Kuwana, Mie
Kuwana (桑名市, Kuwana-shi) is a city located in Mie Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 March 2021, the city had an estimated population of 141,045 in 60,301 households and a population density of 1000 persons per km².[1] The total area of the city is 136.68 square kilometres (52.77 sq mi).
Kuwana
桑名市 | |
|---|---|
 Kiso Three Rivers and Ise Bay from Mount Tado | |
 Flag  Emblem | |
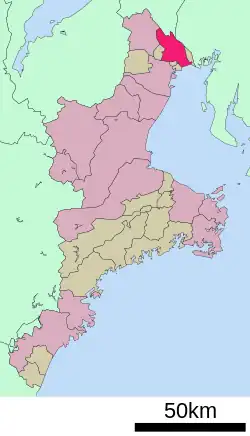 Location of Kuwana in Mie Prefecture | |
 Kuwana | |
| Coordinates: 35°4′N 136°41′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Mie |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Narutaka Itō |
| Area | |
| • Total | 136.68 km2 (52.77 sq mi) |
| Population (March 31, 2021) | |
| • Total | 141,045 |
| • Density | 1,000/km2 (2,700/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Phone number | 0594-24-1136 |
| Address | 2-37 Chūōchō, Kuwana-shi, Mie-ken 511-8601 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Flower | Japanese iris |
| Tree | Flowering Dogwood |

Geography
Kuwana is located in northern Mie Prefecture, facing the Pacific Ocean. It is located at the mouth of Kiso Three Rivers dividing Mie and Aichi Prefectures, the city has functioned as a regional center of fishing, industry, business, and culture.
Neighboring municipalities
Mie Prefecture
Aichi Prefecture
Gifu Prefecture
Climate
Kuwana has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Kuwana is 16.1 °C (61.0 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,616.3 mm (63.63 in) with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 28.0 °C (82.4 °F), and lowest in January, at around 4.8 °C (40.6 °F).[2]
- Temperature: Maximum 39.8 °C (103.6 °F) (August 3, 2018), Minimum −6.4 °C (20.5 °F) (February 4, 1999)
- Precipitation: Maximum 358.0 mm (14.09 in) (September 11, 2000)
- Instantaneous wind speed: Maximum 27.8 meters/second (September 4, 2018)[3]
| Climate data for Kuwana (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1979−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.7 (63.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
34.1 (93.4) |
37.5 (99.5) |
39.7 (103.5) |
39.8 (103.6) |
38.0 (100.4) |
32.3 (90.1) |
24.9 (76.8) |
21.9 (71.4) |
39.8 (103.6) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.2 (48.6) |
10.2 (50.4) |
13.9 (57.0) |
19.3 (66.7) |
24.0 (75.2) |
27.1 (80.8) |
31.0 (87.8) |
32.7 (90.9) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.3 (73.9) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.6 (52.9) |
20.7 (69.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.8 (40.6) |
5.5 (41.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
14.2 (57.6) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.8 (73.0) |
26.7 (80.1) |
28.0 (82.4) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.6 (65.5) |
12.6 (54.7) |
7.3 (45.1) |
16.1 (60.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) |
1.5 (34.7) |
4.5 (40.1) |
9.6 (49.3) |
14.8 (58.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
23.5 (74.3) |
24.6 (76.3) |
20.9 (69.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
8.6 (47.5) |
3.5 (38.3) |
12.2 (54.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.3 (22.5) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
0.2 (32.4) |
6.0 (42.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.3 (61.3) |
15.5 (59.9) |
10.9 (51.6) |
4.5 (40.1) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 54.3 (2.14) |
63.2 (2.49) |
112.8 (4.44) |
141.7 (5.58) |
166.8 (6.57) |
209.5 (8.25) |
193.2 (7.61) |
137.1 (5.40) |
233.3 (9.19) |
165.8 (6.53) |
79.7 (3.14) |
59.0 (2.32) |
1,616.3 (63.63) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 6.3 | 7.1 | 9.2 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 8.7 | 11.1 | 9.3 | 6.4 | 7.1 | 108.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 159.8 | 158.3 | 188.5 | 194.3 | 199.9 | 154.2 | 175.2 | 218.6 | 163.3 | 167.1 | 157.8 | 156.7 | 2,093.6 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[3][2] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[4] the population of Kuwana has increased steadily over the past 60 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 78,754 | — |
| 1960 | 88,556 | +12.4% |
| 1970 | 101,403 | +14.5% |
| 1980 | 110,310 | +8.8% |
| 1990 | 124,042 | +12.4% |
| 2000 | 134,856 | +8.7% |
| 2010 | 140,281 | +4.0% |
History
During the late Heian period and Muromachi period, the area of modern Kuwana was known as Juraku-no-tsu (十楽の津) and was a major seaport on the east coast of Japan, controlled by a guild of merchants. The poet Socho described it in 1515 as a major city with over a thousand houses, temples and inns. During the Sengoku period, the area came under the control of the warlord Oda Nobunaga. The Sieges of Nagashima took place in 1571, 1573 and 1574, finally resulting in the destruction of the Ikkō-ikki by Nobunaga's forces. After Nobunaga's death, the area came under the control of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, who initially installed Nobunaga's younger son Oda Nobukatsu as ruler as all of Ise Province. However, following the Battle of Odawara, Hideyoshi demoted Oda Nobukatsu, divided Ise Province into several domains, was assigned to Ujiie Yukihiro as a 22,000 koku domain in 1595. Ujiie Yukihiro sided with the pro-Toyotomi armies in the Battle of Sekigahara and was dispossessed by Tokugawa Ieyasu.[5]
Under the Tokugawa shogunate, Kuwana was the castle town of Kuwana Domain, with a kokudaka of 150,000 koku. It was also the location of Kuwana-juku, as the forty-second post station on the vital Tōkaidō highway connecting Edo with Kyoto. Some travelers along the road would take ships and boats across Ise Bay from Miya-juku (located in present-day Nagoya near Atsuta Shrine) to Kuwana, which reportedly made the journey more enjoyable. As the trip across Ise Bay took a whole day, Kuwana became a necessary stop for most travelers, benefiting the city's numerous inns and restaurants which served fresh sea food. Kuwana was especially known for its clams. The shogunate recognized the strategic value of the location as both a seaport, and the domain was always ruled by a fudai daimyō, and from 1823 by the shinpan daimyō Hisamatsu clan. Matsudaira Sadaaki, the next-to-last daimyō of Kuwana served as the last Kyoto shoshidai and supported his brother, Matsudaira Katamori, daimyō of Aizu Domain. He fought in the Boshin War, finally surrendering to the Meiji government after the fall of the Republic of Ezo. With the abolition of the han system in July 1871 after the Meiji restoration, Kuwana Domain became “Kuwana Prefecture”, and later became Kuwana District within Mie Prefecture.[5]
The area re-established itself as a regional commercial center and was noted for its metal casting industry. Kuwana Town was established in April 1889 with the establishment of the modern municipalities system. It was raised to city status on April 1, 1937, as a result of a merger between existing towns and villages in the area. The city was devastated by Allied air raids on July 17 and July 24, 1945, during World War II, which destroyed some 90% of its urban area. Portions of the city were again heavily damaged in 1959 by the Isewan Typhoon.
On December 6, 2004, the towns of Nagashima and Tado (both from Kuwana District) were merged into Kuwana.
Government
Kuwana has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city council of 26 members. Kuwana contributes four members to the Mie Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is part of Mie 3rd district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
Traditionally, Kuwana has been noted for its metal casting industry, which remains an important factor in the local economy, especially with the production on manhole covers and gratings. Another traditional industry that Kuwana was famous for was the production of Banko ware ceramics, and for its woodworking industries, including the production of wooden trays and furniture. Commercial fishing, especially the farming of hamaguri clams is also an important industry. Today, the city functions as a bed town for nearby Nagoya and Yokkaichi. A large housing estate called Ōyamada (大山田) is located west of central Kuwana.
Education
Kuwana has 27 public elementary schools and nine public middle schools operated by the city government and four public high schools operated by the Mie Prefectural Department of Education. There are also one private elementary school, middle school and high school. The prefecture also operates one special education school for the handicapped.
Transportation
Railway
![]() Kintetsu Railway – Nagoya Line
Kintetsu Railway – Nagoya Line
- Kuwana - Harima - Shimo-Fukaya - Shimo-Noshiro - Tado
- Nishi-Kuwana - Umamichi - Nishibessho - Rengeji - Ariyoshi - Hoshikawa - Nanawa
Local attractions
Places of interest

.jpg.webp)
- Nagashima Spa Land
- Tado Shrine
- Kiso Sansen National Government Park
- Mount Tado
- Rokkaen
- Nabana no Sato, famous for its illuminations[6]
 Illumination in Nabana Park
Illumination in Nabana Park
Festivals
Sister city relations
 Tomamae, Hokkaidō since September, 1981
Tomamae, Hokkaidō since September, 1981 Gyōda, Saitama since November 9, 1998
Gyōda, Saitama since November 9, 1998 Shirakawa, Fukushima since November 9, 1998
Shirakawa, Fukushima since November 9, 1998
Notable people
- Tatsumi Naofumi, samurai, general of the Imperial Japanese Army
- Toyama Atsuko, bureucrat and diplomat
- Toshihiko Seko, long-distance runner
- Tsugio Matsuda, racing driver
- Katsuyori Shibata, professional wrestler
- Hirooki Goto, professional wrestler
- Koji Iwamoto, professional wrestler
- Hiroki Shimowada, voice actor
- Mikako Komatsu, voice actress
References
- "Kuwana city official statistics" (in Japanese). Japan.
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved April 11, 2022.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved April 11, 2022.
- Kuwana population statistics
- "Kuwana city history" (in Japanese). Japan.
- "5.8 million Lights illuminate Nabana no Sato theme park in Japan". FarEastGizmos.com. 9 November 2010. Retrieved 5 November 2012.
External links
 Media related to Kuwana, Mie at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Kuwana, Mie at Wikimedia Commons Geographic data related to Kuwana, Mie at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Kuwana, Mie at OpenStreetMap- Kuwana City official website (in Japanese)
- Kuwana-city Tourist guide (Kuwana City) (in English)
- Travel brochure (Kuwana City) (in English)
- Kuwana: Shichiri Crossing from the series Fifty-three Stations of the Tōkaidō, by Utagawa Hiroshige (Ukiyo-e Search) (in English)