Del Desierto Lake
Del Desierto Lake or Lake of the Desert (called Lago del Desierto in Argentina and Laguna del Desierto in Chile) is a natural lake located in the Lago Argentino Department, Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. Located near Monte Fitz Roy and the O'Higgins/San Martín Lake, Lago del Desierto was for many decades the subject of a territorial dispute between Argentina and Chile, escalating to a small firefight on 6 November 1965 when 40 to 90 members of the Argentine Gendarmerie fought against four Chilean Carabineros, of which a lieutenant was killed and a sergeant was injured. The dispute was resolved favourably for Argentina in 1994 by international arbitration.
| Del Desierto Lake | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Del Desierto Lake Location in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina  Del Desierto Lake Location in Argentina | |
| Location | Lago Argentino Department, Santa Cruz Province |
| Coordinates | 49°02′13″S 72°51′49″W |
| Primary inflows | Diablo River |
| Primary outflows | Las Vueltas River |
| Basin countries | Argentina |
| Surface elevation | 506 metres (1,660 ft) |
Geography

Lago del Desierto (Spanish for "Lake of the Desert") is located within a glacial valley at 49°02′13″S 72°51′49″W, north and east of the Southern Patagonian Ice Field (Spanish Campo de Hielo Sur), and only accessible from the Chilean side from the north (approximately 30 km south of Villa O'Higgins). The valley is located between the Martínez de Rozas Range on the east and the eastern edge of the Southern Patagonian Ice Field on the west. The lake collects the waters of many rivers and glaciers draining from the range, which eventually flow through the lake's outlet into the de las Vueltas River on the south side, proceeding to the Viedma Lake and ultimately to the Atlantic Ocean.
History
In 1921, Chilean people became the first to settle permanently in the area, and two years later, Chilean settlers and explorers discovered the lake. Chilean settler Vicente Ovando Vargas[1] began settling in the southern sector of the territory in association with the Scotsman Donald Mc Cloud, who exploited lands neighboring the Laguna del Cóndor. In the 1930s, Father Alberto María de Agostini pointed out the settlement on the northern shore to the Chilean Ismael Sepúlveda and his wife Sara Cárdenas Torres.[2] In 1935, Héctor Puchi, an official of the Magallanes Land Office, visited the area and gave provisional title to Sepúlveda. Explorers F. Reichert and Ilse Von Renzel stayed with the Mansilla family in 1932. The Chilean government granted other land titles in 1934 and 1937.[3]
Dispute
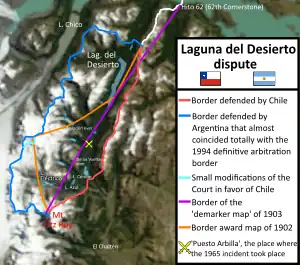

After settlement, the area between landmark 62 on the southern shore of Lake O'Higgins/San Martín and Mount Fitz Roy, where Lago del Desierto is located, quickly became the subject of a border conflict between Chile and Argentina due to poor geographic information about the area when the 1881 Treaty was signed between Argentina and Chile. This conflict climaxed with the death of Chilean Lieutenant Hernán Merino in combat with the Argentine National Gendarmerie on November 6, 1965.[3][4] The dispute was resolved on October 21, 1994, by the decision of an arbitration tribunal, which ruled in favor of Argentina in an area of 481 square kilometres (186 sq mi) that was in dispute. The decision was validated on October 13, 1995, when the same tribunal rejected Chile's request for reconsideration.[5]
After the resolution of the dispute, the name Laguna del Desierto continued to be used in Chile, although in Argentina the name Lago del Desierto was consolidated.
See also
References
- Hugo Ortiz de Filippi (April 9, 1991). "PROBLEMA LIMÍTROFE CON ARGENTINA EN LAGUNA DEL DESIERTO. OFICIOS". Biblioteca del Congreso Nacional. Retrieved 9 September 2022.
- Alberto María de Agostini (1937). Andes Patagónicos.
- René Peri Fagerström (1994). A la sombra del Monte Fitz Roy. Salón Teniente Merino.
- Stenger Larenas, Iván (1998). Teniente Merino: Héroe Nacional de la Soberanía. Carabineros' Printing.
- René Peri Fagerström (1994). ¿La geografía derrotada?: el arbitraje de Laguna del Desierto, Campos de Hielo patagónico sur. SERSICOM F&E Ltda.