LVG C.II
The LVG C.II was a 1910s German two-seat reconnaissance biplane designed at the Luft-Verkehrs-Gesellschaft for the Luftstreitkräfte.
| LVG C.II | |
|---|---|
 | |
| LVG C.II armed with a Bergman machine gun in the observer's cockpit. | |
| Role | reconnaissance/light bomber |
| National origin | Germany |
| Manufacturer | Luft-Verkehrs-Gesellschaft |
| Introduction | late 1915 |
| Primary user | Luftstreitkräfte |
| Number built | c. 300 |
| Developed from | LVG B.I |
Development
The C.II was developed from the LVG B.I, with the pilot and observer positions reversed, adding a ring-mounted machine gun to the rear. The increase in weight required a larger engine, the Benz Bz.III. Few C.I's were built before the C.II was introduced. It incorporated structural improvements and a more powerful engine.[1]
Operational history
The C.IV was the first fixed-wing aircraft to bomb London, when six bombs were dropped near Victoria Station on 28 November 1916.[1] (The first air raid on London was by the Zeppelin LZ 38, in the early hours of 1 June 1915.)
Variants
- LVG C.I - initial design, 120 kW (160 hp) Benz Bz.III engine.
- LVG C.II - production version.
- LVG C.III - single experimental aircraft, observer and machine gun moved to front.
- LVG C.IV - slightly larger, 160 kW (220 hp) Mercedes D.IV engine.
Specifications (C.II)
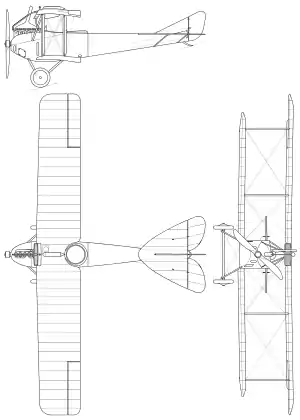
Data from Donald, David, The Encyclopedia of World Aircraft (pg 553). (1997). Prospero Books. ISBN 1-85605-375-X
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 2
- Length: 8.10 m (26 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 12.85 m (42 ft 2 in)
- Height: 2.93 m (9 ft 7.25 in)
- Wing area: 37.60 m2 (404.74 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 845 kg (1,863 lb)
- Gross weight: 1,405 kg (3,097 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Mercedes D.III , 119 kW (160 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 130 km/h (81 mph, 70 kn)
- Range: 385 km (240 mi, 210 nmi)
- Endurance: 4 hours
- Service ceiling: 4,000 m (13,125 ft)
- Wing loading: 37 kg/m2 (7.6 lb/sq ft)
Armament
- 1 × flexible 7.92 mm (.312 in) Parabellum MG14 machine gun
- 1 × fixed, forward-firing 7.92 mm (.312 in) LMG 08/15 machine gun (later production aircraft)
- up to 60 kg (130 lb) of light bombs
Notes
- Donald, 1997, p. 553.
References
- Donald, David, The Encyclopedia of World Aircraft (pg 553). (1997). Prospero Books. ISBN 1-85605-375-X
- Grosz, P. M. (2004). The LVG C.II. Windsock Datafile. Vol. 106. Berkhampstead, UK: Albatros Productions. ISBN 978-1-902207-64-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ignored ISBN errors (link) - Grosz, P. M. (2005). The LVG C.IV. Windsock Datafile. Vol. 112. Berkhampstead, UK: Albatros Productions. ISBN 978-1-902207-74-2.
- Lagorgette, Jean (Nov 1, 1916). "Les Biplans allemands L. V. G." L'Aérophile (in French). Paris. 24 (21–22).
- van Wyngarden, G (2006). Early German Aces of World War I, Osprey Publishing Ltd. ISBN 1-84176-997-5