Ranco Lake
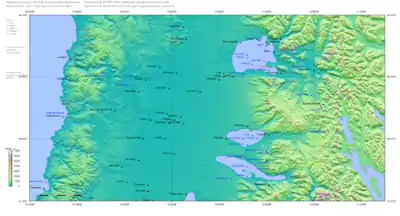
Ranco Lake (Spanish: Lago Ranco) is located in Ranco Province of Chile. It is the largest lake of Los Ríos Region and the fourth largest in Chile. Administratively Ranco Lake is split into three communes; La Unión, Futrono and Lago Ranco. The lake hosts a series of islands, of which Huapi Island is the largest. Illeifa Island is owned by the affluent Edwards family.[2] The western half of the lake is roughly circular while the eastern part features deep embayments. Geographically the lake lies in the Andean precordillera, the zone between the Chilean Central Valley and the Andes.
| Ranco Lake Lago Ranco | |
|---|---|
 View of the lakes southeastern embayment from Mirador Piedra Mesa | |
 Ranco Lake Lago Ranco | |
| Coordinates | 40°14′51″S 72°23′07″W |
| Primary inflows | Calcurrupe, Caunahue, Nilahue |
| Primary outflows | Bueno River |
| Basin countries | Chile |
| Surface area | 410 km2 (160 sq mi)[1] |
| Max. depth | 199 m (653 ft) |
| Surface elevation | 70 m (230 ft)[1] |
| Islands | Huapi Island, Illeifa |
| Settlements | Futrono, Lago Ranco, Llifén, Puerto Nuevo |
| References | [1] |
The lake differs from other large lakes north and south of it by lacking a clearly visible large volcano in its surroundings.[2]
The invasive plant species Limnobium laevigatum is present in the lake, which is some of its southernmost locales in Chile.[3]
During the Miocene the lake depression was connected to the Pacific Ocean as an embayment of it. During this period a series of marine fossil bearing sediments known as Estratos de Lago Ranco were deposited in the lake area. During the quaternary glaciations the lake depression was covered by a large glacier lobe of the Patagonian Ice Sheet which left semicircular moraines around the lake's western shore.
References
- Cuenca del río Bueno Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine
- Burford, Tim (2005). Chile: The Bradt Travel Guide. p. 475. ISBN 9781841620763.
- San Martín, Cristina; Contreras, Domingo; Vidal, Osvaldo; Solís, José Luis; Ramírez, Carlos (2021). "Distribución en Chile y colonización del río Cayumapu (Valdivia) por el macrófito acuático invasor Limnobium laevigatum" [Distribution in Chile and colonization in Cayumapu river (Valdivia) of the invasive aquatic macrophyte Limnobium laevigatum]. Gayana. Botánica (in Spanish). 78 (1).