Landesbank
In German-speaking jurisdictions, Landesbank (plural Landesbanken), lit. 'bank of the Land', generally refers to a bank operating within a territorial subdivision (Land) that has autonomy but not full sovereignty. It is occasionally translated as "provincial bank".
Austria-Hungary
In the Austro-Hungarian Empire under the rule of the Habsburg monarchy, Landesbanken were government-sponsored banks established in some of the kingdoms and lands of the crown:[1]
- Landesbank des Königreichs Galizien und Lodomerien mit dem Grossherzogtum Krakau, est. 1883 in Lemberg (now Lviv) for the Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria and the Grand Duchy of Kraków
- Landesbank des Königreiches Böhmen, est. 1890 in Prague for the Kingdom of Bohemia
- Landesbank für Bosnien und Herzegowina, est. 1895 in Sarajevo for Bosnia and Herzegovina under Austro-Hungarian rule
- Bukowinaer Landesbank, est. 1905 in Czernowitz (now Chernivtsi) for the Duchy of Bukovina
- Kroatische Landesbank, est. 1909 in Esseg (now Osijek) for the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia
- Krainische Landesbank, est. 1912 in Laibach (now Ljubljana) for the Duchy of Carniola
By contrast, Vienna's Länderbank (est. 1880) and its short-lived affiliate the Ungarische Landesbank (1881-1887) were private-sector initiatives. The name Landesbank also survives in regional entities of the Raiffeisen Group in Austria and, similarly, the Raiffeisen Landesbank Südtirol – Cassa Centrale Raiffeisen dell'Alto Adige in the Italian region of South Tyrol.
Germany
Evolution over time
The current Landesbanken are the product of numerous episodes of development and consolidation starting in the 18th century, tracking the formation of Germany itself. In mid-1931, the default of the Landesbank der Rheinprovinz, following aggressive and uncontrolled expansion of its credit to German municipalities, was a major trigger of Germany's economic depression - unlike other Landesbanken such as the Mitteldeutsche Landesbank, which survived the episode largely unscathed.[3] With the delineation of West Germany's Länder between 1948 and 1957, the Landesbanks started acting as "house banks" of their respective Land, thus expanding into some of largest foreign issuers in Germany.
Northern Germany
- 1765: Herzogliche Leyhaus established in Braunschweig
- 1840: Hannoversche Landeskreditanstalt established in Hanover
- 1869: Oldenburgische Landesbank AG in Oldenburg
- 1883: Bodencredit-Anstalt des Herzogtums Oldenburg established in Oldenburg
- 1906: Bodencredit-Anstalt des Herzogtums Oldenburg renamed Staatliche Kreditanstalt des Herzogtums Oldenburg, shortened in 1922 to Staatliche Kreditanstalt Oldenburg
- 1917: Landesbank Schleswig-Holstein Girozentrale (LB Kiel) established in Kiel
- Landesbank der Provinz Hannover established in Hanover
- 1918: Stadtschaft für die Provinz Hannover established in Hanover
- 1919: Herzogliche Leyhaus in Braunschweig renamed Braunschweigische Staatsbank
- 1928: Hansa-Bank established in Bremen
- 1938: Hansa-Bank and Staatliche Kreditanstalt Oldenburg merge to form the Staatlichen Kreditanstalt Oldenburg-Bremen
- Bremer Landesbank – Girozentrale established in Bremen
- Hamburgischen Landesbank – Girozentrale (HLB) established in Hamburg
- 1970: Braunschweigische Staatsbank, Hannoversche Landeskreditanstalt, Niedersächsische Landesbank Girozentrale, Braunschweigische Landessparkasse, and Niedersächsische Wohnungskreditanstalt Stadtschaft merged to form NORD/LB
- 1983: Bremer Landesbank – Girozentrale and Staatlichen Kreditanstalt Oldenburg-Bremen merged to form Bremer Landesbank Kreditanstalt Oldenburg – Girozentrale (also known as Bremer Landesbank, or BLB)
- 2003: Hamburgischen Landesbank – Girozentrale and Landesbank Schleswig-Holstein Girozentrale merged to form HSH Nordbank AG, with joint head offices in Hamburg and Kiel; Investitionsbank Schleswig-Holstein spun out
- 2017: BLB merged into NORD/LB
- 2019: HSH Nordbank privatized and renamed Hamburg Commercial Bank; Landesbank role in Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein taken up by NORD/LB
![Verwaltungsbezirk building on Ruhfäutchenplatz [de] in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank until 1966](../I/Dankwardstra%C3%9Fe_1_Braunschweig_20170921_001.jpg.webp) Verwaltungsbezirk building on Ruhfäutchenplatz in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank until 1966
Verwaltungsbezirk building on Ruhfäutchenplatz in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank until 1966


 Building at Georgsplatz 2 in Hanover, head office of Niedersächsische Landesbank Girozentrale from 1958 to 1970, then of NORD/LB until 2002[7]
Building at Georgsplatz 2 in Hanover, head office of Niedersächsische Landesbank Girozentrale from 1958 to 1970, then of NORD/LB until 2002[7] High-rise wing of the former Niedersächsische Landesbank Girozentrale complex in Hanover
High-rise wing of the former Niedersächsische Landesbank Girozentrale complex in Hanover![Former Alter Bahnhof [de] building or Ottmerbau in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank (1966-1970), Nord/LB (1970-2002), then Braunschweigische Landessparkasse (since 2008)](../I/Nord_LB_BS.jpg.webp) Former Alter Bahnhof building or Ottmerbau in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank (1966-1970), Nord/LB (1970-2002), then Braunschweigische Landessparkasse (since 2008)
Former Alter Bahnhof building or Ottmerbau in Braunschweig, head office of Braunschweigische Staatsbank (1966-1970), Nord/LB (1970-2002), then Braunschweigische Landessparkasse (since 2008)![NORD/LB Head Office Building [de] opened in 2002 in Hanover](../I/Nord-LB_office_building_Aegidientorplatz_Hannover_Germany.jpg.webp) NORD/LB Head Office Building opened in 2002 in Hanover[8]
NORD/LB Head Office Building opened in 2002 in Hanover[8] Former Bremer Landesbank head office in Bremen, inaugurated in 2016 a year before the bank's absorption by NORD/LB[9]
Former Bremer Landesbank head office in Bremen, inaugurated in 2016 a year before the bank's absorption by NORD/LB[9]
Western and central Germany
- 1819: Landesanstalt zur Beförderung des Geld- und Kreditverkehrs established in Altenburg, later renamed Herzogliche Landesbank
- 1832: Provinzial-Hülfskasse Westfalen established in Münster, sometimes referred to as the first Landesbank[10]
- Landeskreditkasse established in Kassel
- 1840: Nassauische Landesbank established in Wiesbaden
- 1847: Sächsische Provinzialbank established in Merseburg
- 1854: Rheinische Provinzial-Hülfskasse established in Cologne; relocated in 1877 to Düsseldorf, and renamed in 1888 Landesbank der Rheinprovinz
- 1890: Provinzial-Hülfskasse Westfalen renamed Landesbank der Provinz Westfalen
- 1903: Hessische Landes-Hypothekenbank AG established in Darmstadt
- 1914: Landesbank der Rheinprovinz becomes the payments clearing house (German: Girozentrale) for the savings banks in the Rheinisch-Westfälische Sparkassentag, in substitution of the Stadtsparkasse Köln which had taken up that role in 1911 for the Rhine Province of Prussia
- 1923: Hessische Landesbank - Staatsbank established in Darmstadt
- 1929: Landeskommunalbank - Girozentrale für Hessen established in Darmstadt
- 1931: Landesbank der Rheinprovinz in distress, suspends payments despite emergency liquidity assistance from Deutsche Girozentrale, Preussische Staatsbank and the Reichsbank; [3] clearing house role transferred to the Cologne branch of the Deutsche Girozentrale
- 1935: Landesbank der Rheinprovinz renamed Rheinische Girozentrale und Provinzialbank
- 1940: Landeskommunalbank - Girozentrale für Hessen, Hessische Landes-Hypothekenbank AG, and Hessische Landesbank - Staatsbank merge to form Hessische Landesbank Darmstadt Girozentrale in Darmstadt
- 1941: Landesbank Saar (later known as SaarLB) established in Saarbrücken
- 1943: Landesbank für Westfalen (Girozentrale) formed from the Rheinische Girozentrale und Provinzialbank's takeover of Westfälisches Pfandbriefamt
- 1953: Landeskreditkasse Kassel, Nassauische Landesbank and Hessische Landesbank Darmstadt Girozentrale merged to form Hessische Landesbank Girozentrale (Helaba)
- 1958: The branch of the Rheinische Girozentrale und Provinzialbank in Koblenz merges with Girozentrale Pfalz und Bayerischen Versicherungskammer (in Kaiserslautern) and Hessen-Nassauische Landesbank (in Mainz) to form Landesbank Rheinland-Pfalz (LRP) in Mainz, Rhineland-Palatinate
- 1969: Rheinische Girozentrale und Provinzialbank and Landesbank für Westfalen (Girozentrale) merged to form Westdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale (WestLB) established with joint head offices in Düsseldorf and Münster, North Rhine-Westphalia, and branches in Cologne, Dortmund, Bielefeld, and Essen
- 1972: WestLB starts developing a foreign branch network by opening in Luxembourg, followed by London in 1973 and New York in 1975.
- 1993: Investitions- und Strukturbank Rheinland-Pfalz spun off from Landesbank Rheinland-Pfalz
- 2002: WestLB spins off a public development bank, NRW.Bank, converts itself into a joint-stock company as WestLB AG, and sells its private banking business to Merck Finck Privatbankiers
- 2012: WestLB dismantled with assets transferred to Portigon Financial Services; Landesbank role in North Rhine-Westphalia taken up by Helaba
 Former Nassauische Landesbank in Wiesbaden
Former Nassauische Landesbank in Wiesbaden Former branch of Landesbank der Rheinprovinz in Aachen
Former branch of Landesbank der Rheinprovinz in Aachen Former Landesbank der Provinz Westfalen in Münster
Former Landesbank der Provinz Westfalen in Münster SaarLB head office in Saarbrücken, 2011
SaarLB head office in Saarbrücken, 2011 Former LRP head office in Mainz, 2015
Former LRP head office in Mainz, 2015 Building at Herzogstrasse 15 in Düsseldorf, built 1974-1986, head office of WestLB until 2012, now Herzogterrassen commercial complex[11]
Building at Herzogstrasse 15 in Düsseldorf, built 1974-1986, head office of WestLB until 2012, now Herzogterrassen commercial complex[11]

 NRW.Bank head office in Düsseldorf
NRW.Bank head office in Düsseldorf Helaba head office in Frankfurt, 2012
Helaba head office in Frankfurt, 2012
Baden-Württemberg
- 1818: Württembergische Landessparkasse established in Stuttgart as national savings bank of the Kingdom of Württemberg
- 1870: Badische Bank established in Mannheim as the note-issuing bank of the Grand Duchy of Baden
- 1871: Württembergische Notenbank established in Stuttgart as the note-issuing bank of the Kingdom of Württemberg
- 1916: Zentralstelle des Württembergischen Giroverbands – Stuttgart established in Stuttgart, later renamed Landesbank Stuttgart
- 1924: Württembergische Wohnungskreditanstalt established in Stuttgart; renamed Württembergische Landeskreditanstalt in 1932
- 1929: Badische Kommunale Landesbank established in Mannheim
- 1932: Badische Bank relocated from Mannheim to Karlsruhe
- 1934: Badische Bank and Württembergische Notenbank deprived of their note-issuing role and repurposed as commercial entities; the latter renamed Württembergische Bank in 1935
- Badische Wohnungsfürsorgekassen and Badische Landeswohnungsfürsorgeanstalt merged into entity based in Karlsruhe and named Badische Landeskreditanstalt für Wohnungsbau in 1935
- 1972: Württembergische Landeskreditanstalt and Badische Landeskreditanstalt für Wohnungsbau merged into Landeskreditbank Baden-Württemberg
- 1975: Württembergische Landessparkasse and Städtische Spar- und Girokasse Stuttgart merged to form Landessparkasse – Girokasse öffentliche Bank in Stuttgart, renamed Landesgirokasse Stuttgart in 1977
- 1978: Badische Bank, Württembergische Bank and Handelsbank Heilbronn merged to form Baden-Württembergische Bank (BW-Bank) in Stuttgart
- 1988: Landesbank Stuttgart and Badische Kommunale Landesbank merged to form Südwestdeutsche Landesbank Girozentrale (SüdwestLB) in Stuttgart
- 1999: Landesgirokasse Stuttgart and SüdwestLB merged with the commercial activities of Landeskreditbank Baden-Württemberg to form Landesbank Baden-Württemberg (LBBW) in Stuttgart
- 2005: BW-Bank merged into LBBW
Bavaria
- 1884: Landeskultur-Rentenanstalt established in Munich
- 1914: Bayerische Girozentrale founded, permanently established in 1917 in Nuremberg and relocated in 1920 in Munich
- 1925: Bayerische Girozentrale reorganized and renamed Bayerische Gemeindebank (Girozentrale) Öffentliche Bankanstalt
- 1949: Landeskultur-Rentenanstalt renamed Bayerische Landesbodenkreditanstalt
- 1972: Bayerische Gemeindebank and Bayerische Landesbodenkreditanstalt merged to form Bayerische Landesbank Girozentrale (BayernLB)
 BayernLB head office in Munich, 2013
BayernLB head office in Munich, 2013 Lion statue in front of BayernLB head office in Munich, 2009
Lion statue in front of BayernLB head office in Munich, 2009 Courtyard of BayernLB head office in Munich, 2014
Courtyard of BayernLB head office in Munich, 2014
Eastern Germany
- 1819: Landesanstalt zur Beförderung des Geld- und Kreditverkehrs established in Altenburg
- 1849: Landeskreditanstalt Meiningen established in Meiningen
- 1915: Girozentrale - Kommunalbank für die Provinz Sachsen, Thüringen und Anhalt established in Magdeburg
- 1922: Thüringische Staatsbank established in Weimar
- 1923: Thüringische Staatsbank takes over the Landesbank in Rudolstadt and the Landeskreditanstalt Meiningen
- 1924: Wohnungsfürsorgegesellschaft Berlin established, renamed Wohnungsbau-Kreditanstalt der Reichshauptstadt Berlin in 1937
- 1928: Girozentrale - Kommunalbank für die Provinz Sachsen, Thüringen und Anhalt and Sächsische Provinzialbank in Merseburg merged to form Mitteldeutsche Landesbank - Girozentrale für die Provinz Sachsen, Thüringen und Anhalt, with head office in Magdeburg
- 1945: Mitteldeutsche Landesbank closed by the Soviet Military Administration in Germany[14]
- 1946: Thüringische Staatsbank absorbed by Landeskreditbank Thüringen
- 1992: Landesbank Sachsen established in Leipzig, Saxony
- 1993: Wohnungsbau-Kreditanstalt Berlin integrated into Landesbank Berlin as Investitionsbank Berlin
- 2004: Investitionsbank Berlin spun off from Landesbank Berlin
Cross-regional consolidation
- 1992: Hessische Landesbank Girozentrale takes up Landesbank role in Thuringia, and is renamed Landesbank Hessen-Thüringen Girozentrale while keeping the shorthand name Helaba
- NORD/LB takes up Landesbank role in Saxony-Anhalt
- 1993: NORD/LB takes up Landesbank role in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- 2001: BayernLB acquires majority control of SaarLB
- 2005: LRP merged into LBBW
- 2008: SachsenLB merged into LBBW
- 2010-2013: Saarland acquires control of SaarLB from BayernLB
Current German Landesbanken
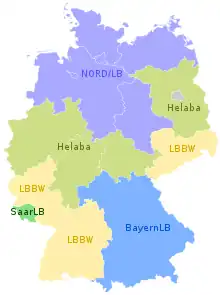
The current Landesbanken are part of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, one of the three pillars of Germany's banking system. Their business is predominantly wholesale banking, partly to serve local savings banks (German: Sparkassen). With a few exceptions, Landesbanken and Sparkassen are chartered by national and state banking laws to pursue a public purpose (German: öffentlicher Auftrag).[15] As of late 2022, they are:
- Landesbank Baden-Württemberg (LBBW) in Stuttgart, covering Baden-Württemberg, Rhineland-Palatinate, and Saxony
- Bayerische Landesbank (BayernLB) in Munich, covering Bavaria
- Landesbank Hessen-Thüringen (Helaba) in Frankfurt and Erfurt, covering Brandenburg, Hesse, North Rhine-Westphalia, and Thuringia
- Norddeutsche Landesbank (NORD/LB) in Hanover, covering Bremen, Hamburg, Lower Saxony, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony-Anhalt, and Schleswig-Holstein
- Landesbank Saar (SaarLB) in Saarbrücken, covering Saarland
 Logo of LBBW
Logo of LBBW Logo of BayernLB
Logo of BayernLB Logo of Helaba
Logo of Helaba Logo of NORD/LB
Logo of NORD/LB Logo of SaarLB
Logo of SaarLB
Four other German institutions are named Landesbank without playing the role of the above five within the public sector:
- Landesbank Berlin (LBB) was converted into a joint-stock company (German: Aktiengesellschaft) in 2007, when the DSGV rescued it and took full ownership of its share capital; it is part of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe
- Hohenzollerische Landesbank Kreissparkasse Sigmaringen is a local public savings bank, part of the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe; its earliest predecessor was established in 1834 as Spar- und Leihkasse für das Fürstentum Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and was renamed Hohenzollerische Landesbank Spar- und Leihkasse in 1930
- Kreissparkasse Birkenfeld, another local public savings bank within the Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe, is also occasionally referred to as Birkenfelder Landesbank because one of its predecessor entities was a local branch of Oldenburgische Landesbank, opened in Birkenfeld in 1914
- Oldenburgische Landesbank (OLB, est. 1869) has always been a private-sector bank, controlled since 2017 by Apollo Global Management.[16]
 Landesbank Berlin head office in Berlin, 2009
Landesbank Berlin head office in Berlin, 2009 Kreissparkasse Birkenfeld in Idar-Oberstein, 2009
Kreissparkasse Birkenfeld in Idar-Oberstein, 2009 Hohenzollerische Landesbank Kreissparkasse in Sigmaringen, 2015
Hohenzollerische Landesbank Kreissparkasse in Sigmaringen, 2015 Oldenburgische Landesbank in Oldenburg, 2010
Oldenburgische Landesbank in Oldenburg, 2010
Liechtenstein

The German name of the National Bank of Liechtenstein is Liechtensteinische Landesbank AG.
See also
- Cantonal banks, the Swiss equivalent of Landesbanken
- Bank of North Dakota
- Puerto Rico Government Development Bank
References
- Ulrich Nachbaur (2008), "Die Hypothekenbank des Landes Vorarlberg 1897 bis 1925" (PDF), Montfort: 54
- Bo Larsson (November 2014). "Czernowitz – Cernăuţi – Černivci" (PDF). Edgar Hauster. p. 24.
- Albert Fischer. "Die Landesbank der Rheinprovinz in der großen Bankenkrise der 1920er Jahre". Portal Rheinische Geschichte.
- "Deutsche Nationalbank". Landesamt für Denkmalpflege Bremen.
- "Sparkassenverband Niedersachsen Hannover". Architektur Bildarchiv.
- "Landesbank/Girozentrale Kiel". Architektur Bildarchiv.
- "Norddeutsche Landesbank Hannover". Architektur Bildarchiv.
- "Bürogebäude Nord/LB Hannover". Architektur Bildarchiv.
- "Bremer Landesbank Headquarters". Caruso St John Architects. 19 November 2019.
- Sparkassenhistorisches Dokumentationszentrum des Deutschen Sparkassen- und Giroverbandes, Geschichte der Sparkassen-Finanzgruppe (PDF), DSGV
- "ehem. WestLB Düsseldorf (Herzogterrassen)". Baukunst-NRW.
- "Ehemaliger Hauptsitz WestLB Münster". Baukunst-NRW.
- "DOC - Dortmunder Centrum für Medizin & Gesundheit (ehemalige WestLB)". Baukunst-NRW.
- "Mitteldeutsche Landesbank, Magdeburg (Bestand)". Deutsche digitale Bibliothek.
- Richard Deeg (1999), Finance Capitalism Unveiled: Banks and the German Political Economy, University of Michigan Press, doi:10.3998/mpub.15451, ISBN 9780472109364, JSTOR 10.3998/mpub.15451
- Stephan Kahl (9 February 2022). "Apollo-Backed German Lender OLB in Talks to Hire IPO Arrangers". Bloomberg.
External links
- http://www.faz.net (Bilanzsummen minus 1.809.100.000.000 Euro) (Stand September 2010) (Schuldenbremse Grundgesetz)

.jpg.webp)








