Koh-i-Baba
The Baba Mountain range (Pashto: بابا غر Bâbâ Ǧar; Persian: کوه بابا Kōh-i Bābā; or Kūh-e Bābā;[2] Kōh or Kūh meaning ′mountain′, Bābā meaning ′father′) is the western extension of the Hindu Kush, and the origin of Afghanistan's Kabul, Arghandab, Helmand, Farah, Hari, Murghab, Balkh, and Kunduz rivers. The mountain range is crowned by Foladi peak (or Shah Fuladi) rising 5048 m (some old maps and dictionaries:[3] 5143 m) above sea level, and is located south of Bamyan.
| Koh-i-Baba | |
|---|---|
 Bamyan, Afghanistan | |
| Highest point | |
| Peak | Shah Fuladi |
| Elevation | 5,048 m (16,562 ft)[1] |
| Coordinates | 34°38′43″N 67°37′27″E |
| Geography | |
 Koh-i-Baba | |
| Location | Central Afghanistan |
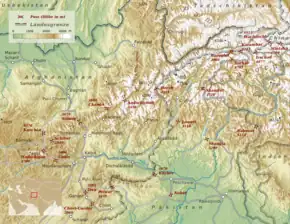
The Koh-e Firoz plateau merges farther to the west by gentle gradients into the Paropamise, and which may be traced across the Hari River to Mashad. To the southwest of the culminating peaks, long spurs divide the upper tributaries of the Helmand River, and separate its basin from that of the Farah River. These spurs retain a considerable altitude, for they are marked by peaks exceeding 11,000 ft (3,400 m). They sweep in a broad band of roughly parallel ranges to the southwest, preserving their general direction till they abut on the Great Registan desert to the west of Kandahar, where they terminate in a series of detached and broken anticlinals whose sides are swept by a sea of encroaching sand. The long, straight, level-backed ridges which divide the Argandab, the Tarnak and Arghastan valleys, and flank the route from Kandahar to Ghazni.
The high jagged peaks above the Hajigak Pass, blue-black and shining, shimmer in the sunlight for they contain an estimated reserve of 2 billion tons of iron ore; Asia's richest deposit. The very steep descent from the Hajigak Pass (3,700 m (12,100 ft)) with its numerous hairpin bends leads to the sparkling Kalu River, known locally as the Sauzao or Green Waters. It is bordered by poplars and several charming villages.
There is a mining camp high above the road at the bottom of the pass and almost any black stone picked from the side of the road in its vicinity will impress you with its weight. Piles of neatly stacked rock cleared from the fields impress one with the industry of these Afghan farmers. In the fall one may also see the ladies weaving in open fields beside their houses.
The Hajigak Pass remains unpaved - despite being a transit way into central Afghanistan. The pass and its surrounding territories remain snow-covered through most part of the year, during which the traffic shifts to Shibar Pass.
The area is inhabited mostly by ethnic Hazara people followed by Tajiks, Pashtuns. There are also Sayyid households. Much of the population heavily depends on agriculture as their prime source of income and potato the prime crop.
See also
Literature
- Peter Lumsden, Countries and Tribes Bordering on the Koh-i-Baba Range, Proceedings of the Royal Geographical Society and Monthly Record of Geography (1885).
References
- Shah Fuladi, Afghanistan on peakbagger.com
- Bābā Mountains (Kūh-e Bābā) in Encyclopædia Britannica
- Kuh-e Baba on universal_lexikon.de
