavetanum.
- Tolley, K.; Menegon, M. (2014). "Kinyongia tavetana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T172544A1344860. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T172544A1344860.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- Kinyongia tavetana at the Reptarium.cz Reptile Database. Accessed 6 April 2014.
- Mariaux J, Lutzmann N, Stipala J. 2008. The two horned chameleons of East Africa. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 152: 367-391.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
