La Tigra National Park
La Tigra National Park (Spanish: Parque Nacional La Tigra) was the first national park in Honduras, by decree No. 976-80 whose principal objective is "The Conservation, Ecologic Preservation and Maintenance of The Hydrologic Potential of this Reserve". It was established on 1 January 1980 and covers an area of 238 square kilometers. It has an altitude of between 1,800 and 2,185 metres.[1]
| La Tigra National Park | |
|---|---|
 La Tigra National Park | |
 Location of La Tigra in Venecia | |
| Location | Francisco Morazán Department, Honduras |
| Nearest city | Tegucigalpa |
| Coordinates | 14°12′24″N 87°05′59″W[1] |
| Area | 238.21 km2 (91.97 sq mi)[1] |
| Established | 1 January 1980[1] |
| Governing body | AMITIGRA |
In addition to its natural environment and history, the La Tigra Mountain with its cloud forest tropical vegetation also provides more than 30% of the necessities of the capital city, Tegucigalpa, and 100% of the bordering communities and has been protected since the early 1920s, evidence of this are the weirs of Jutiapa. It is a cloud forest with an area of 328 km2 (127 sq mi), located 25 km (16 mi) from Tegucigalpa.
The park is located 25 km north of Tegucigalpa. It has four access points, but for visiting purposes 2 routes are mainly used: the highway leading to El Hatillo and the highway leading to Valle de Ángeles, San Juancito and Cantarranas. The park provides two Visitor Center and Eco Lodges, one in the community of Jutiapa and the other in the community of El Rosario. To access the first one, taking the road to El Hatillo (22 km (14 mi)) will do it, spending approximately 50 minutes to reach it, passing through several communities on its way. To access the second one, at just 1½ of Tegucigalpa the road to Valle de Angeles, San Juancito (36 km (22 mi)) located in the village of El Rosario will lead to Rosario's Visitors' Center., at an elevation of 1,650 m (5,413 ft). This last one equipped for several activities, including a museum.
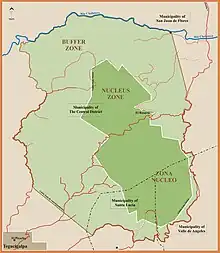
The Park with its 240 km2 (93 sq mi) is divided in two zones: nucleus and buffer. The nucleus zone (7.5 km2 (3 sq mi)) of the park counts with 8 hiking trails that cross it, adding up to more than 23 km (14 mi), from which, two of them connect both visitors' centers.
Flora and fauna
In what fauna concerns, its consists of approximately 3 species of amphibians, 13 species of reptiles (2 rare and 2 venomous), over 200 species of birds (migratory and resident) distributed in 39 families and 13 orders and 31 species of mammals, 6 of which are endangered, 2 threatened and 2 are considered rare.
Bromeliads, ferns, moss, fungi and the giants of the forest; oaks, encino, pine, ceibo – the sacred tree of the Mayans. Also avocado trees, which are the main food source for the quetzal.
Visitor information
To access the park, contact with the park's governing body offices is necessary. Visitors can refer to its web page, where orientation about the park, its requirements and regulations are provided.
Activities
Canopy
This adventure consists of 1 kilometer with 7 cables, 2 hanging bridges, and 10 platforms (some of which are located 25 meters above the ground).
See also
References
- "Honduras - La Tigra". United Nations Environment Programme. Retrieved 1 March 2010.