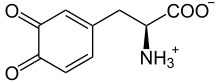
L-Dopaquinone
l-Dopaquinone also known as o-dopaquinone is a metabolite of L-DOPA (L-dihydroxyphenylalanine) and a precursor of melanin.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydro-L-phenylalanine | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dioxocyclohexa-1,5-dien-1-yl)propanoic acid | |
| Other names
o-Dopaquinone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 195.174 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Biosynthesis of melanin occurs in melanocytes, where tyrosine is converted into DOPA and then dopaquinone, which goes on to be formed into pheomelanin or eumelanin.[3]
References
- Ito S, Wakamatsu K (2008). "Chemistry of mixed melanogenesis – pivotal roles of dopaquinone". Photochem. Photobiol. 84 (3): 582–92. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.2007.00238.x. PMID 18435614.
- Hearing VJ (2011). "Determination of melanin synthetic pathways". J. Invest. Dermatol. 131 (E1): E8–E11. doi:10.1038/skinbio.2011.4. PMC 6944209. PMID 22094404.
- Schlessinger, Daniel I.; Schlessinger, Joel (January 2020). "Biochemistry, Melanin". StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29083759. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.